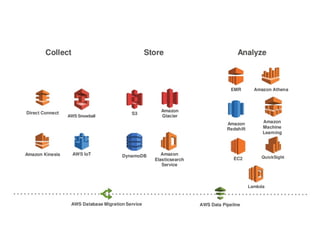
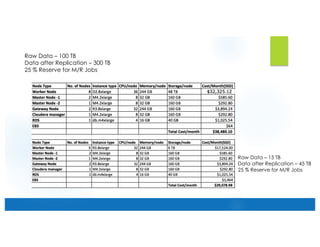
This document provides an overview of building a big data architecture on AWS. It discusses key AWS services like EC2, EBS, S3, RDS, Route 53, Direct Connect, IAM, EMR, CloudWatch and CloudFormation. It describes using these services for persistent and transient big data clusters, including considerations around capacity planning, security best practices, and advantages of each approach. Transient clusters launched through EMR are recommended for transient workloads, with S3 as the persistent data store.