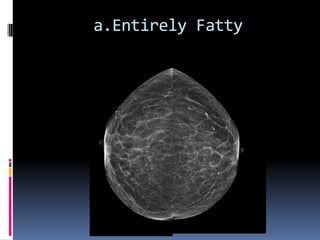
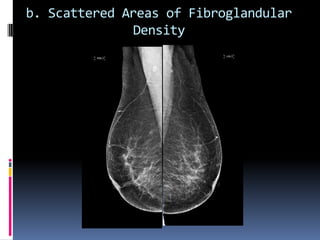
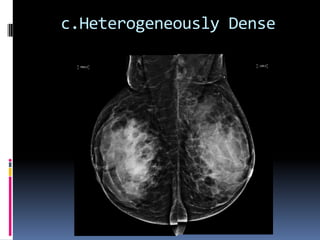
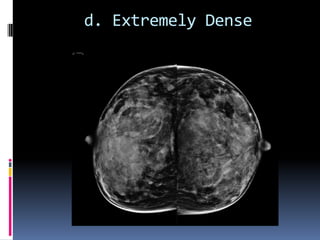
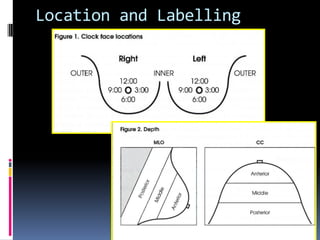
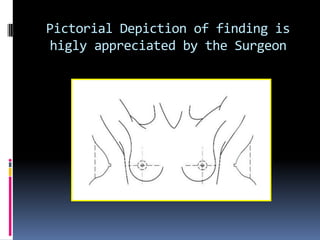
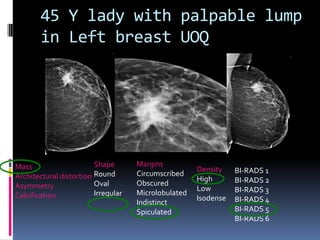
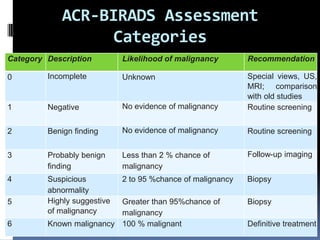
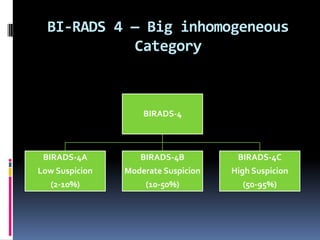
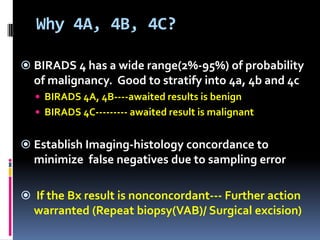
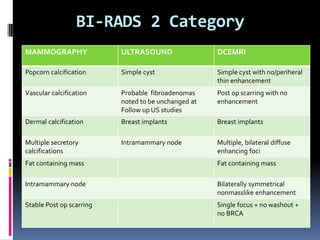
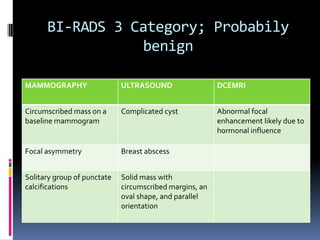
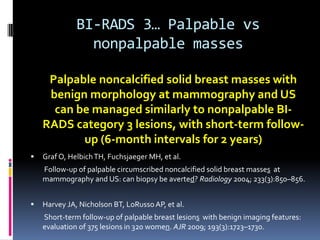
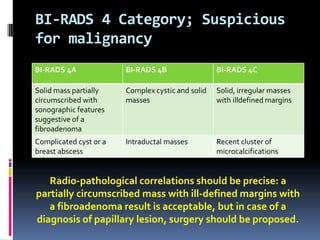
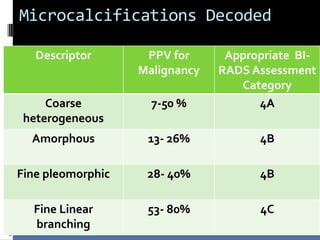
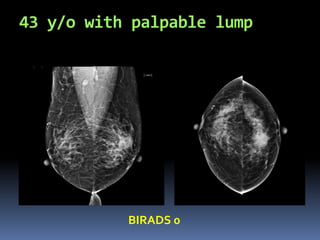
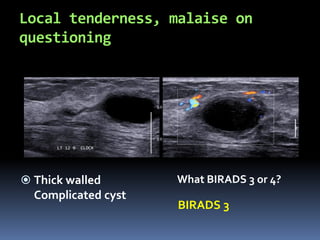
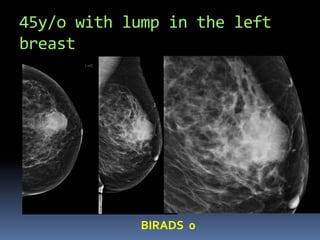
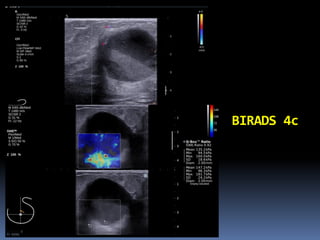
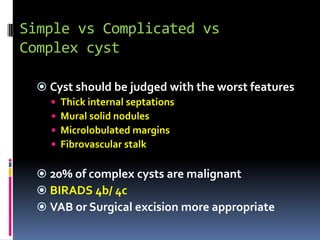
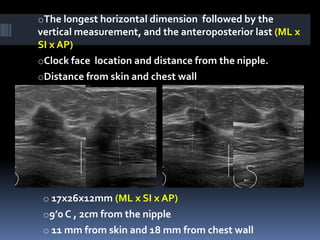
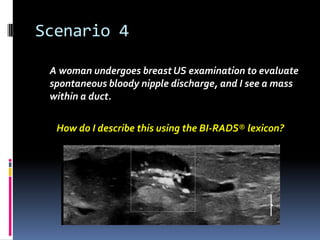
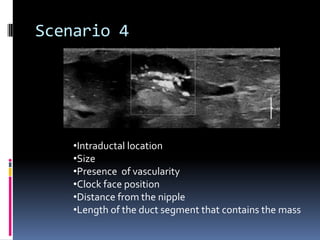
The document provides excerpts from the latest edition of the ACR BI-RADS Atlas, which standardizes breast imaging reporting and management recommendations. It discusses key components of the BI-RADS system including standardized terminology, assessment categories from 0-6 with associated likelihood of malignancy and recommendations, and guidelines for reporting findings from mammography, ultrasound, and MRI exams. Standardized reporting aims to improve communication and allow for outcome auditing.