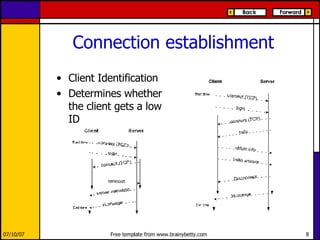
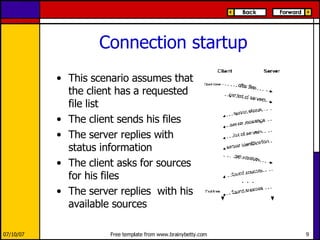
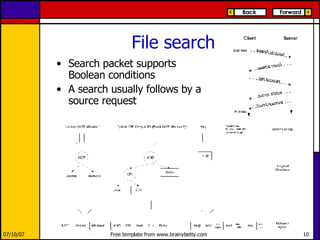
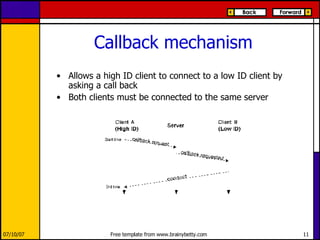
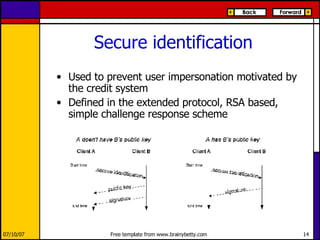
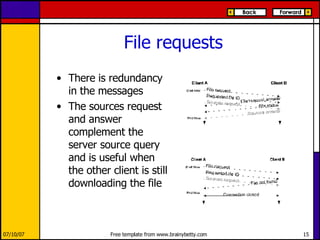
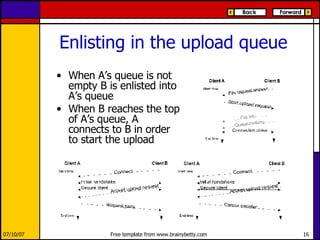
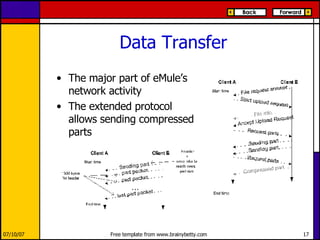
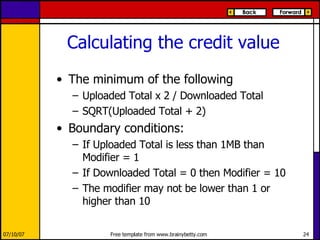
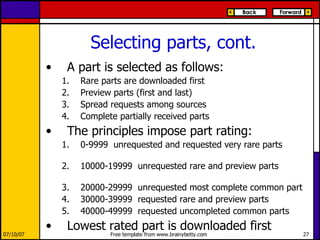
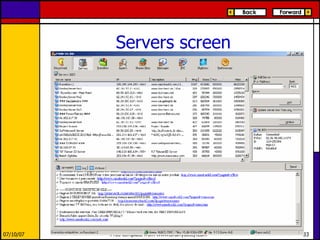
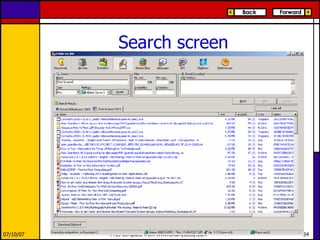
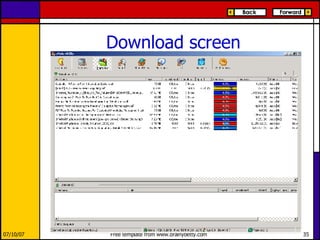
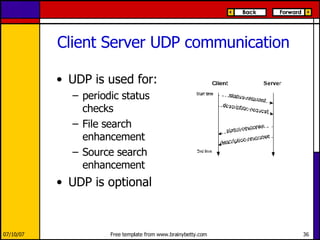
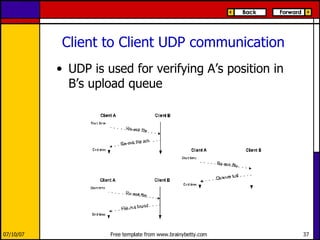
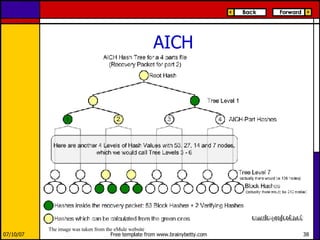
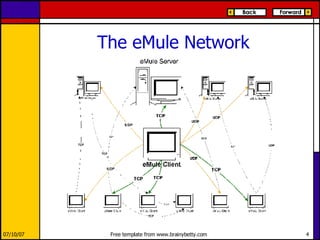
eMule is a peer-to-peer file sharing application that uses both client-server and peer-to-peer protocols. The client connects to servers to search for files and sources. It then connects directly to peer clients to download and upload file parts. Key aspects of the protocol include credit systems to incentivize uploads, queue management, and mechanisms to detect and recover from corrupted downloads.


![The Protocol Each message starts with a 6 byte header [protocol, size ,type] Empty messages are allowed Encoded are Integers, Strings and bit sets Strings are encoded using a 2 byte length, value encoding Message tags](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/the-emule-application-of-the-edonkey-protocol2670/85/The-eMule-application-of-the-eDonkey-protocol-6-320.jpg)