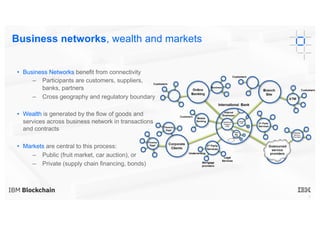
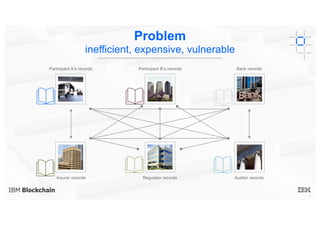
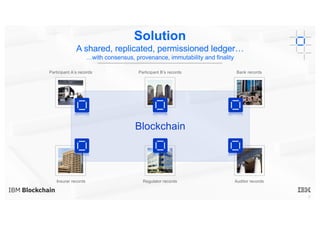
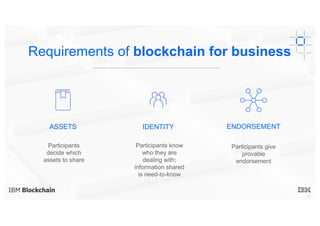
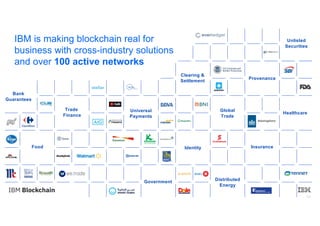
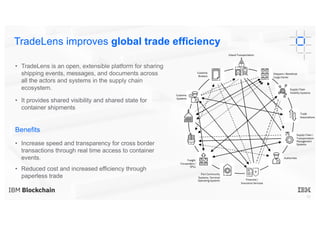
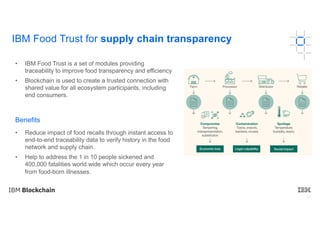
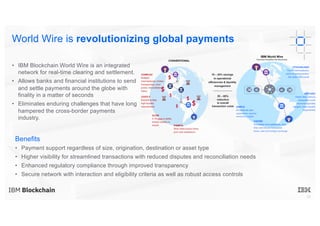
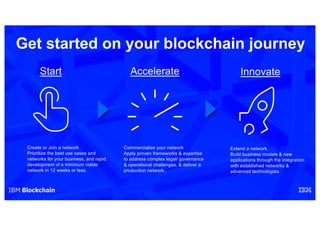
Blockchain explained is a document that introduces blockchain technology for business use. It discusses how blockchain can help solve inefficiencies in sharing records between participants in a business network by providing a shared, replicated ledger. It describes different types of blockchains and requirements for business blockchains, including how they handle assets, identity, and transaction endorsement. The document provides examples of IBM blockchain networks and solutions and how IBM can help organizations create or join networks to address business challenges through blockchain.