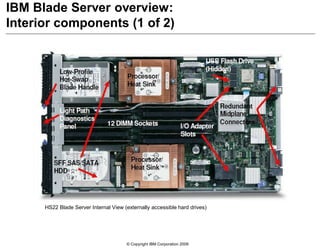
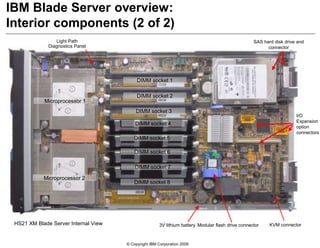
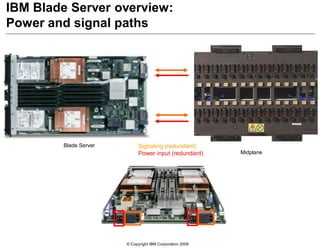
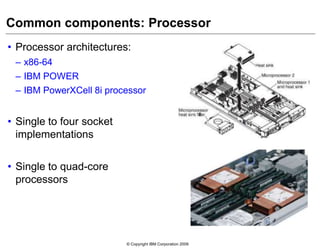
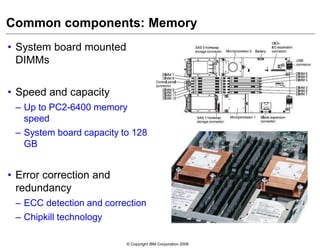
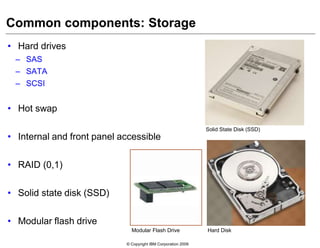
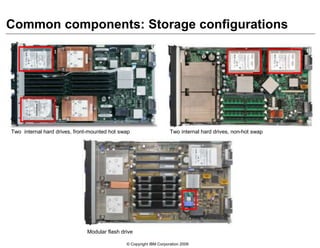
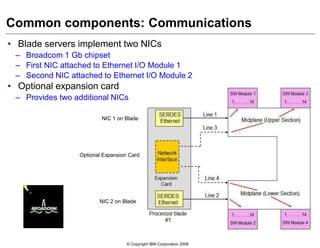
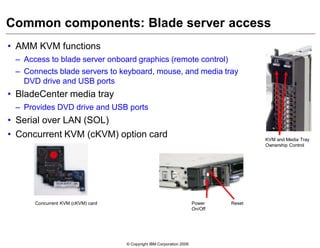
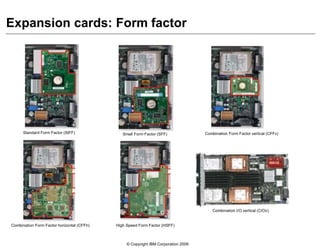
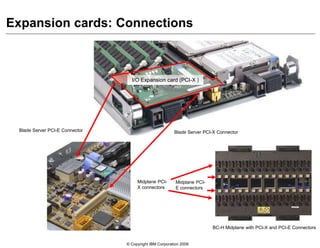
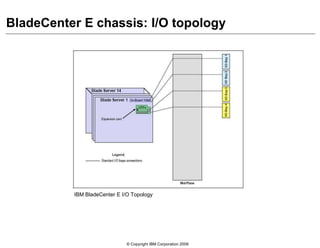
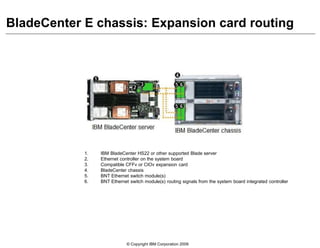
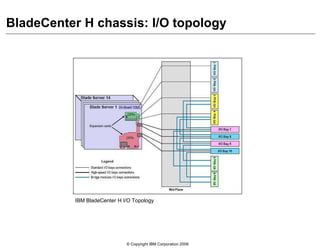
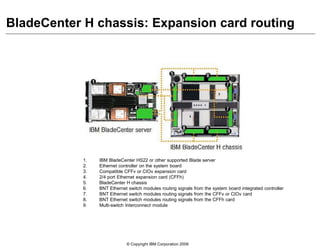
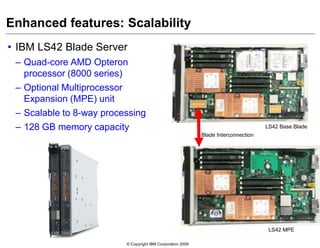
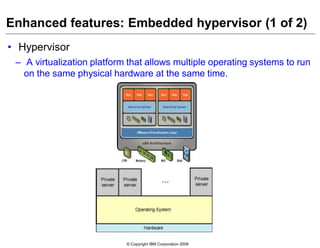
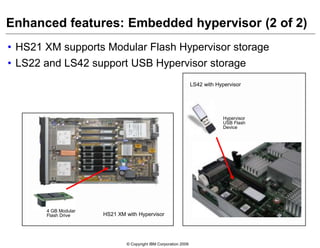
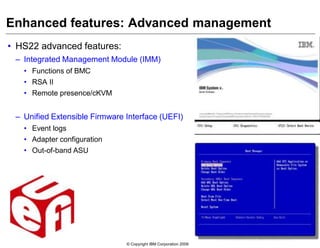
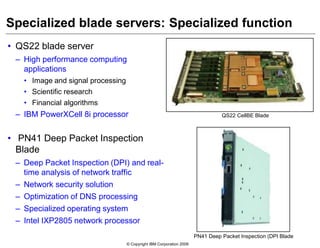
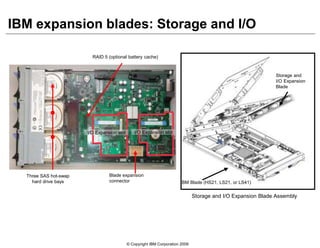
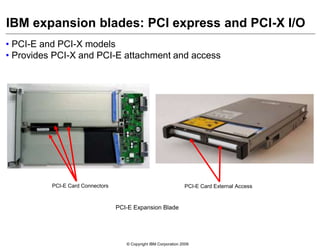
This document provides an overview of IBM blade server technology. It describes the key components of blade servers, including processors, memory, storage, networking interfaces, and expansion options. It also covers blade server communications and management features. Various IBM blade server models are compared and specialized blades for functions like high performance computing and deep packet inspection are highlighted.