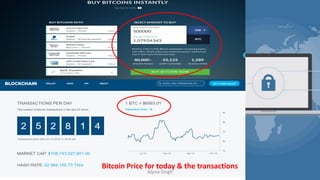
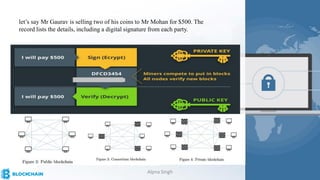
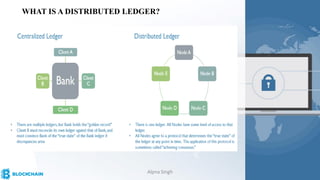
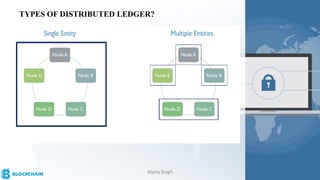
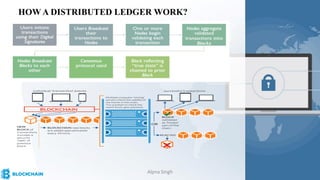
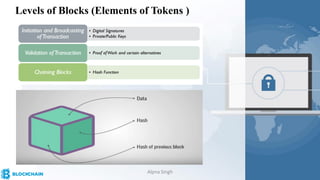
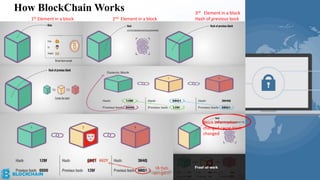
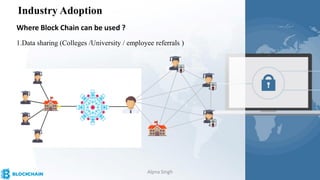
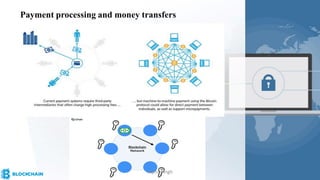
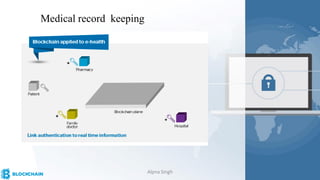
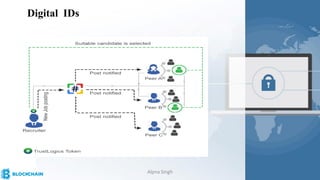
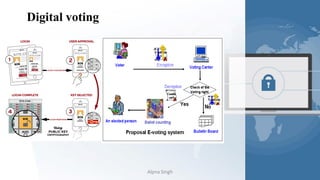
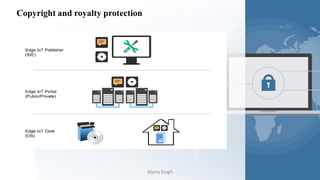
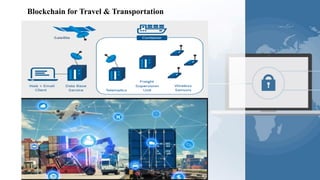
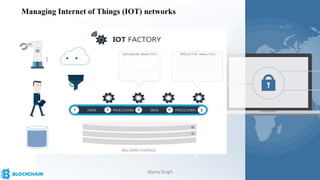
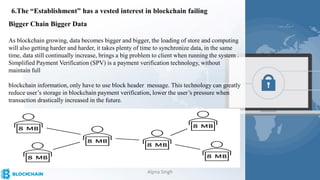
The document provides a comprehensive overview of blockchain technology, its origins with Bitcoin, and the functionality of cryptocurrencies and smart contracts. It highlights various applications of blockchain beyond cryptocurrency, including its adoption in industries like finance and healthcare, while also discussing challenges such as security, regulation, and public perception. Lastly, it emphasizes the potential for blockchain to revolutionize numerous sectors by enhancing transparency and reducing reliance on intermediaries.