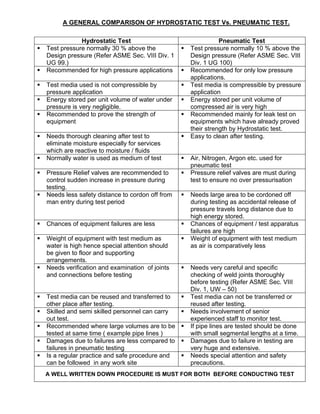
Pneumatic testing involves higher risks than hydrostatic testing due to the compressibility and stored potential energy of air. A minor leak during pneumatic testing can lead to a rapid rupture and explosion before remedial action can be taken. Hydrostatic testing uses incompressible water, stores much less energy, and allows leaks to be detected sooner through a pressure drop. Proper procedures and safety precautions are required when conducting pneumatic tests to prevent damage and injury.