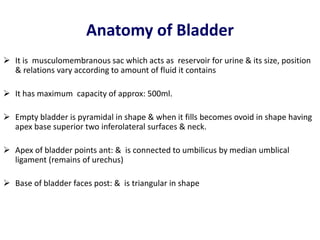
The document describes the anatomy, blood supply, innervation, and common cancers of the urinary bladder. It discusses the following key points:
- The bladder wall has four layers - serous, muscular, submucosal, and mucosal coats. The detrusor muscle in the muscular layer allows the bladder to expand and contract.
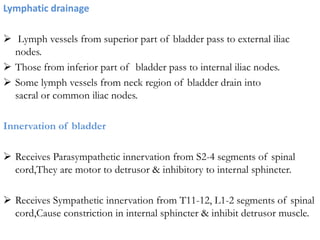
- The main arteries supplying the bladder are branches from the internal iliac arteries. Lymph drainage is to the external and internal iliac and sacral nodes.
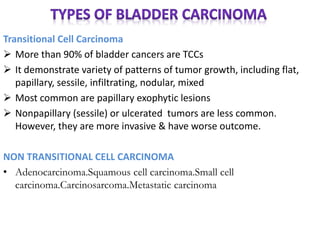
- Over 90% of bladder cancers are transitional cell carcinomas. Risk factors include smoking, occupational exposures, schistosomiasis infection, and certain drugs.
-