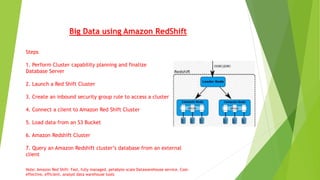
This document provides steps for performing big data analytics using Amazon Redshift, EC2, and S3. It outlines how to 1) plan and launch a Redshift cluster, 2) connect a client and load data from S3, and 3) query the Redshift database from an external client. Key points are that Redshift is a fast, managed data warehouse service, optimized for processing large datasets ranging from GB to PB for low cost compared to other solutions. It also takes on administrative tasks so users can focus on analytics.