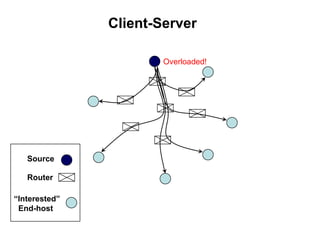
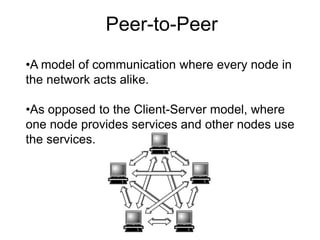
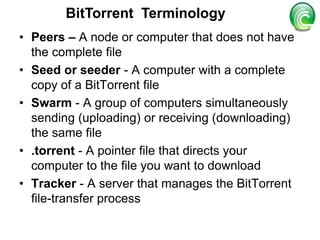
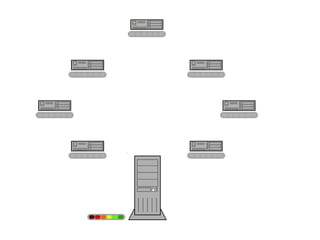
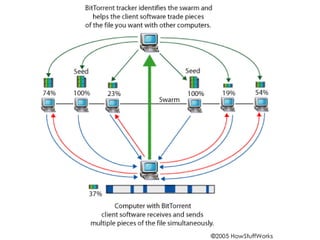
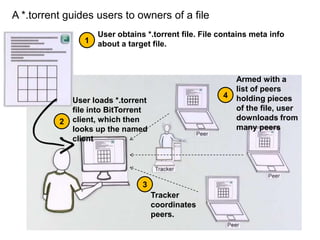
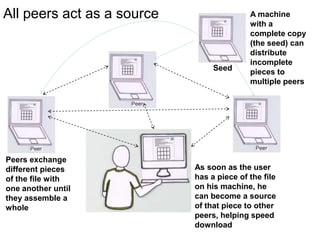
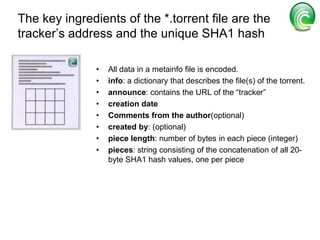
BitTorrent is a peer-to-peer protocol for distributing large files across the Internet. It allows users to download files from multiple sources at once, reducing bandwidth strain on any single source. The protocol works by breaking files into pieces that can be downloaded in any order from other users who already have pieces of the file. This "swarming" approach scales well as more users join a download. BitTorrent has proven highly effective for distributing popular content to millions of users and accounts for a significant portion of Internet traffic today.