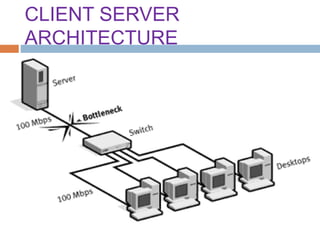
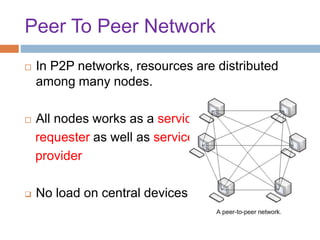
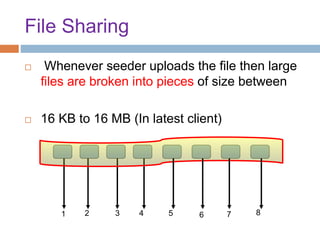
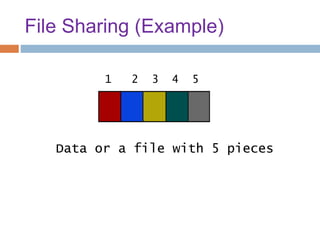
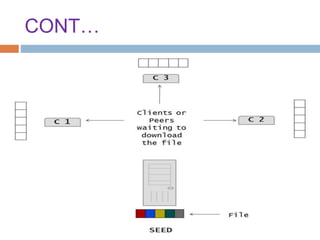
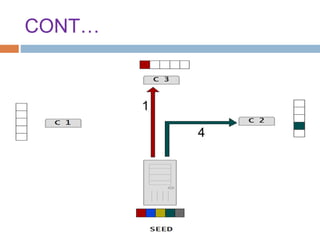
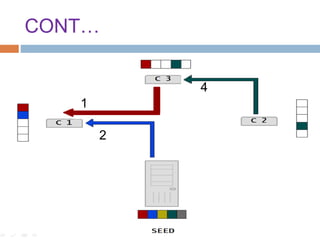
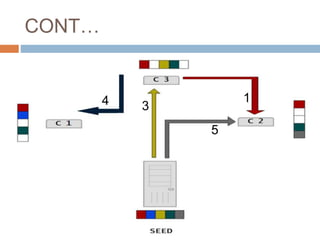
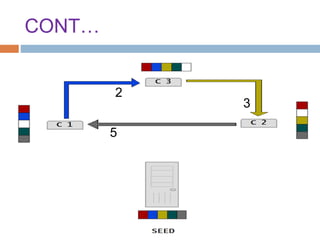
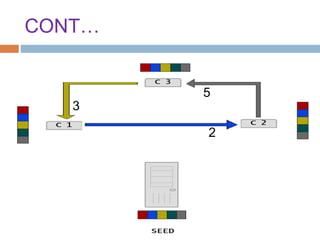
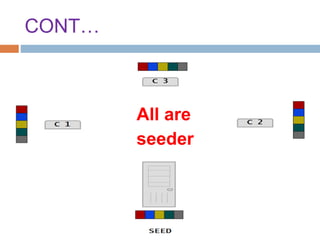
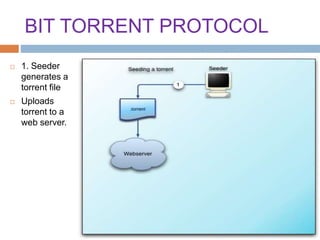
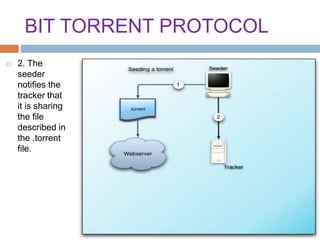
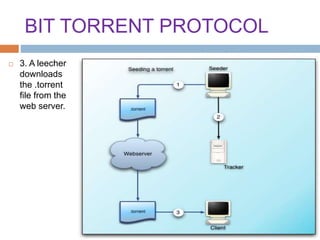
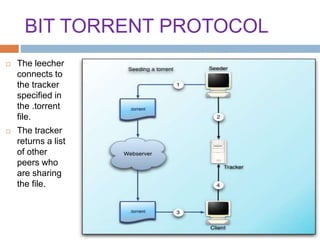
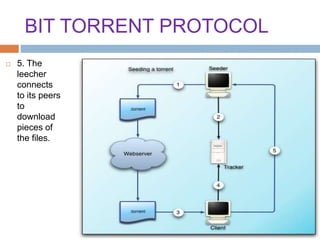
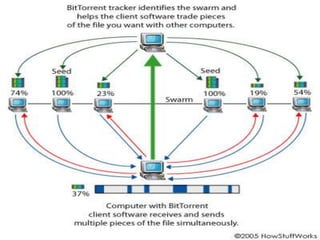
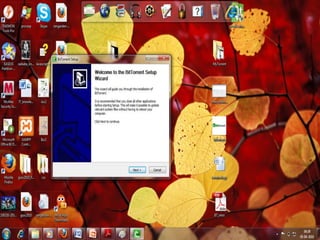
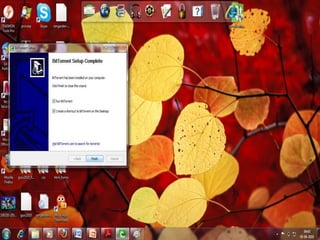
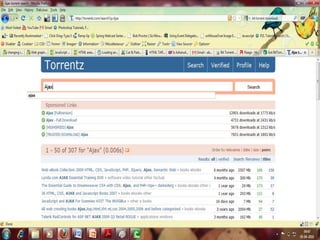
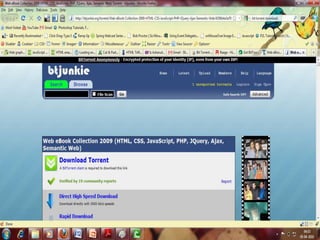
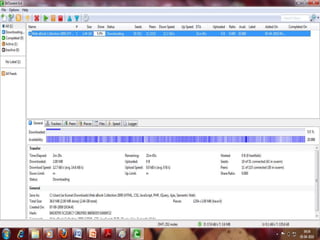
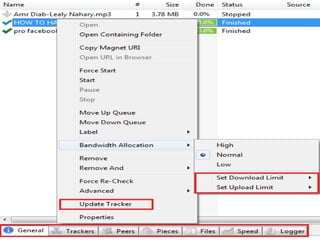
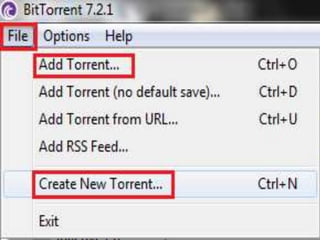
This document provides an overview of the BitTorrent protocol. It describes how BitTorrent works by breaking files into pieces that can be downloaded simultaneously from multiple users, reducing load on servers. Key components are explained, including torrent files, trackers, peers, seeders and leechers. Advantages of BitTorrent include faster download speeds and reduced bandwidth usage. Limitations include potential slow speeds until more peers join and a reliance on trackers.