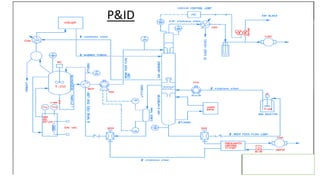
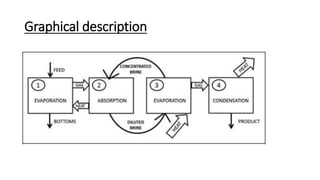
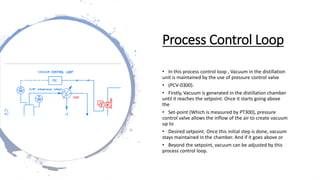
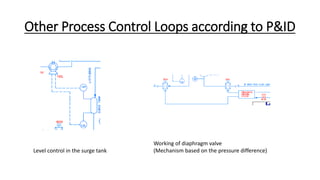
This document describes a concurrent alcohol recovery and fermentation (CARAF) process using pass-through distillation. The process involves 4 blocks where fermentation broth is evaporated in block 1, the gas is absorbed by a brine solution in block 2, heat is applied in block 3 to vaporize the ethanol, and the ethanol is condensed in block 4. This continuous process recovers ethanol at a low energy and temperature compared to conventional methods. Actuators like pumps, valves, and agitators control the flow of materials between blocks. Sensors monitor temperature and pressure to control loops that maintain the vacuum in the distillation unit. Compatible materials like stainless steel, PVC, glass and copper are used to interact with the