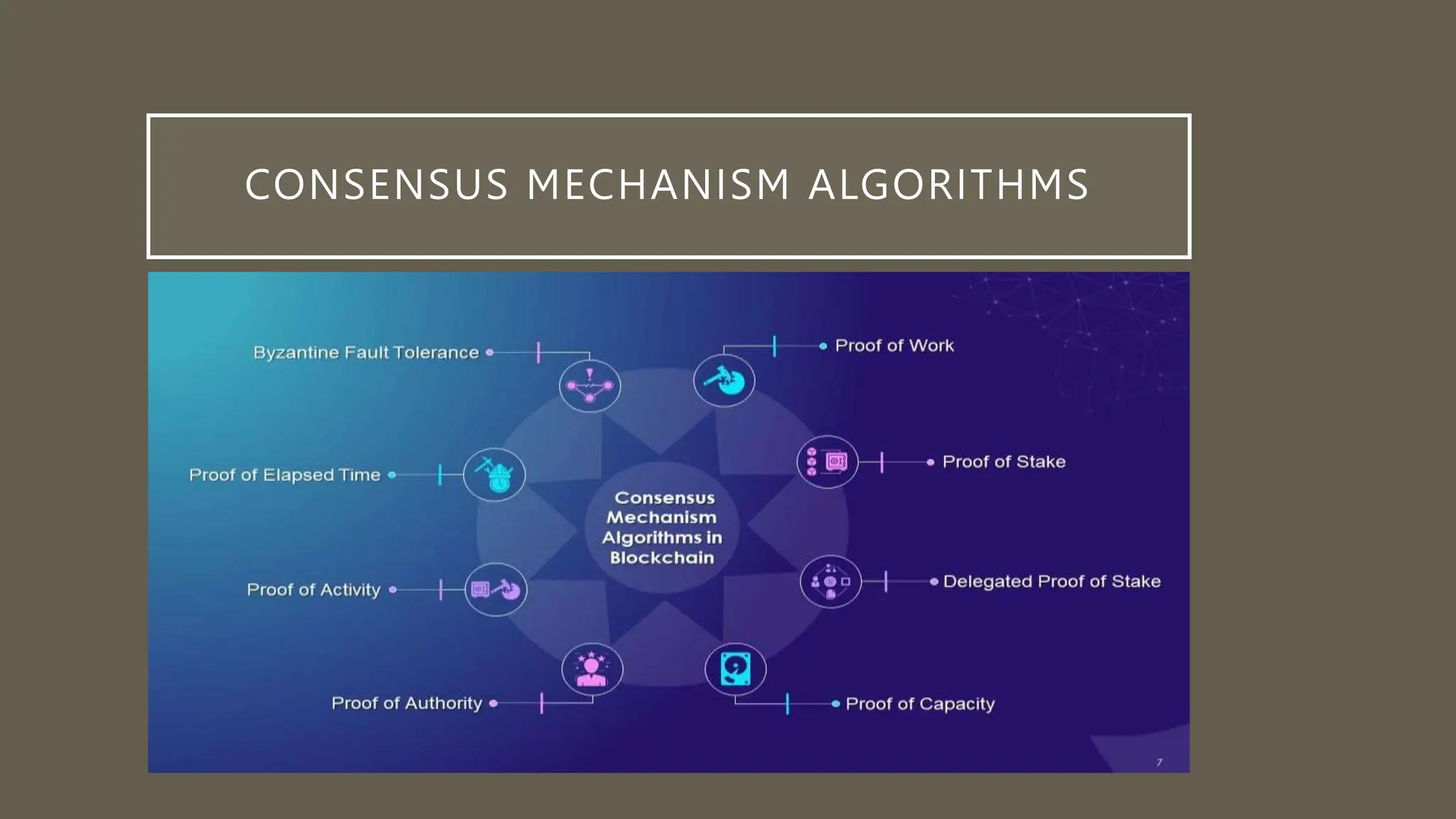
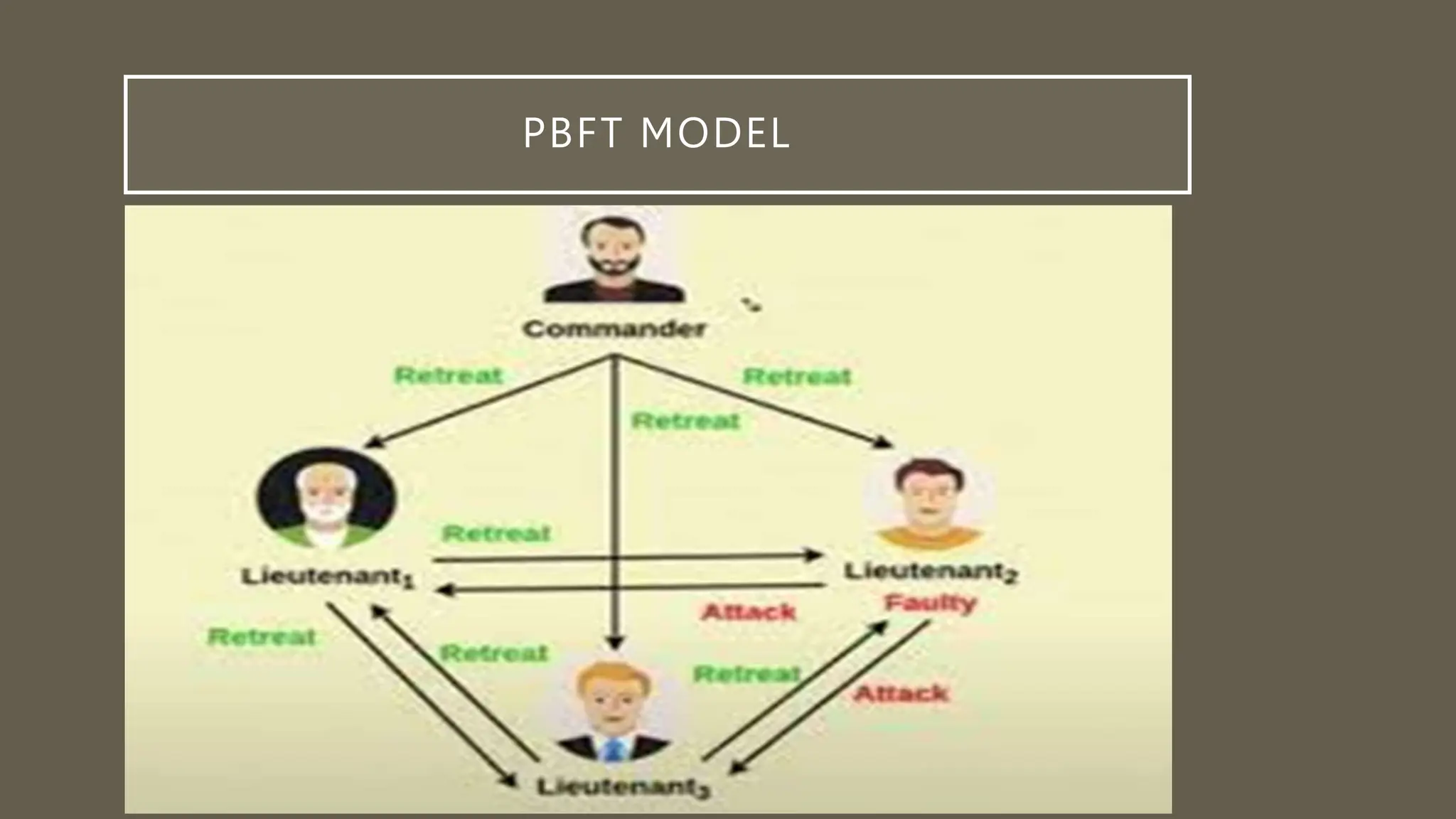
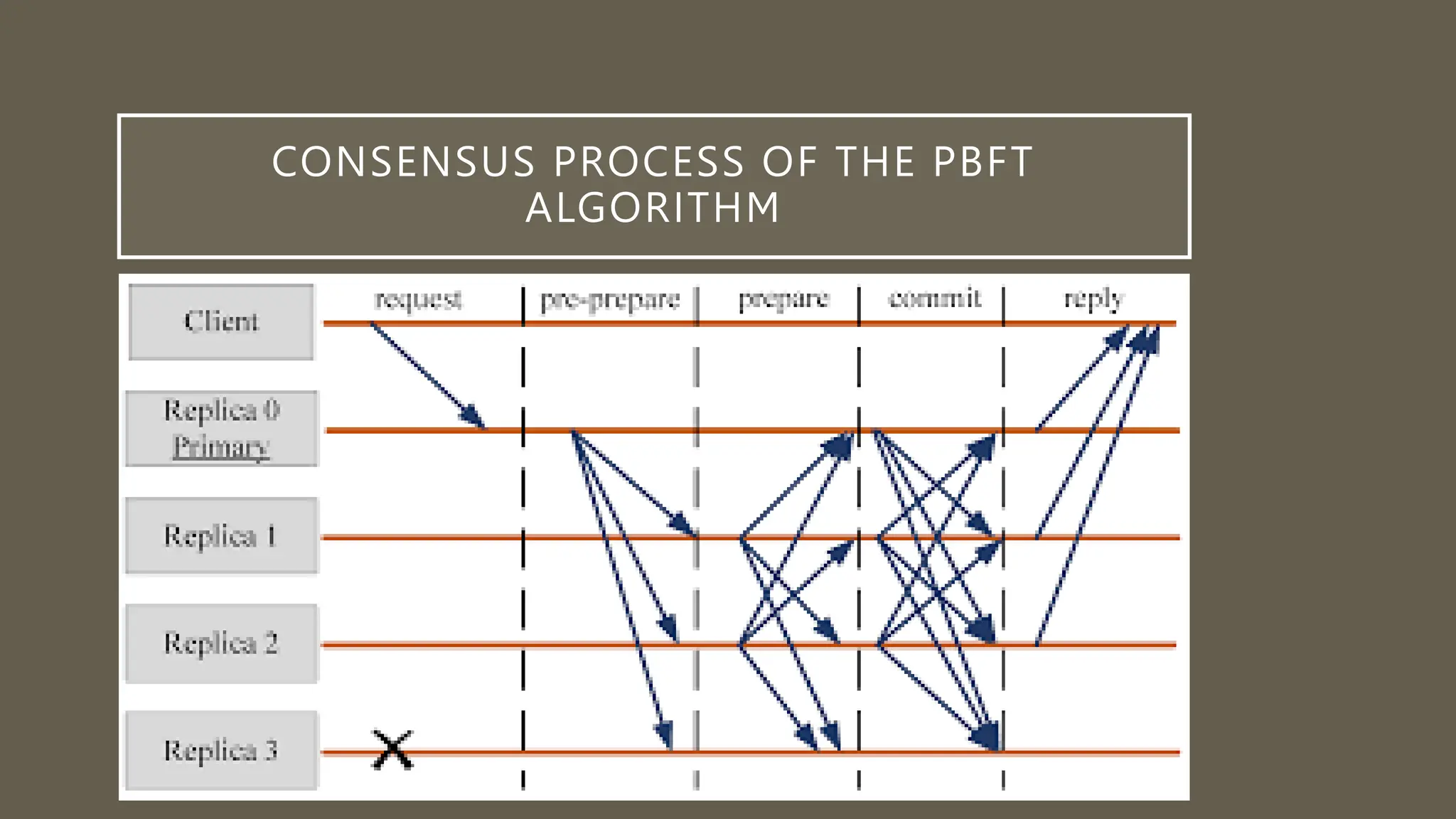
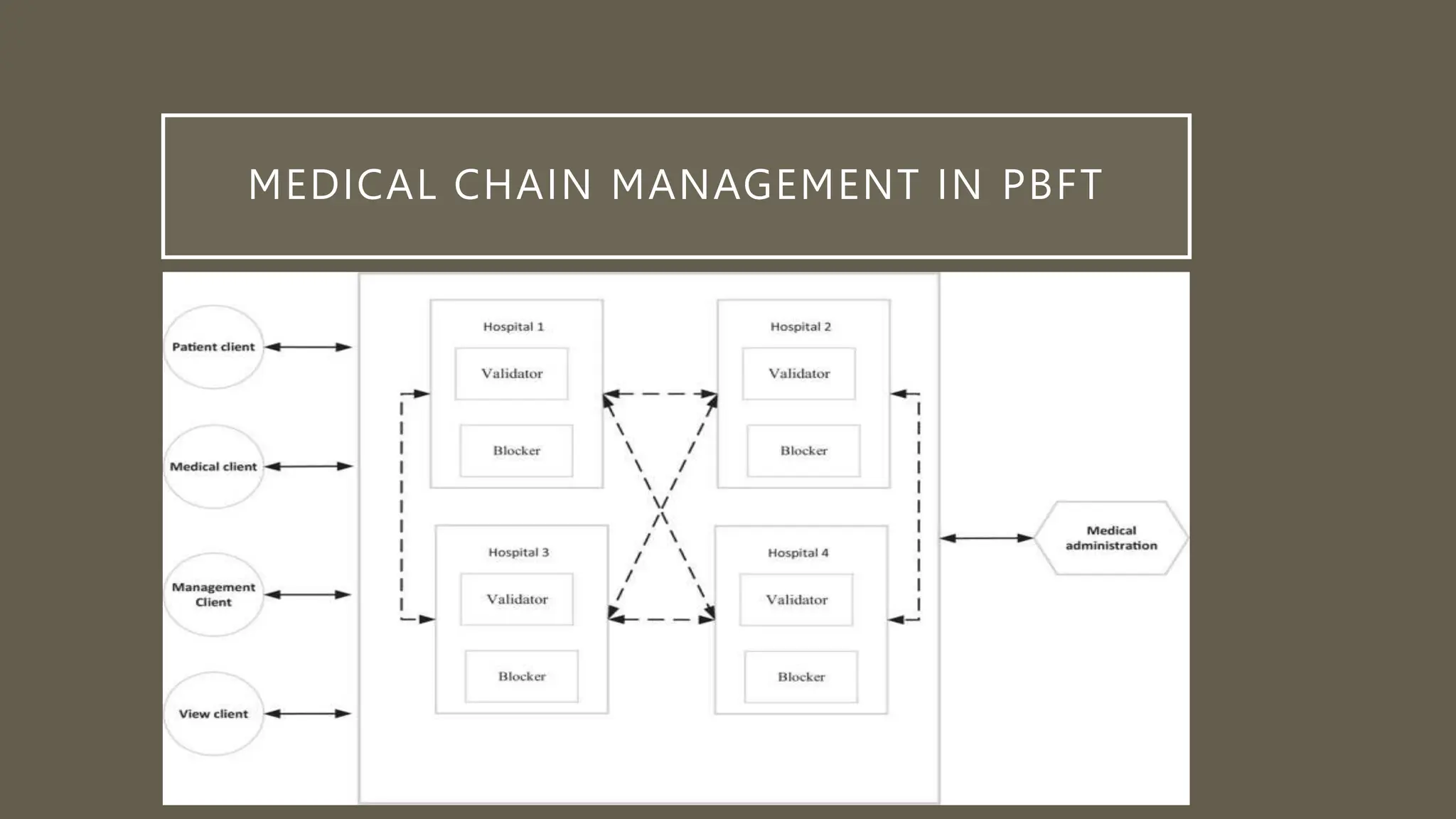
This document discusses blockchain in distributed computing. It provides an introduction to blockchains and how they are integrated into distributed computing through their decentralized architecture, immutability, smart contracts, and consensus mechanisms. The document specifically examines the Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT) consensus algorithm and how the Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT) algorithm works through voting between nodes to reach agreement. An example use case of PBFT for securely sharing electronic health records between healthcare providers is also provided.