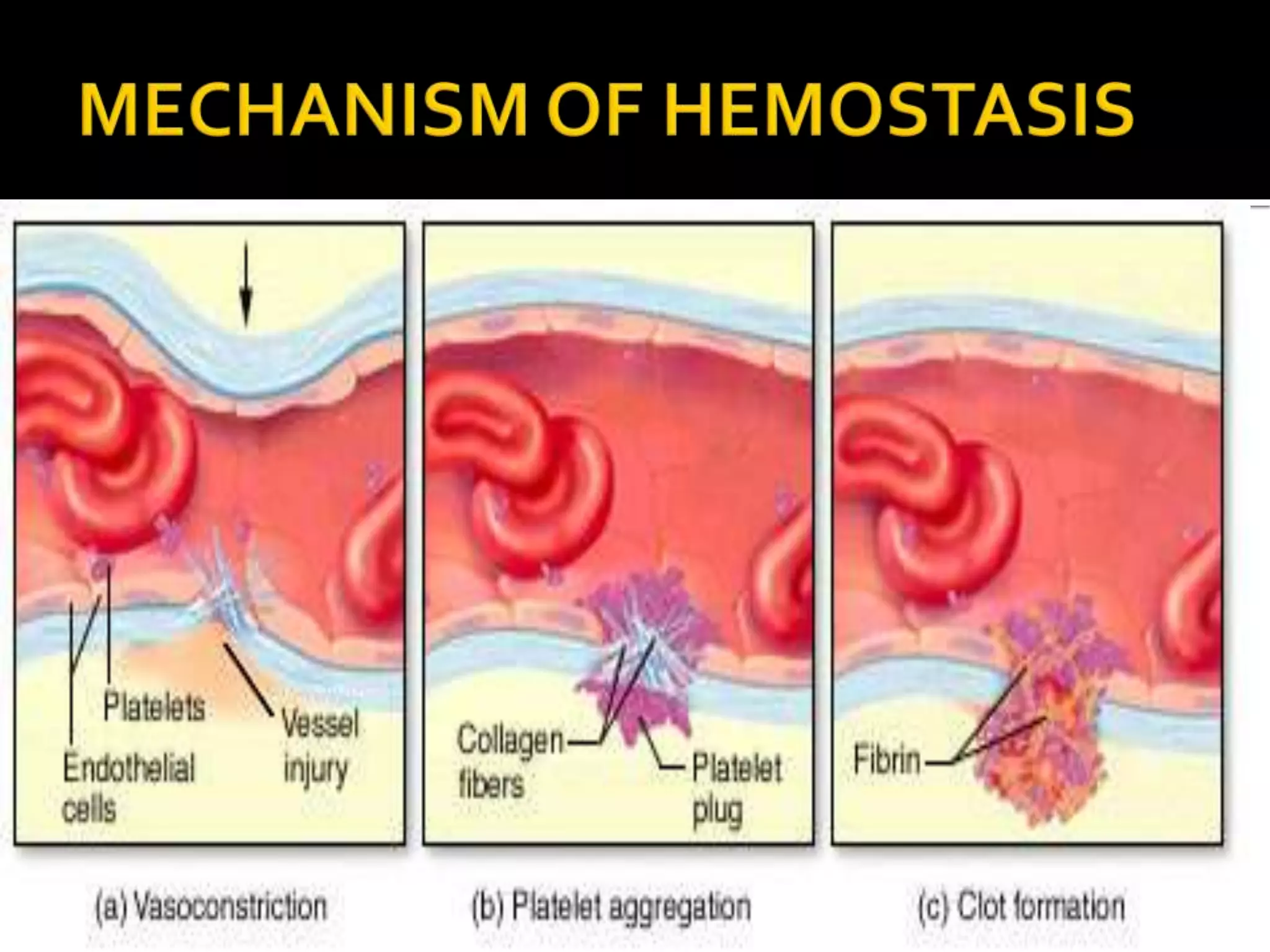
This document discusses the process of blood clot formation and prevention of blood loss. It describes that vascular constriction, platelet plug formation, and blood clotting close holes in veins. Platelets are formed from megakaryocytes, contain enzymes and glycoproteins, and adhere to collagen in damaged blood vessels to form platelet plugs. The clotting cascade involves the extrinsic and intrinsic pathways activating coagulation factors and converting prothrombin to thrombin and fibrinogen to fibrin to form a clot. Deficiencies in coagulation factors can cause bleeding disorders like hemophilia A, B, and C.