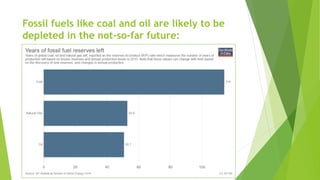
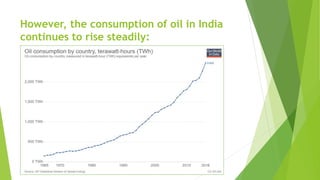
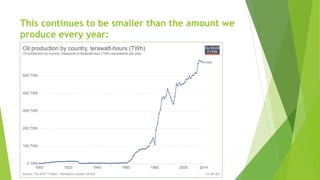
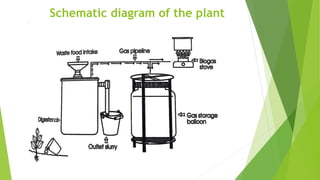
The document discusses the generation of biogas from kitchen waste as a renewable energy source to replace fossil fuels like LPG. It outlines the process of recycling biomass through anaerobic digestion to produce methane, its advantages, and the simple infrastructure required for implementation. Additionally, it addresses safety concerns, potential challenges, and necessary precautions for optimal biogas production.