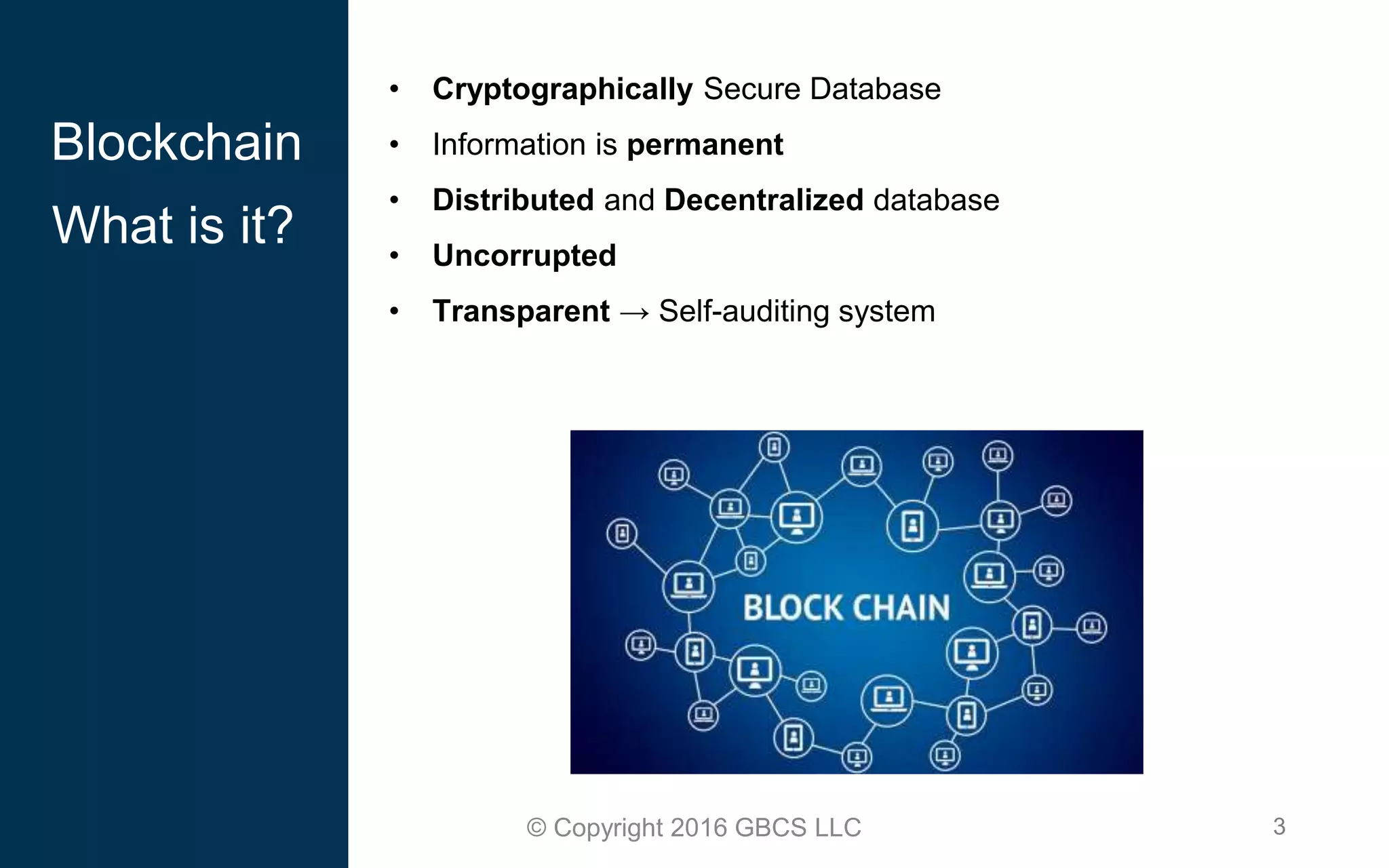
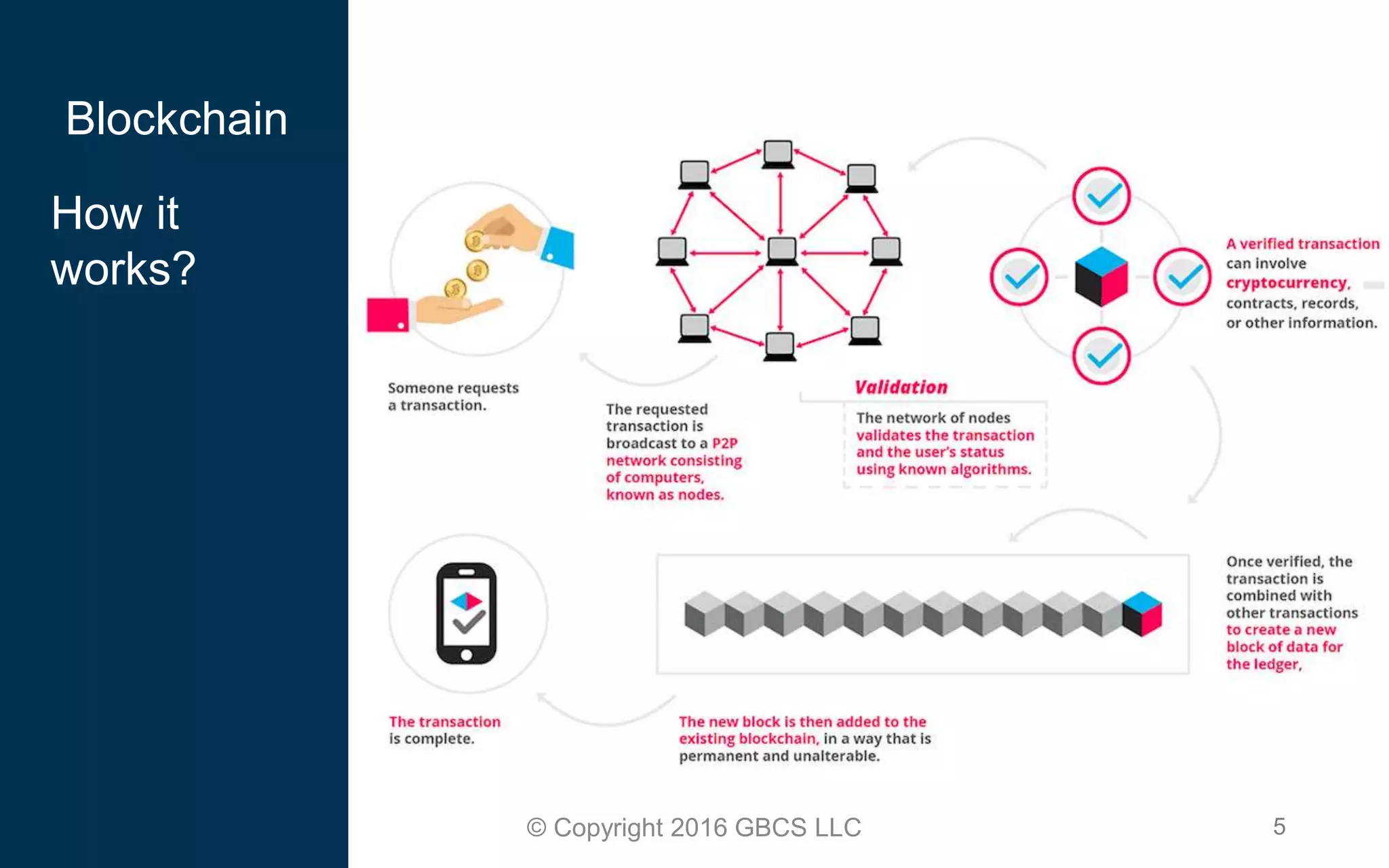
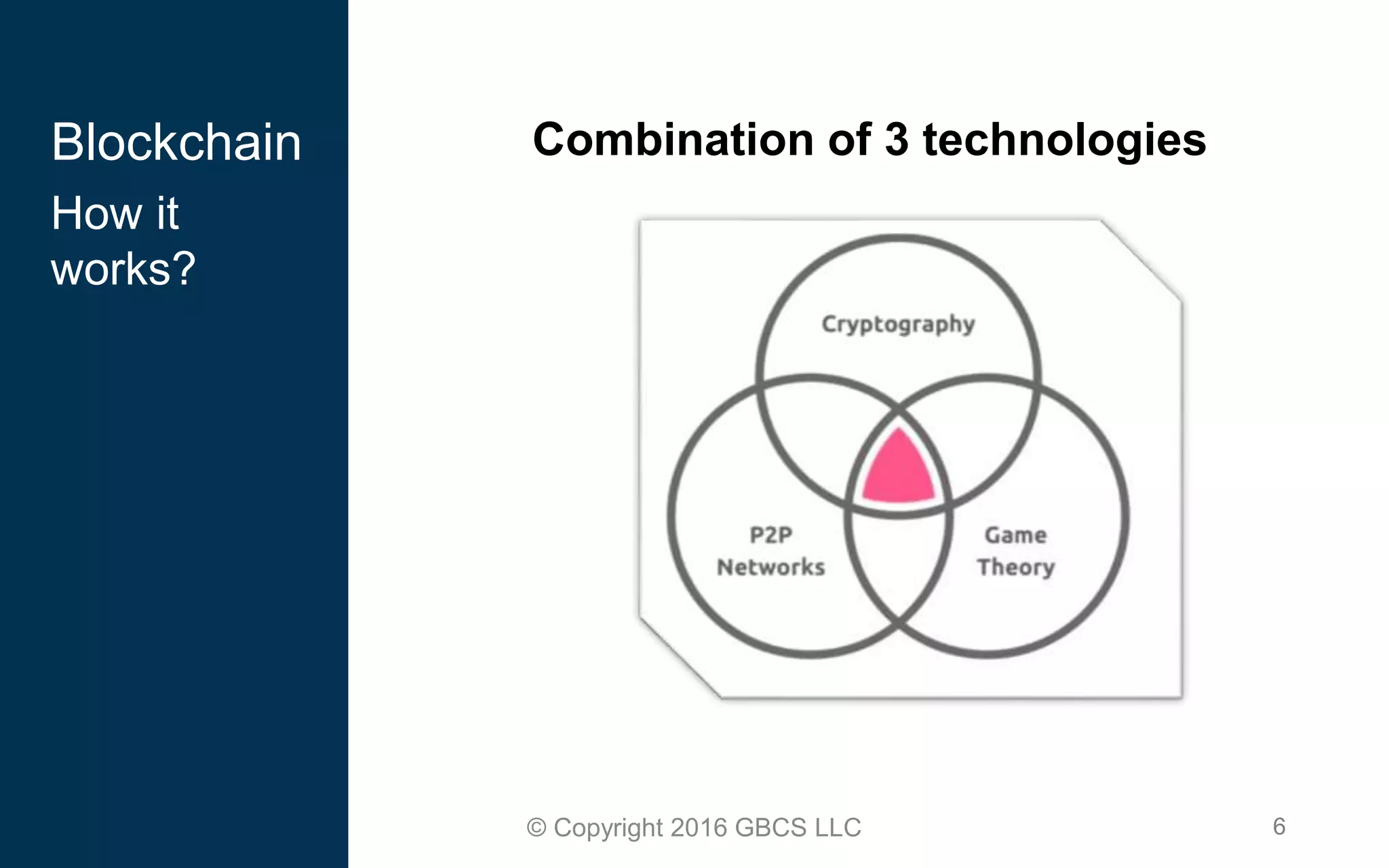
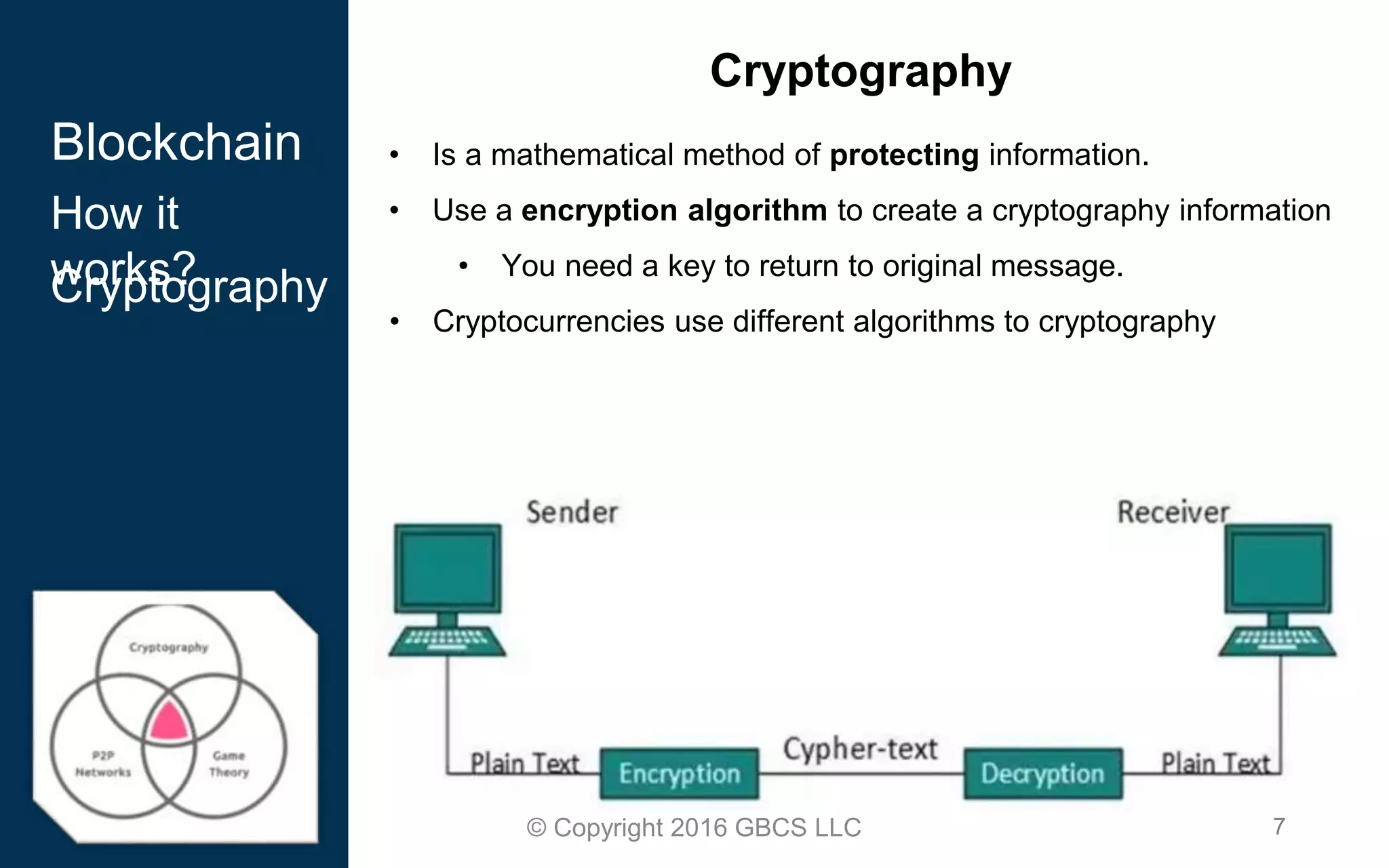
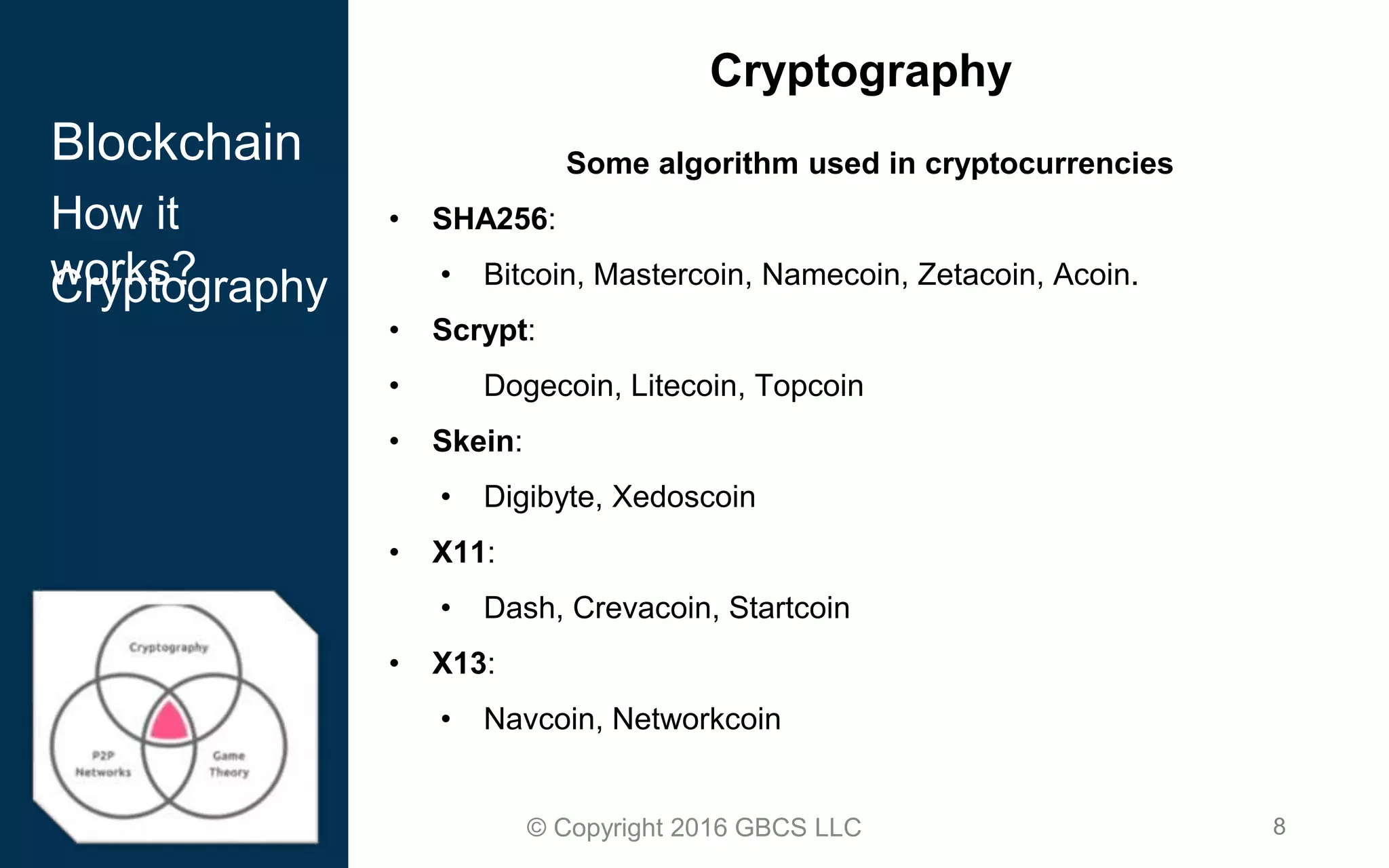
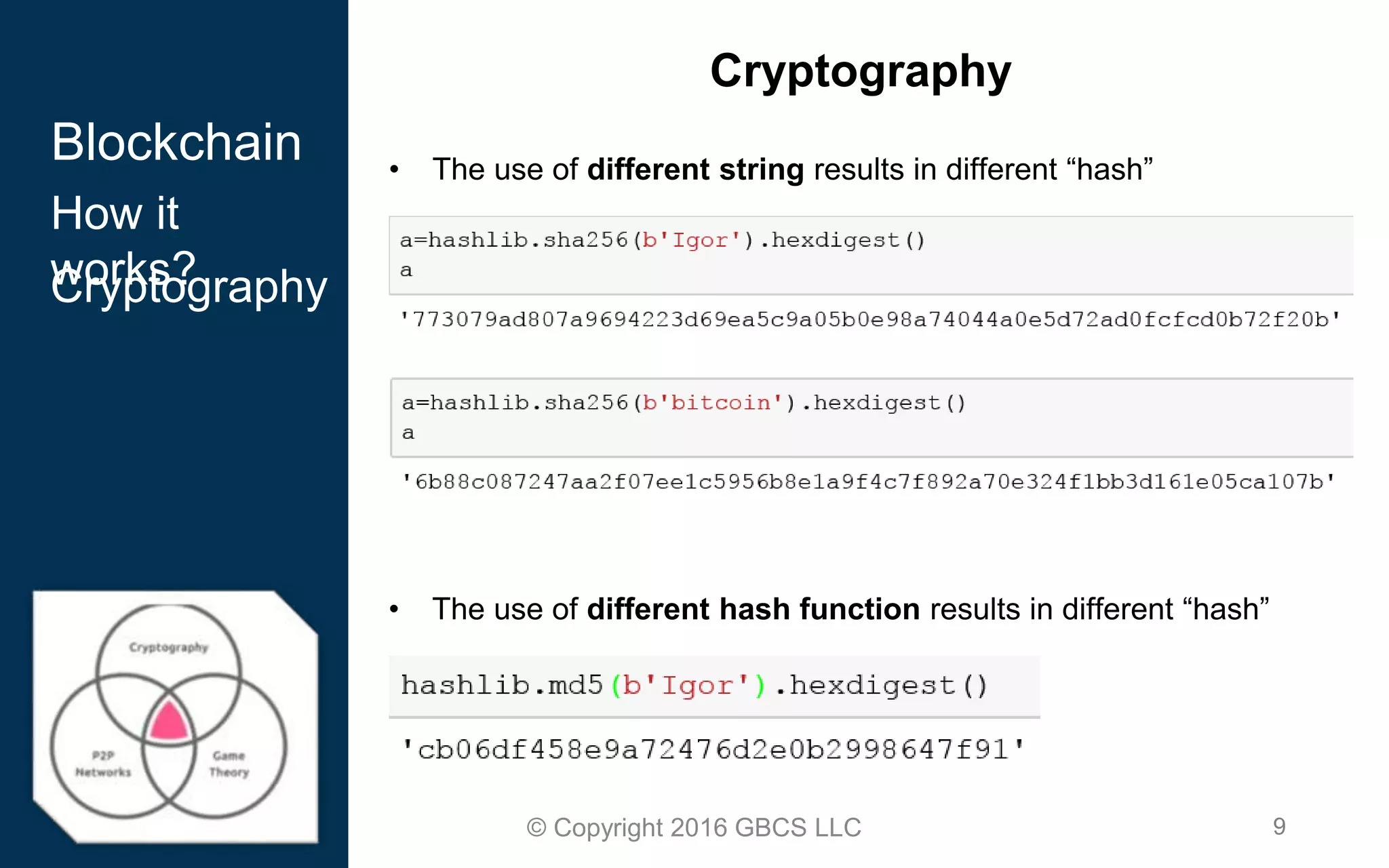
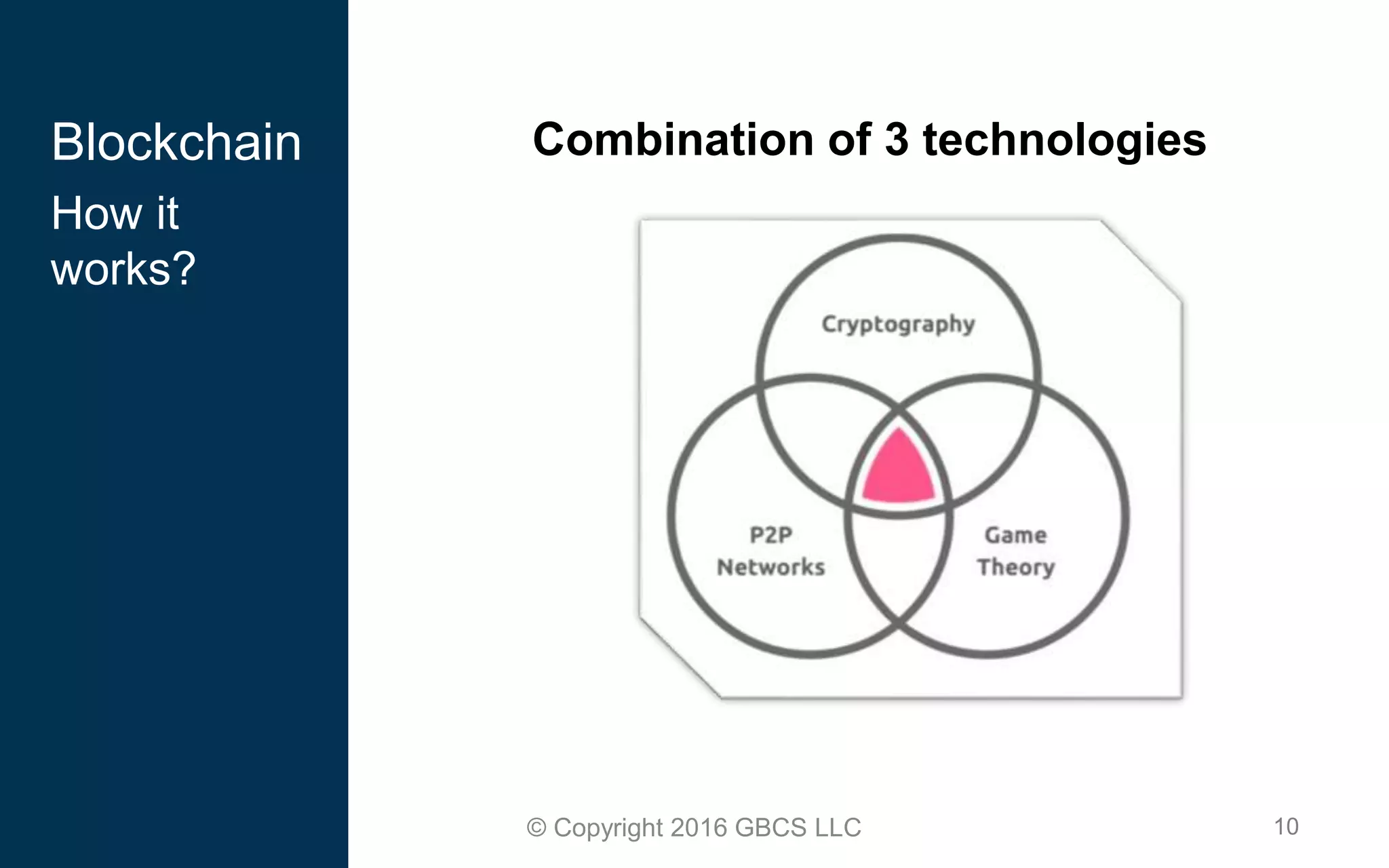
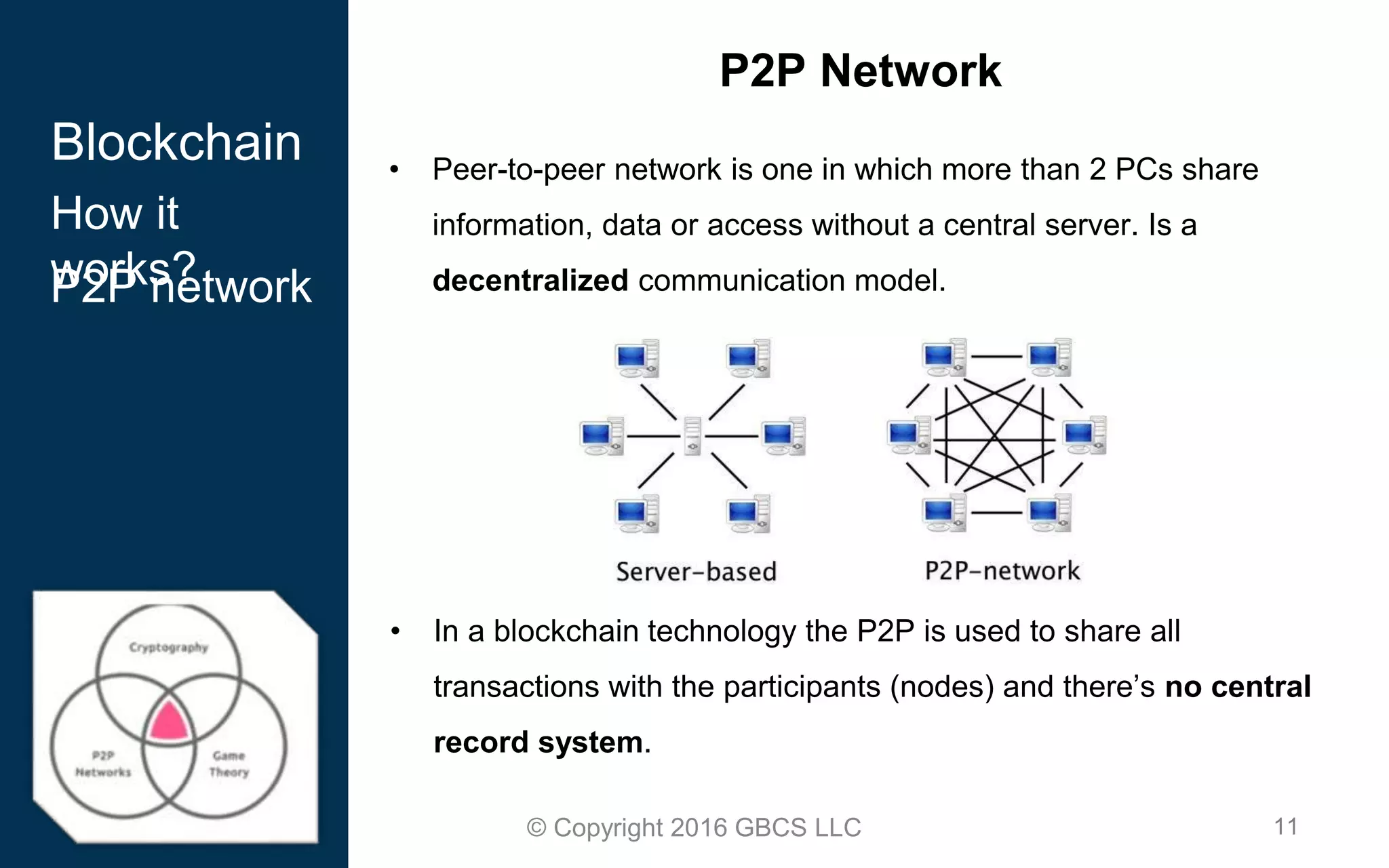
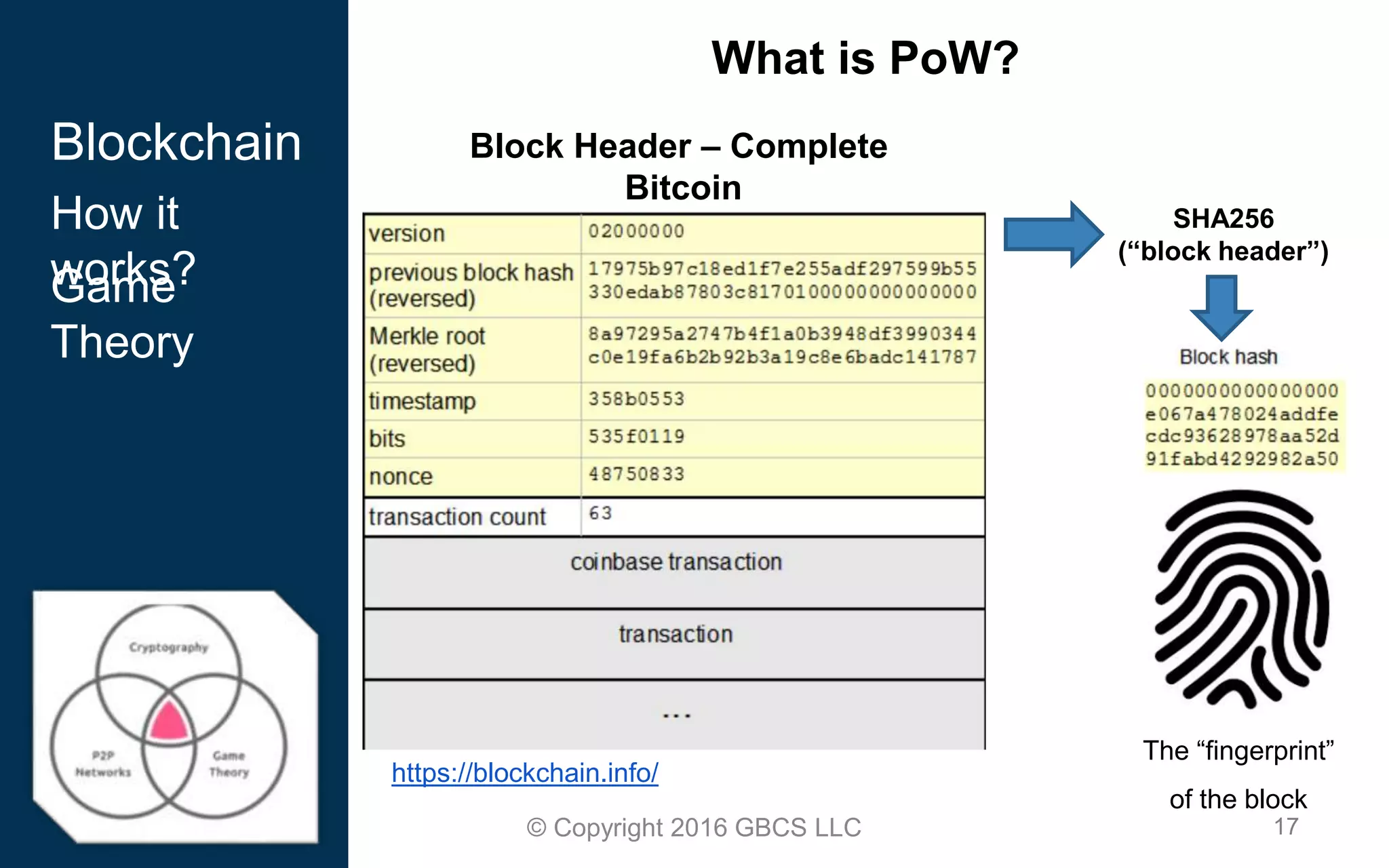
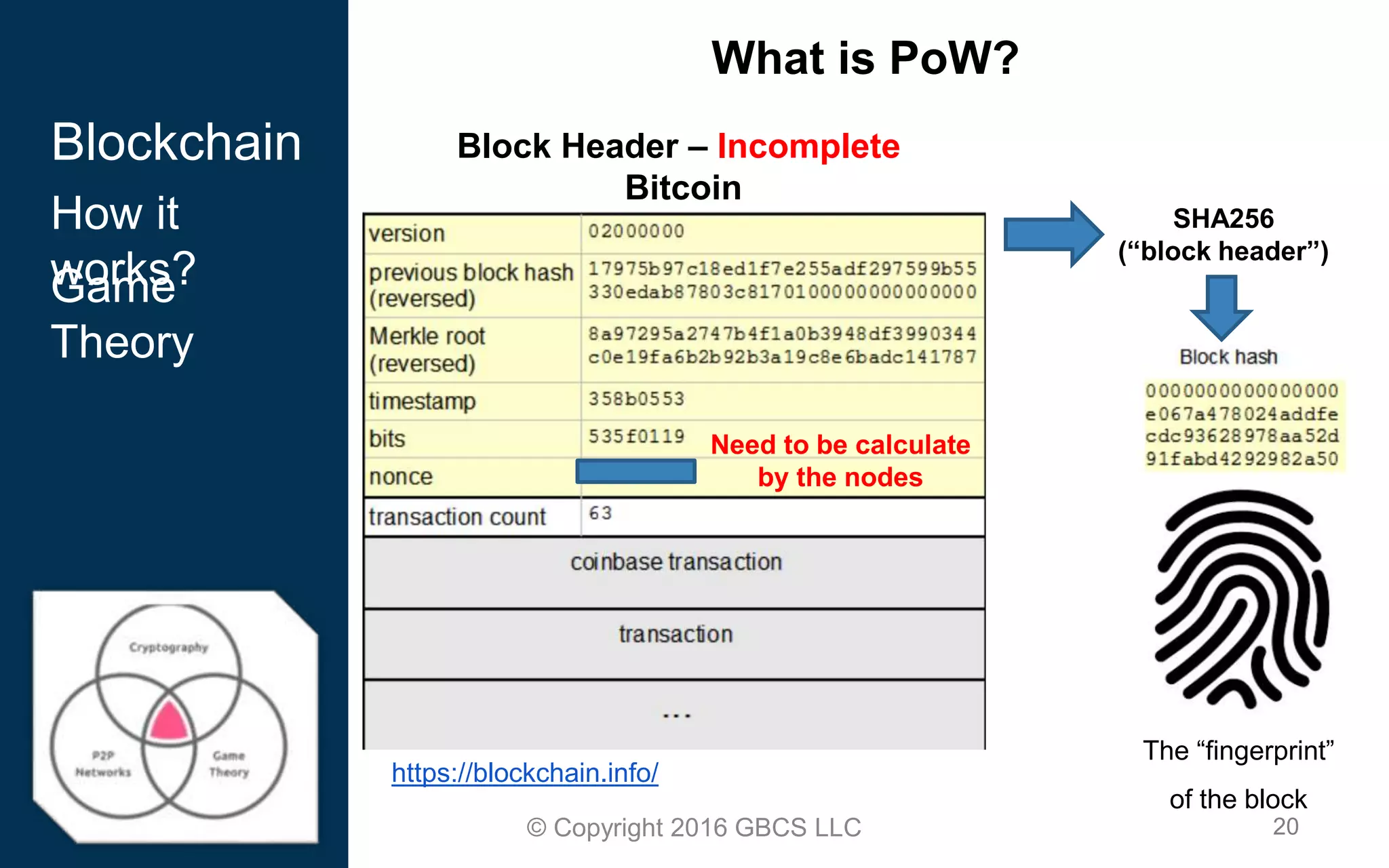
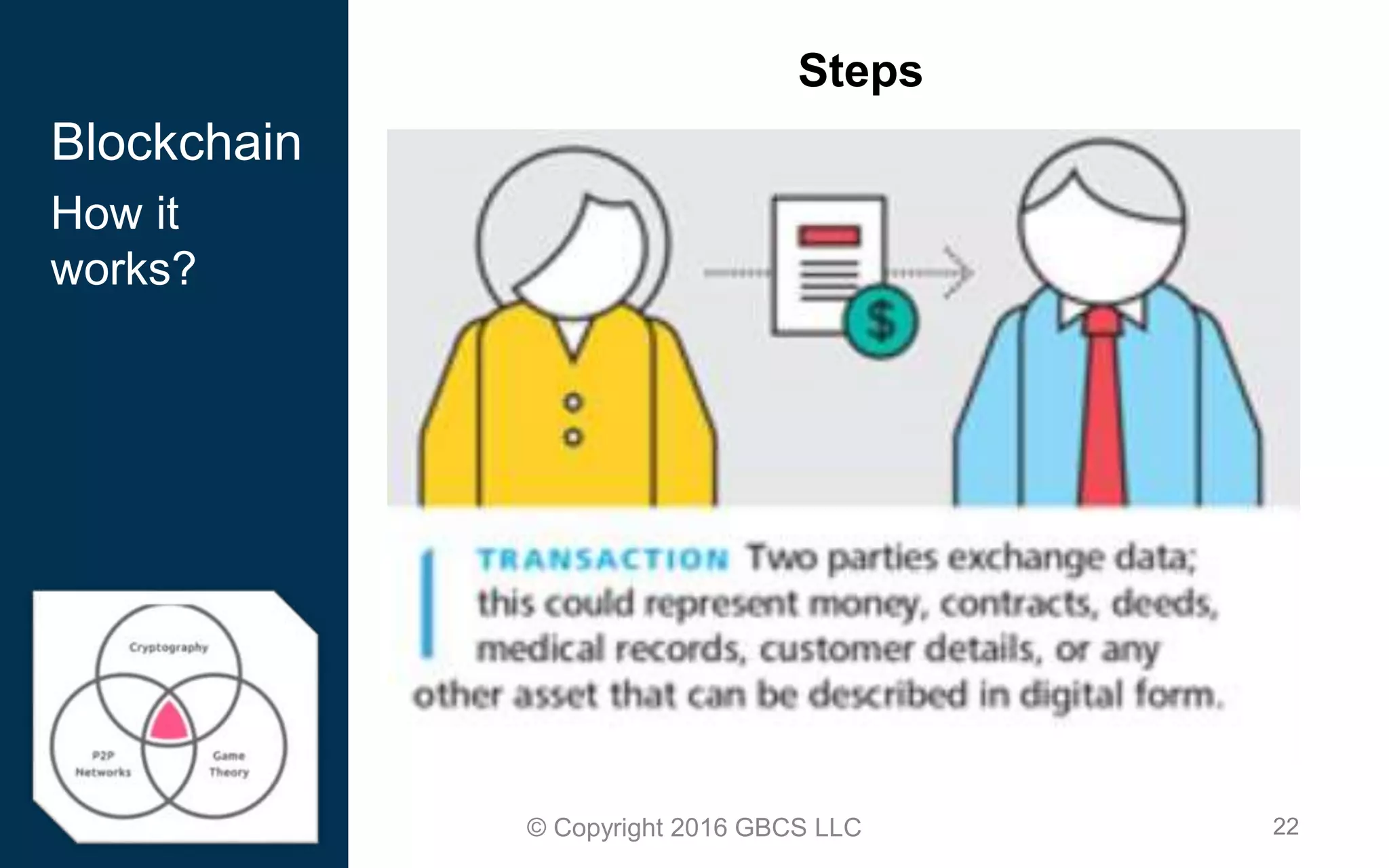
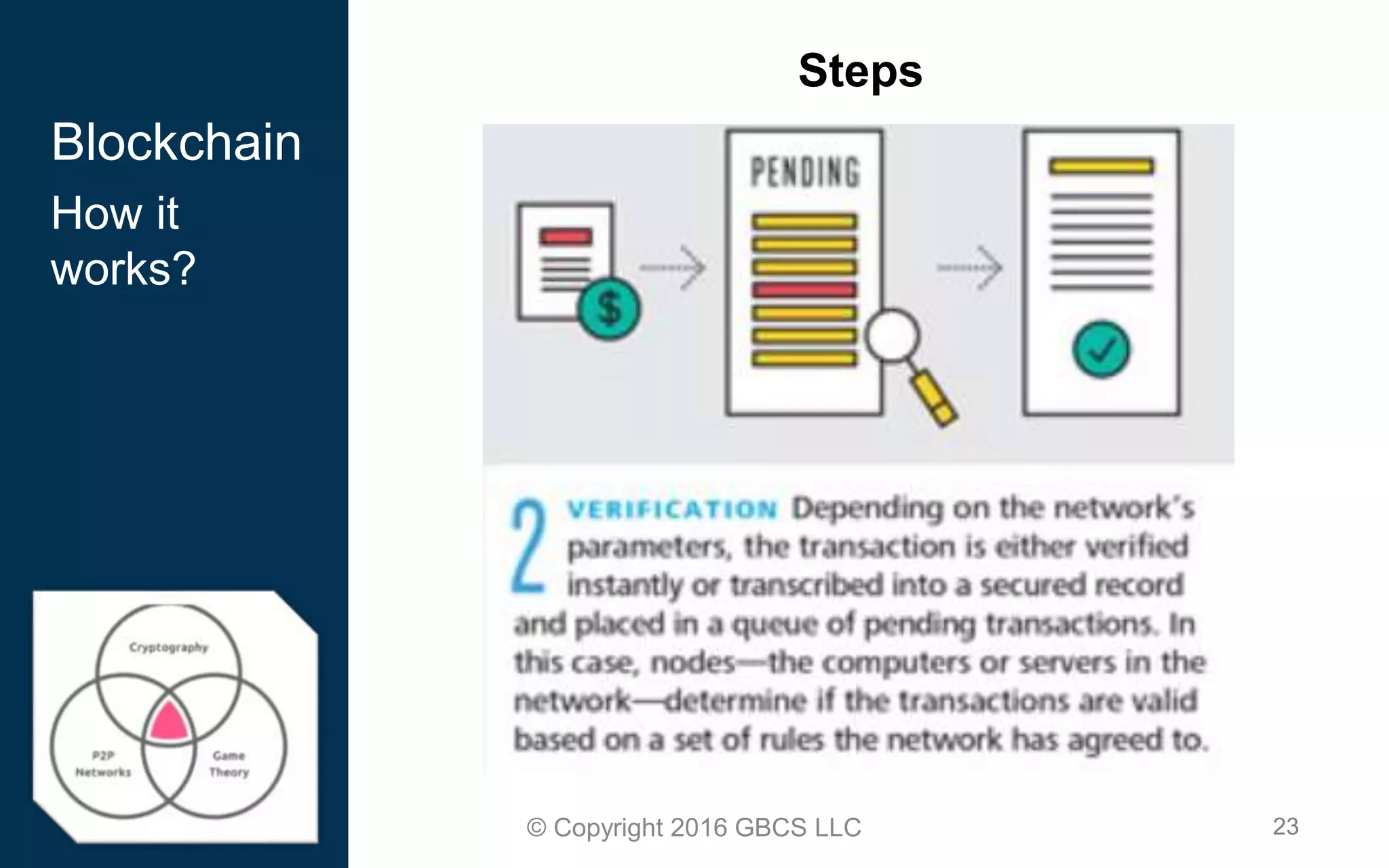
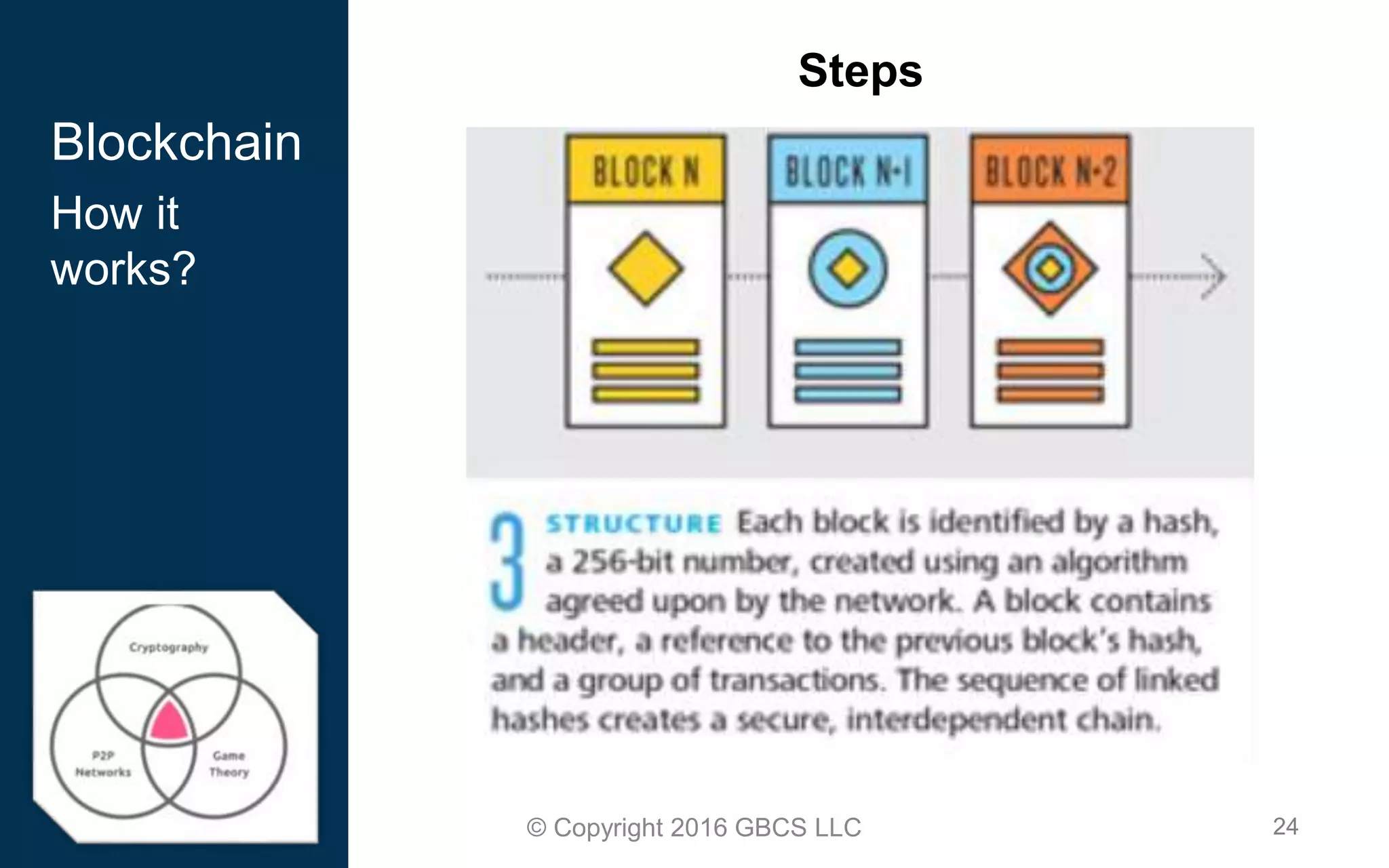
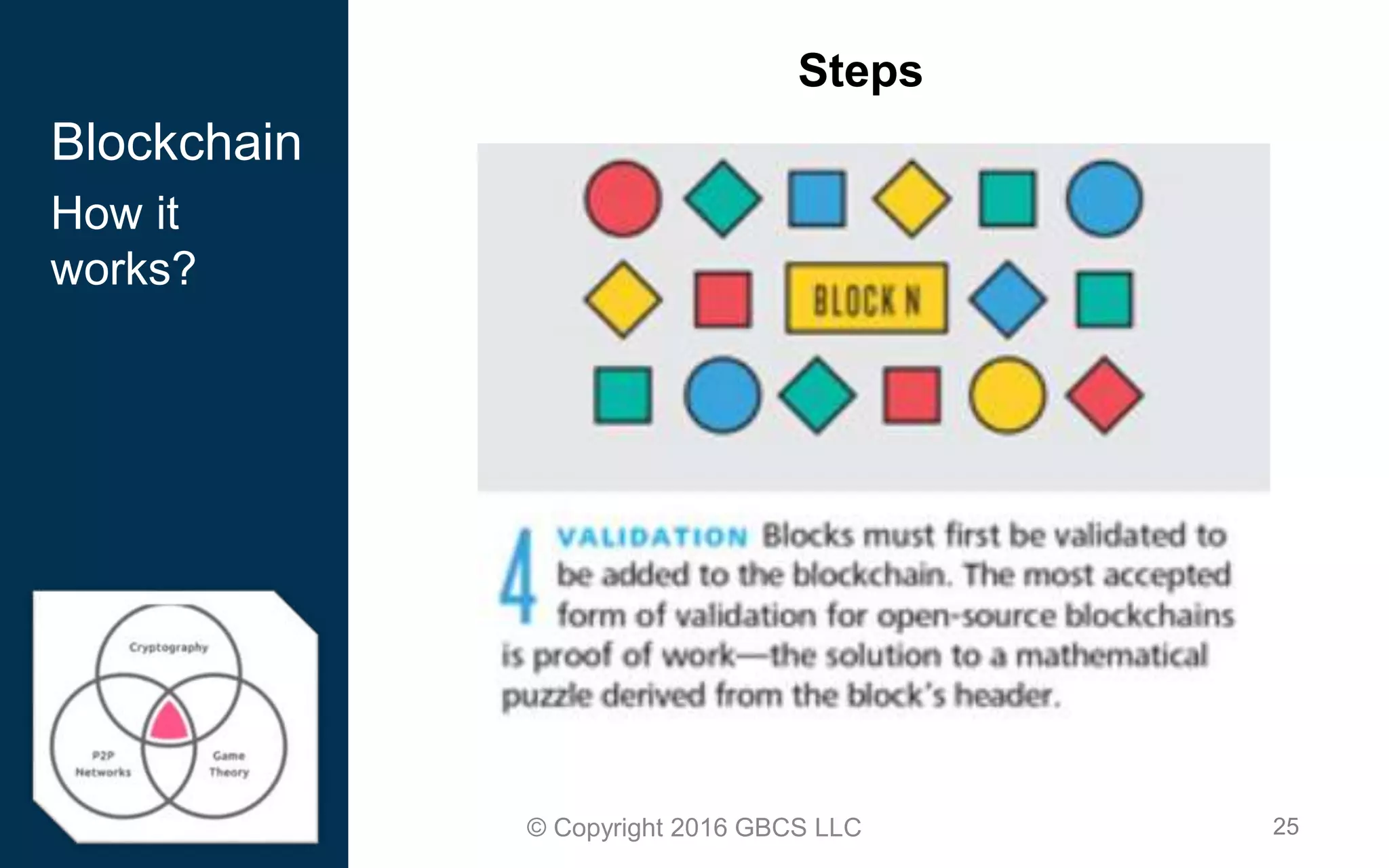
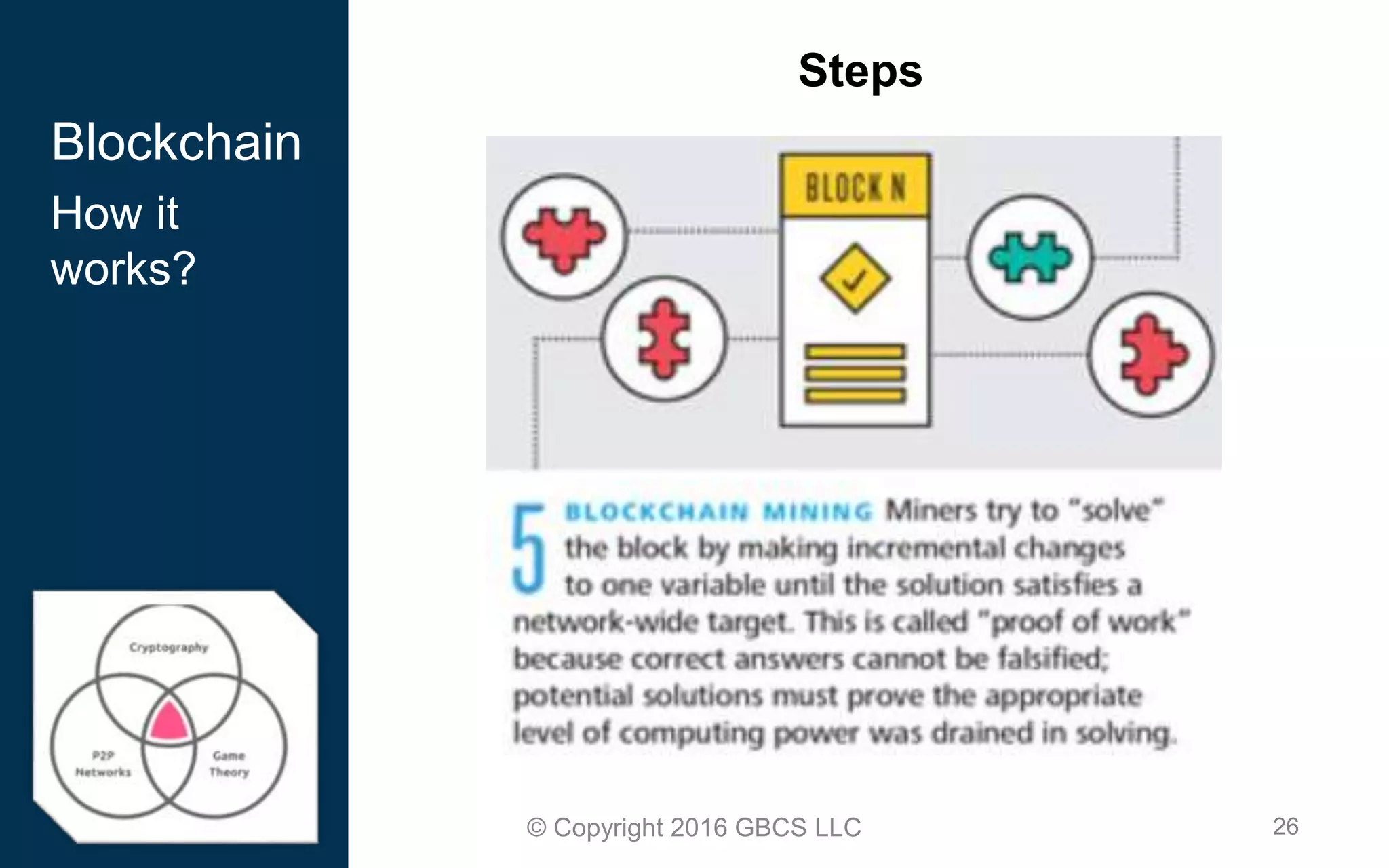
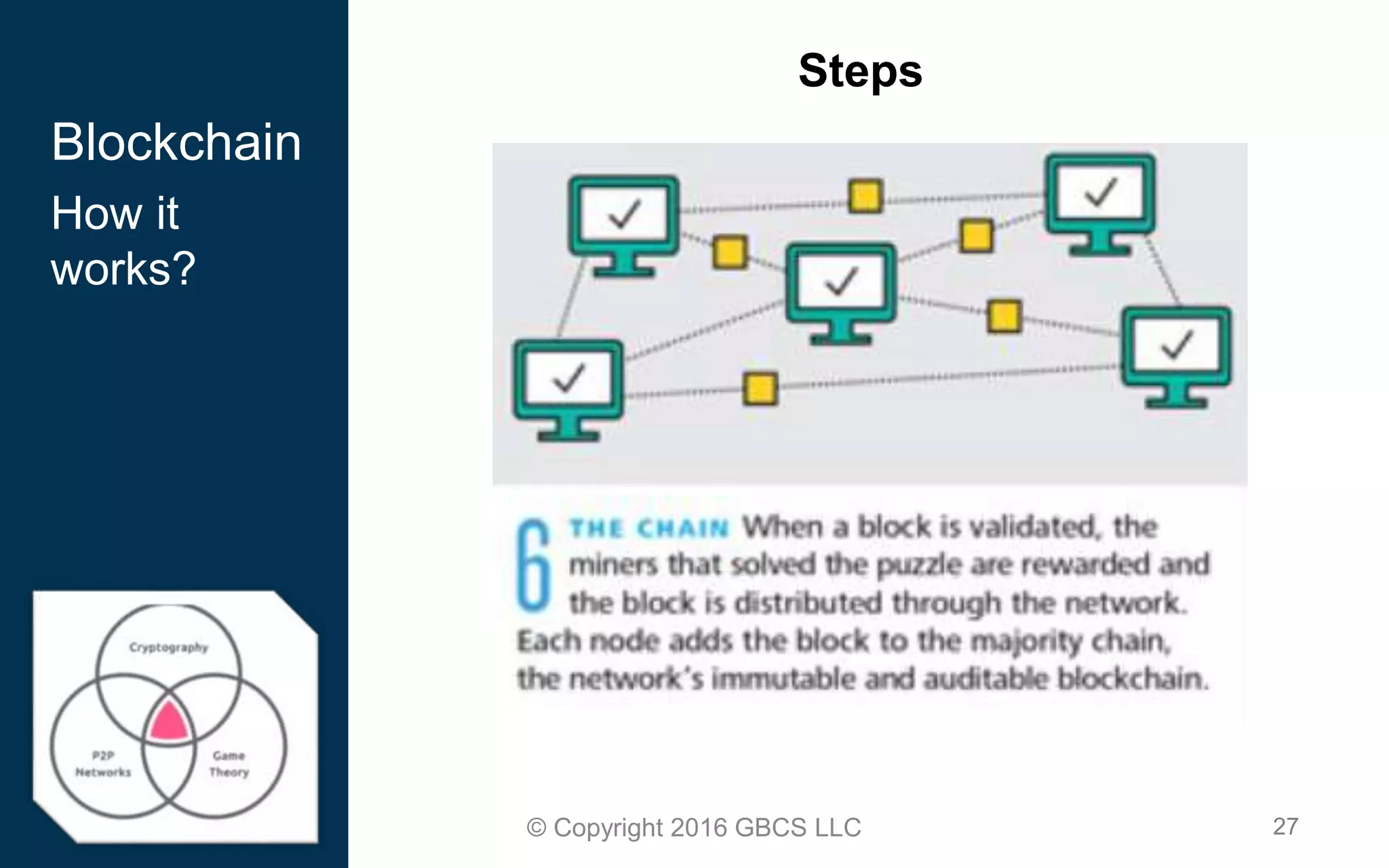
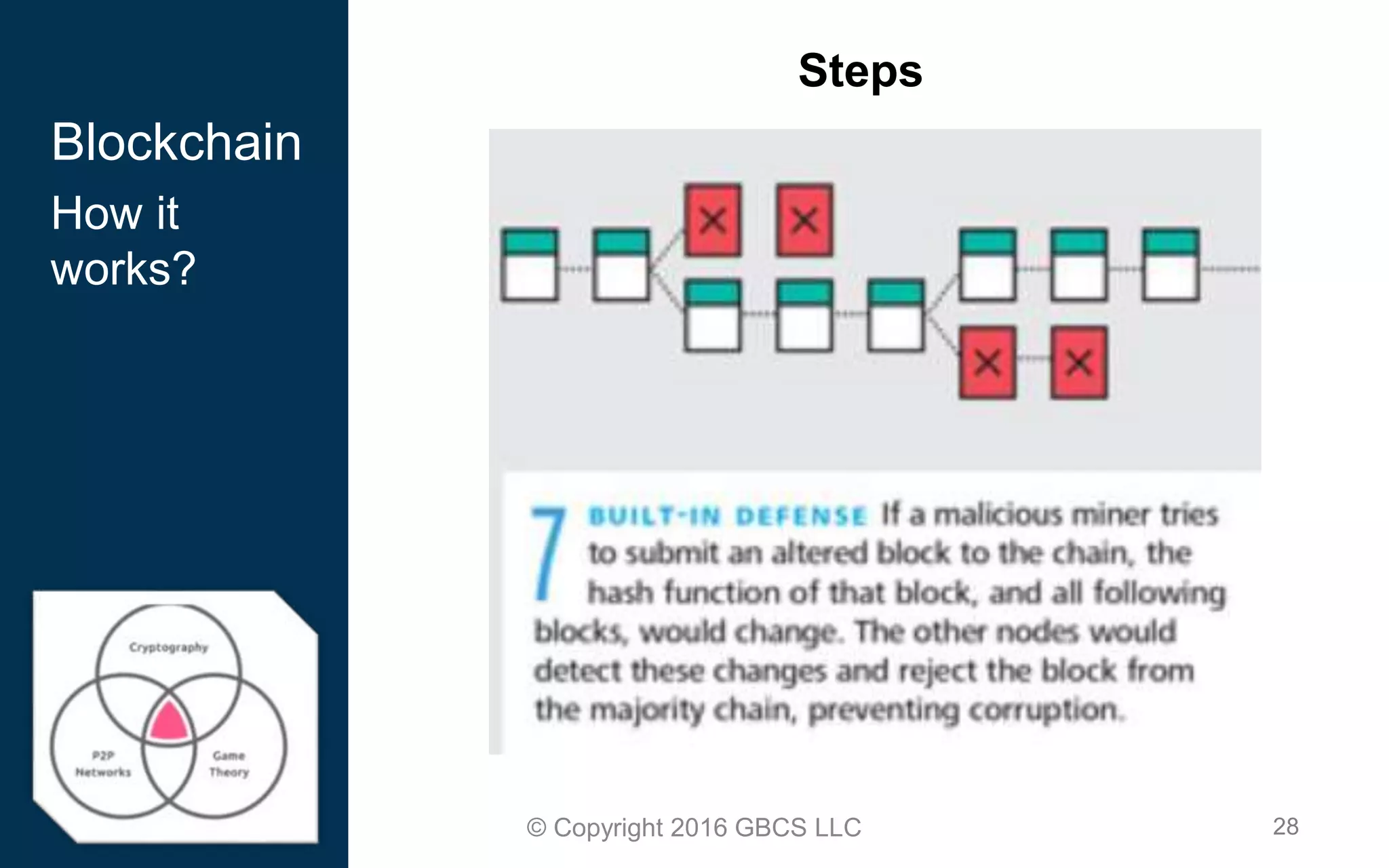
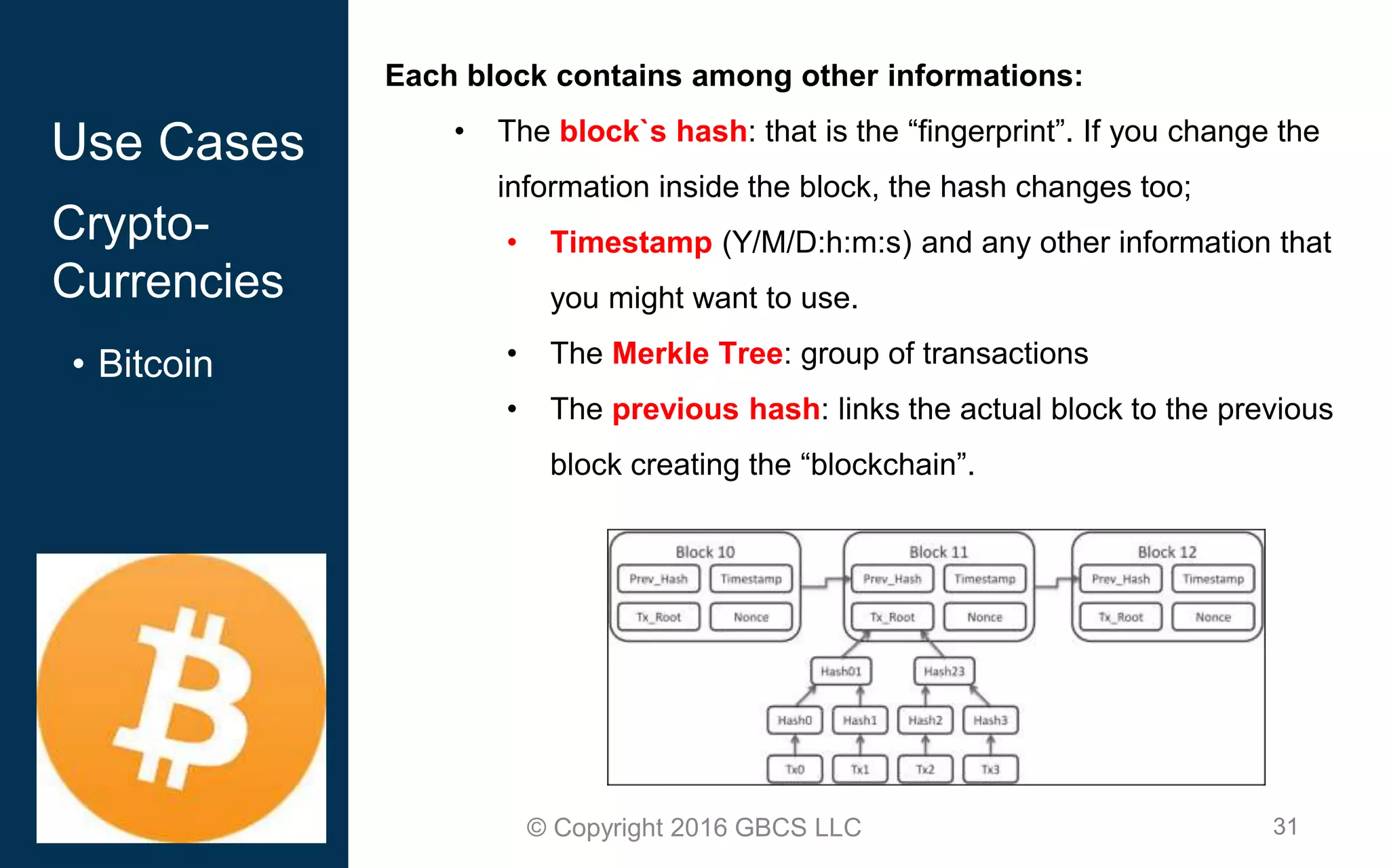
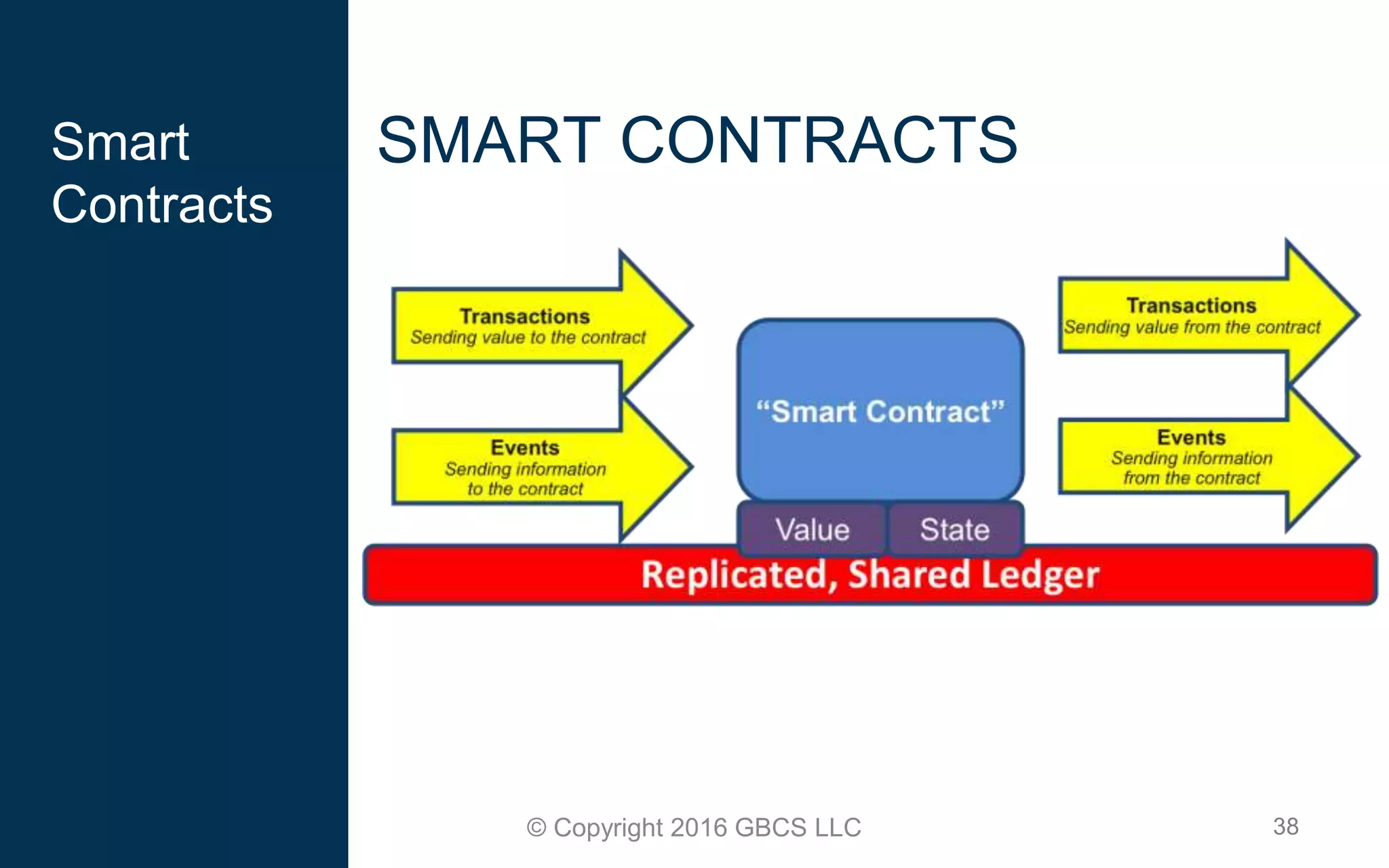
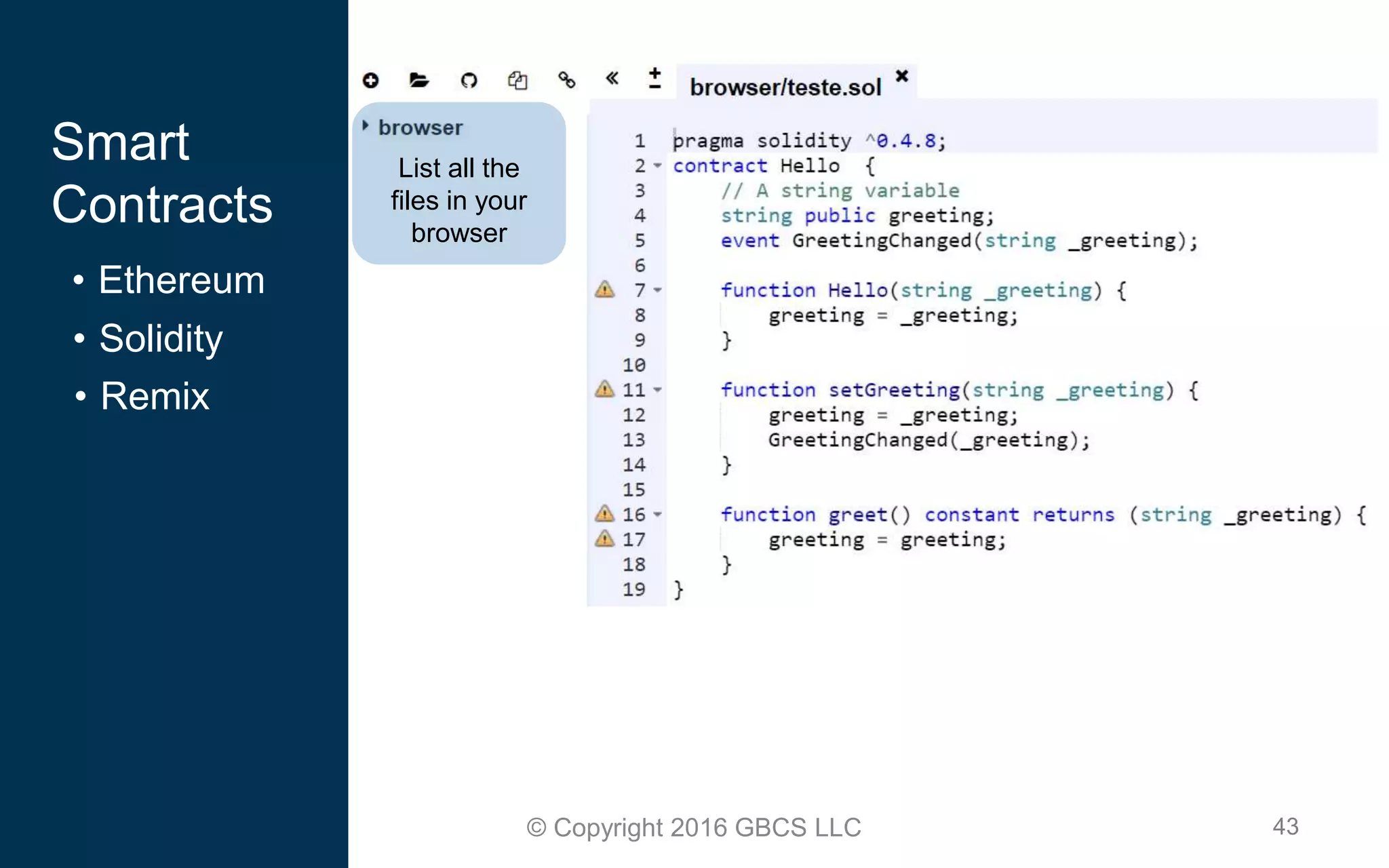
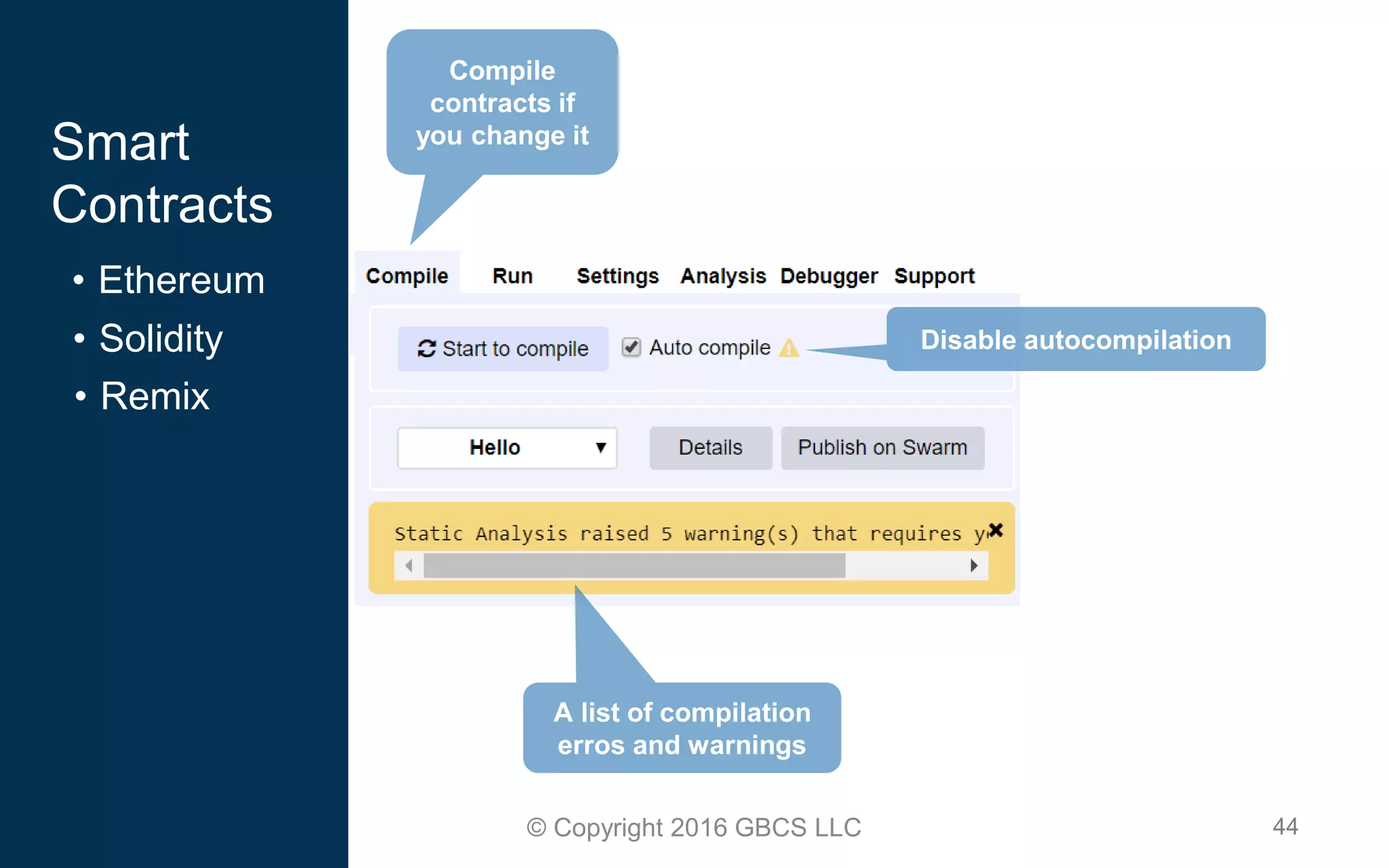
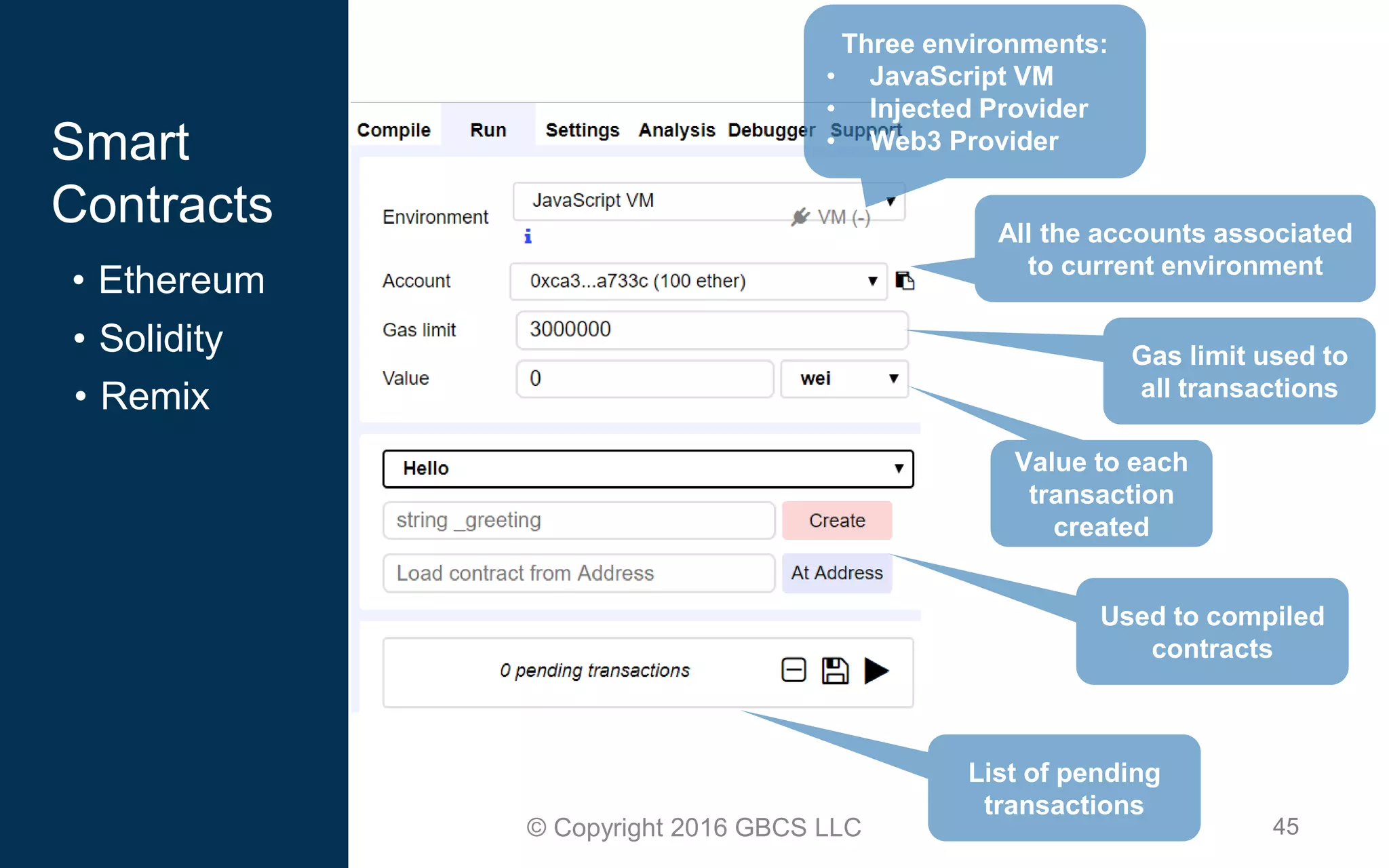
This document provides an introduction to blockchain technology and cryptocurrency. It discusses what blockchain is, how it works using cryptography, peer-to-peer networks, and game theory. It also covers use cases like Bitcoin, altcoins, tokens, ICOs, smart contracts on Ethereum using Solidity, and the Remix IDE. The document gives high-level overviews of these key blockchain concepts and technologies in under 3 sentences.