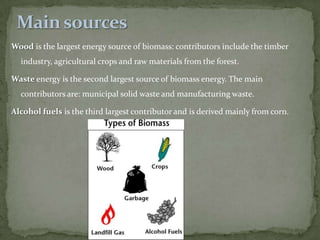
Biomass is a renewable source of energy derived from organic matter such as waste wood, agricultural crops, and municipal solid waste. It can be burned to produce heat and electricity, with wood being the largest biomass energy source. In California, over 60 million tons of biomass sources like agricultural waste, dead trees, and livestock manure could generate enough electricity for about 2 million homes each year. While biomass power generation reduces landfill waste, it is generally more expensive than other energy sources.