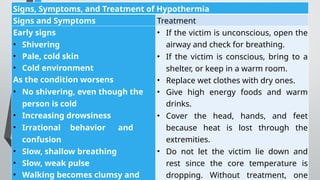
The document outlines various dance forms and emphasizes the importance of personal safety protocols while engaging in physical activities like dance. It discusses hydration, overexertion, hypothermia, and hyperthermia, detailing symptoms, prevention, and treatments for each condition. Additionally, it provides information about cultural festivals in the Philippines, specifically the Sinulog and Panagbenga festivals, highlighting their history and significance.