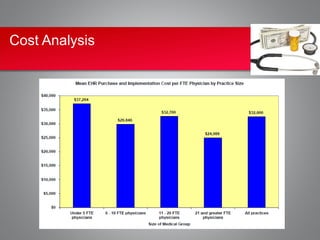
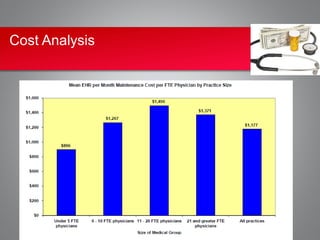
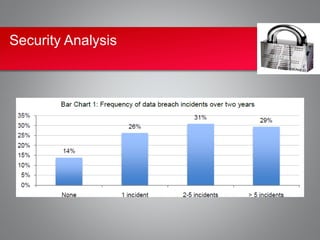
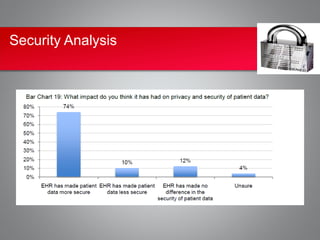
Implementing an electronic health record (EHR) system presents significant cost and security challenges for healthcare organizations. Costs include high upfront expenses for purchasing and installing EHR software and hardware, ongoing maintenance fees, and staff training costs. Security risks involve the potential for data breaches through theft, hacking, or improper access of electronic health information. While EHRs allow for improved accuracy, efficiency and audit trails, the costs are often prohibitive, especially for small practices, and security remains a top concern due to numerous reported data breaches. Careful planning around funding, vendor selection, training, and security protocols is needed to maximize the benefits and minimize the risks of EHR adoption.














![References
• Breaches affecting 500 or more individuals. (2010). Retrieved from
http://www.hhs.gov/ocr/privacy/hipaa/administrative/breachnotificationrule/postedbreaches.html
• Ponemon Institute LLC, Initials. (2010, November 9). Dgs health law blog [Web log message].
Retrieved from http://www.dgshealthlaw.com/uploads/file/Ponemon_Benchma
k_Study_on_Patient_Privacy_and_Data_Security%5B1%5D%281%29.pdf](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/blueteamppfinal4-12-111-130221162644-phpapp01/85/Blue-team-pp_-final_4-12-11-1-19-320.jpg)
