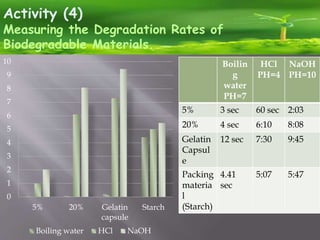
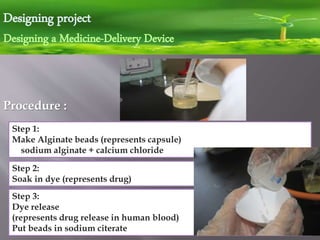
This document discusses a student project on biodegradable materials and converting biomass to energy. It includes 4 activities: 1) comparing biodegradable packing materials, 2) identifying biodegradable objects, 3) processing and testing gelatin, and 4) measuring degradation rates of materials. It also describes a design project to create a medicine delivery device using alginate beads that degrade. The document discusses how converting biomass to energy through methane production can help Qatar reduce waste and dependence on fossil fuels according to its 2030 vision.