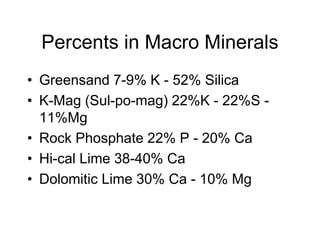
This document outlines strategies for high bionutrient crop production, including addressing limiting soil factors, supporting soil biology, and achieving nutrient density in plants. It discusses testing soils and balancing minerals, inoculating soils biologically, designing potting soils, using minimum tillage, and methods for fertigation, foliar spraying, and applying macronutrients and micronutrients. Target levels are provided for soil minerals and conversions for application rates. The document emphasizes building soil health to grow healthy, nutritious plants and supporting the soil food web.