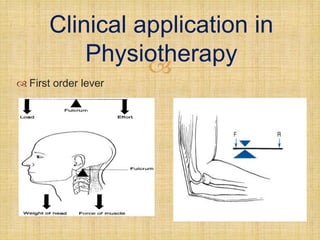
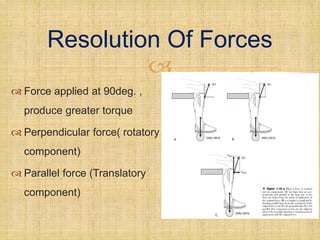
This document discusses levers and their application in physiotherapy. It defines the three types of levers - first, second, and third order - and provides examples of their clinical use. Torque, force couples, and the resolution of forces are also explained. The roles of bones, joints, and muscles as lever systems in the body are described. Finally, references used in creating the document are listed.