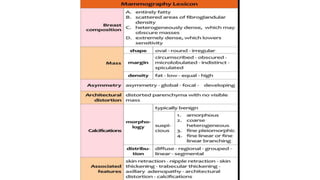
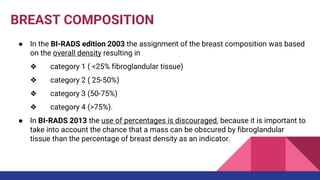
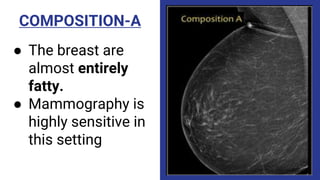
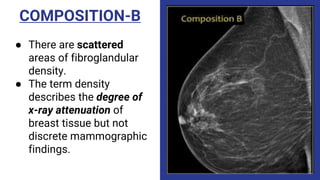
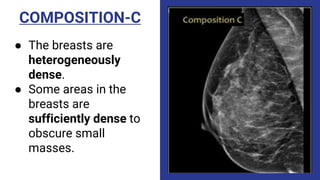
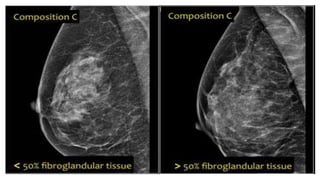
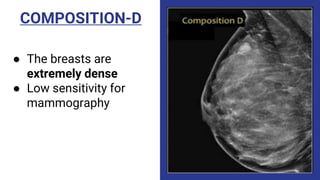
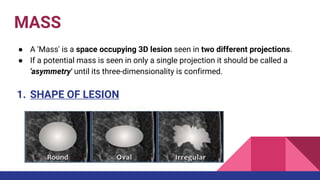
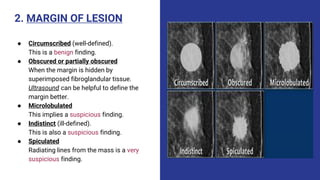
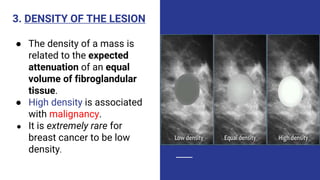
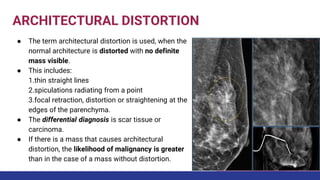
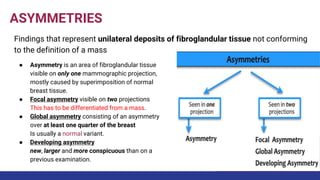
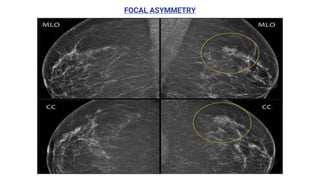
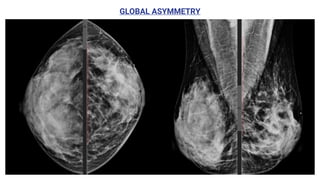
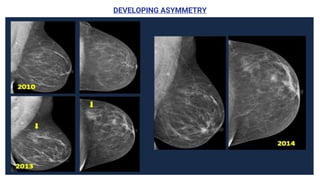
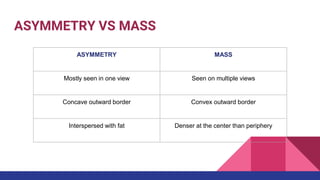
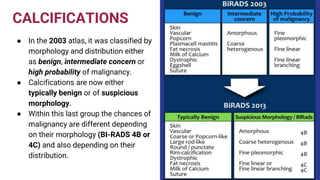
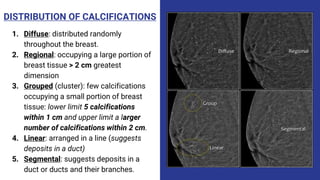
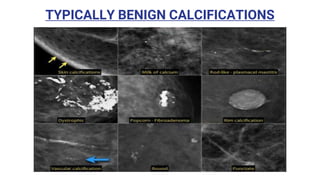
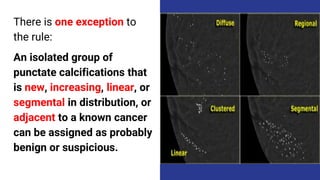
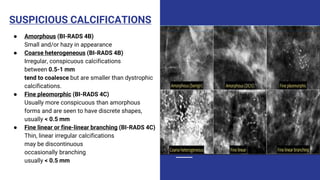
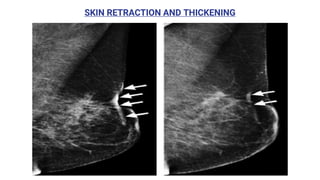
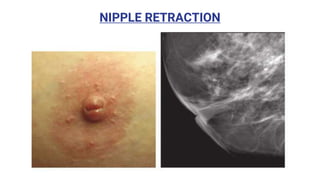
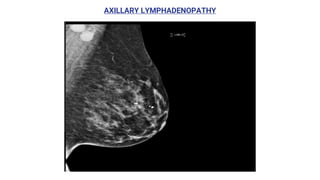
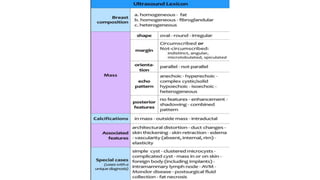
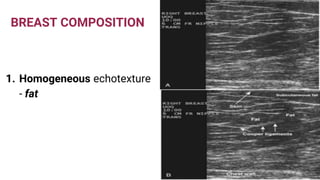
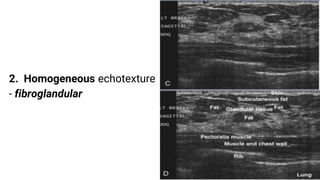
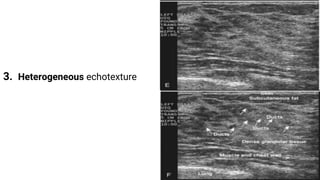
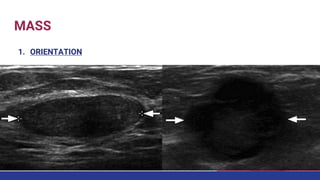
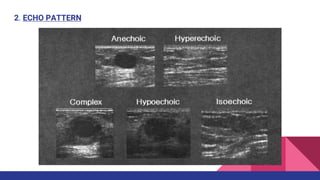
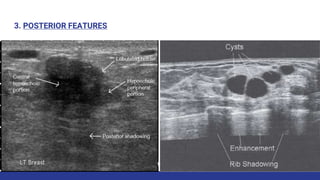
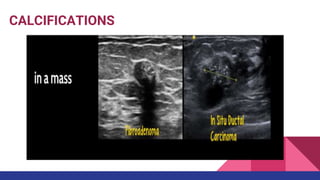
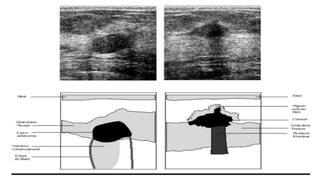
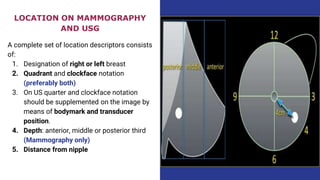
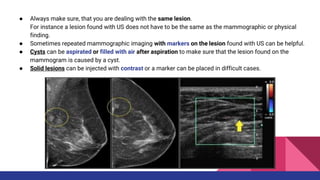
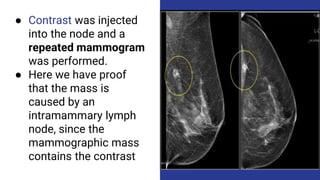
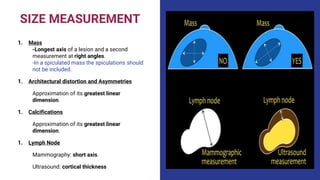
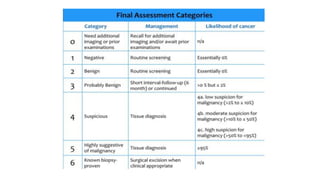
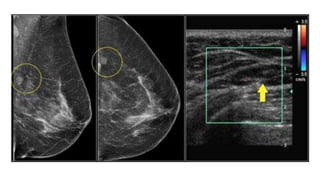
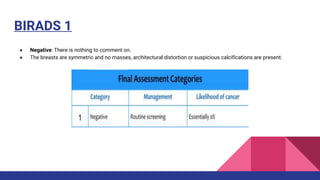
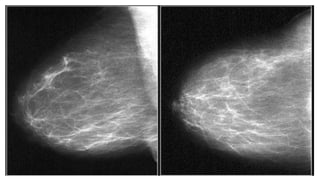
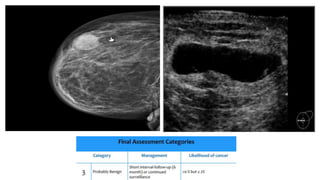
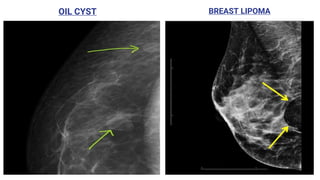
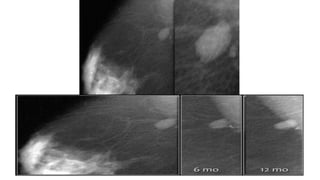
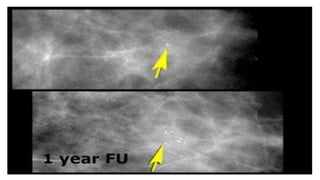
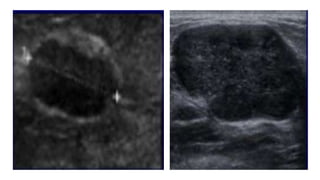
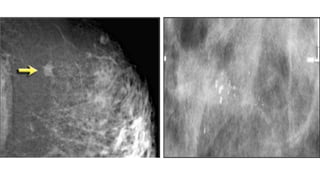
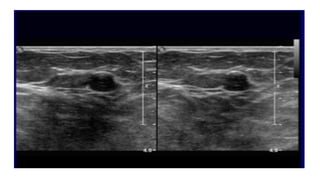
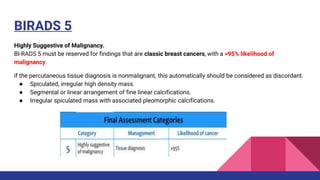
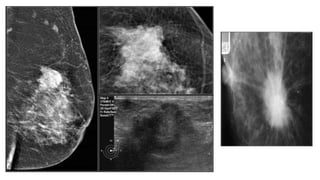
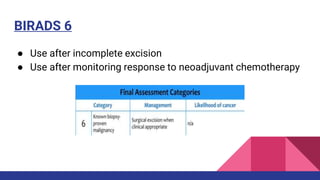
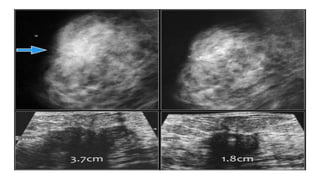
This document provides an overview of the BI-RADS lexicon for mammography and ultrasound reporting. It discusses the standardized terminology and descriptors used to report breast composition, masses, calcifications, asymmetries and other findings. Key points include the BI-RADS categories for final assessment ranging from negative (1) to highly suggestive of malignancy (5). Standardized reporting aims to reduce confusion and facilitate monitoring and quality assessment.