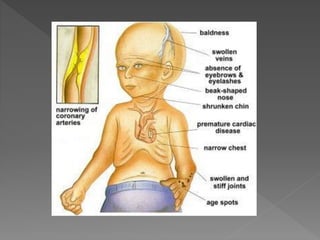
Progeria, a condition characterized by premature aging, is believed to result from a dominant gene mutation affecting the lamin A protein, causing cellular instability. It is not hereditary, manifesting in children as early as 10 to 24 months with symptoms like growth failure, joint stiffness, and cardiovascular issues, with an average life expectancy of 13 years. Currently, there is no cure, but treatments exist to slow progression, affecting approximately 1 in 4-8 million newborns globally.