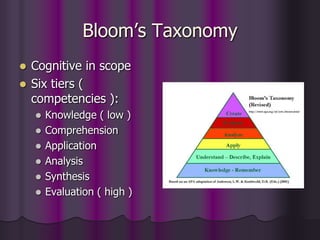
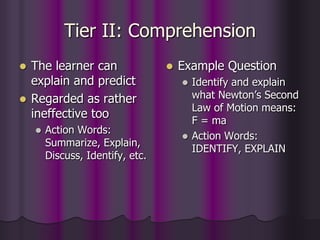
Bloom's Taxonomy outlines six levels of cognitive skills: knowledge, comprehension, application, analysis, synthesis, and evaluation. These levels progress from basic recall to more complex and abstract higher-order thinking skills. The taxonomy was created by educational psychologist Benjamin Bloom and focuses on the cognitive domain, but it can also apply to the affective and psychomotor domains. In the cognitive domain, the levels build upon each other from basic recall to more evaluative skills like assessing and debating ideas. The taxonomy provides a framework for teachers to test students' understanding at varying levels of complexity.