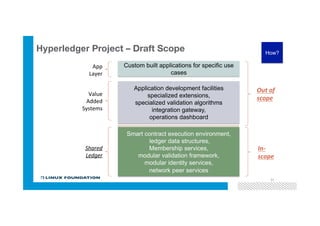
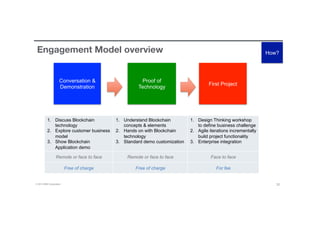
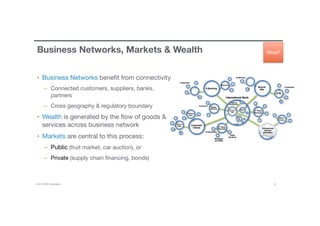
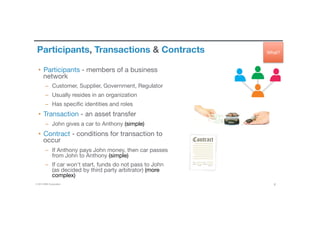
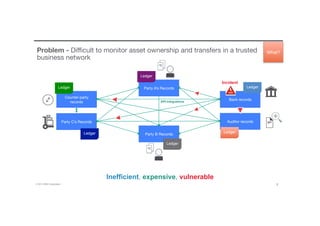
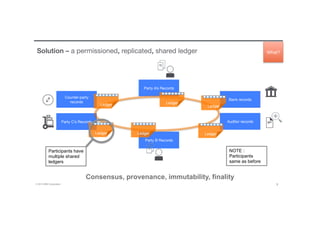
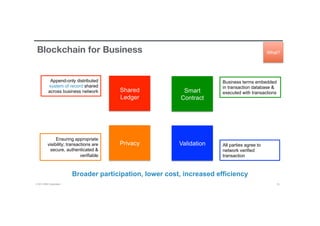
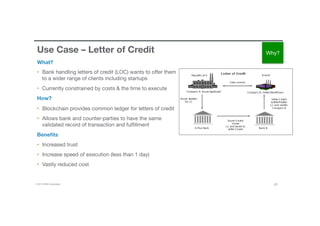
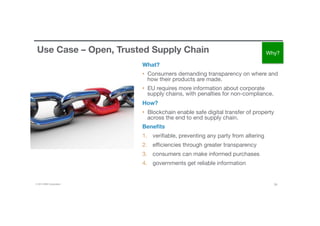
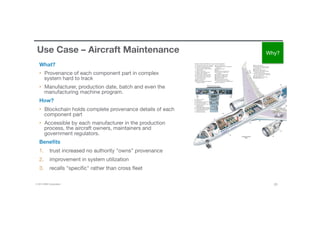
Blockchain is a shared, replicated ledger technology that can open up business networks by reducing costs, improving efficiencies, and increasing accessibility. IBM supports an open standards, open source, open governance blockchain through contributions to the Linux Foundation Hyperledger project, which is developing shared ledger technology. IBM offers customers an engagement model to explore blockchain concepts, show proof of technology applications, and integrate blockchain solutions into their enterprise systems.


![© 2016 IBM Corporation 5
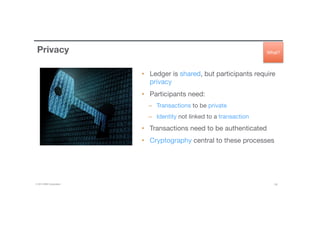
Ledgers are Important
• Ledger [1] is THE system of
record for a business
– records asset transfer between
participants.
• Business will have multiple
ledgers for multiple business
networks in which they
participate.
[1] The principal book (or computer file) for recording and
totaling financial transactions by account type, with debits and
credits in separate columns and a beginning monetary
balance and ending monetary balance for each account.
What?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/blockchain-explained-v2-161022182016/85/Making-Blockchain-Real-for-Business-Explained-ibm-5-320.jpg)













![© 2016 IBM Corporation
Hyperledger Project Members [1]
30
[1] At 17th December 2015
How?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/blockchain-explained-v2-161022182016/85/Making-Blockchain-Real-for-Business-Explained-ibm-30-320.jpg)