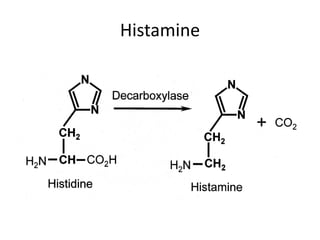
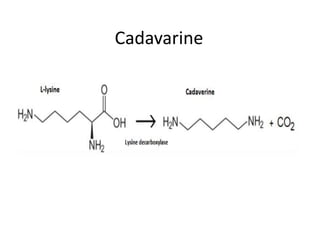
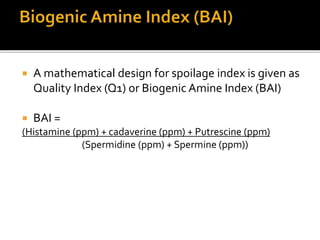
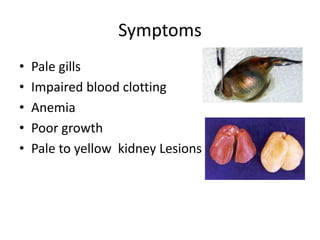
Biogenic amines, such as histamine, cadaverine, and putrescine, are significant for determining fish safety and quality, with histamine being especially critical due to its association with scombroid poisoning. Symptoms of poisoning can occur quickly, and prevention strategies include rapid chilling of fish and good hygiene practices. Aflatoxins, produced by certain fungi, pose serious health risks and can be controlled through proper storage and testing methods.