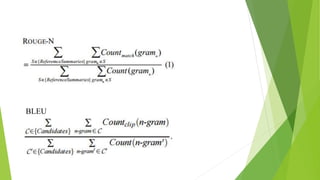
BLEU evaluates machine translations by comparing n-grams to reference human translations, while ROUGE evaluates summaries by measuring co-occurrence of n-grams between machine and human summaries. ROUGE measures recall by counting overlapping n-grams between the reference and machine summaries, while BLEU measures precision by counting n-grams in the machine translation that appear in the reference translations. Both are complementary metrics as high BLEU indicates more words from the machine translation are in the references and high ROUGE means more words from the references are in the machine translation.