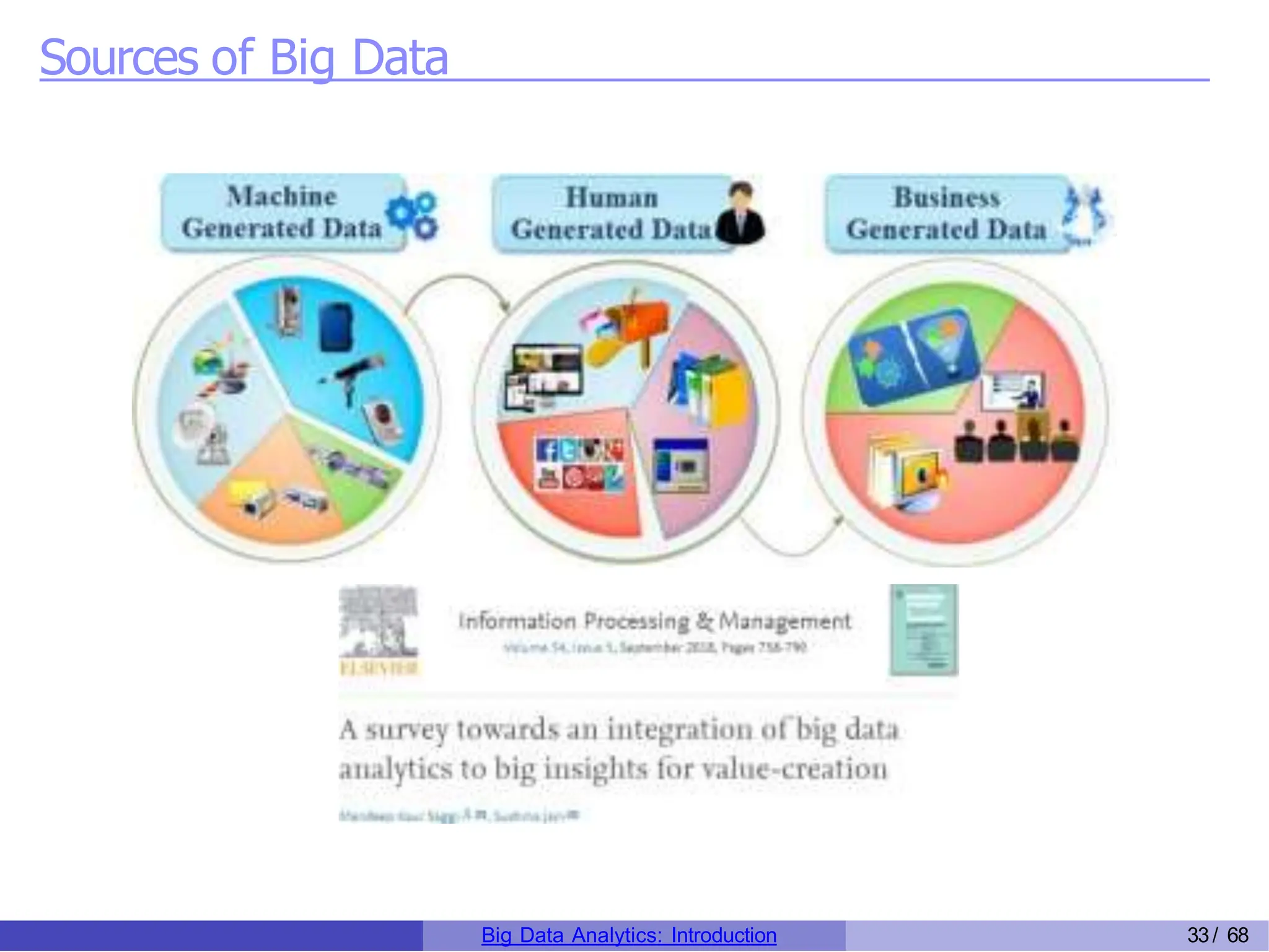
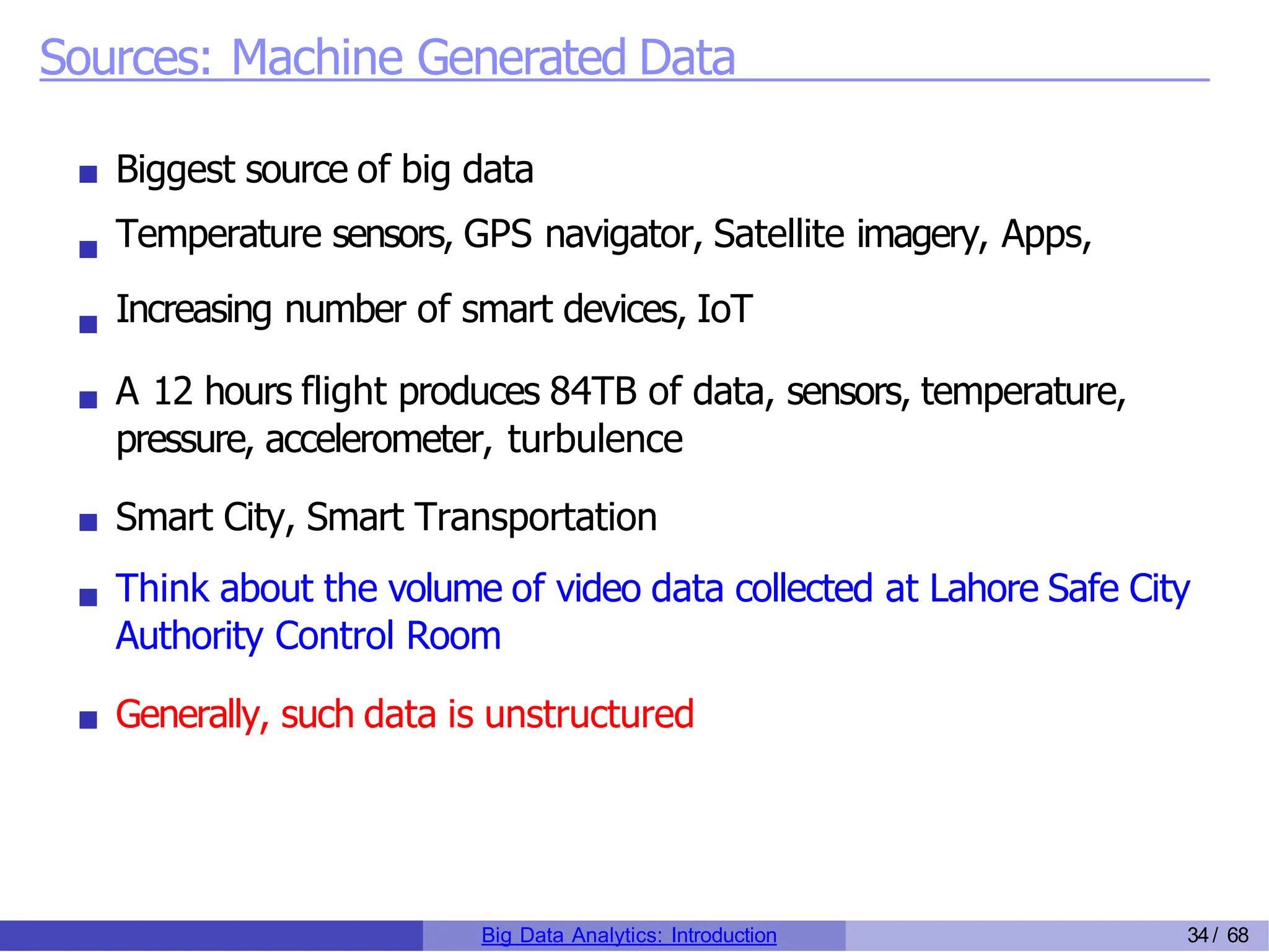
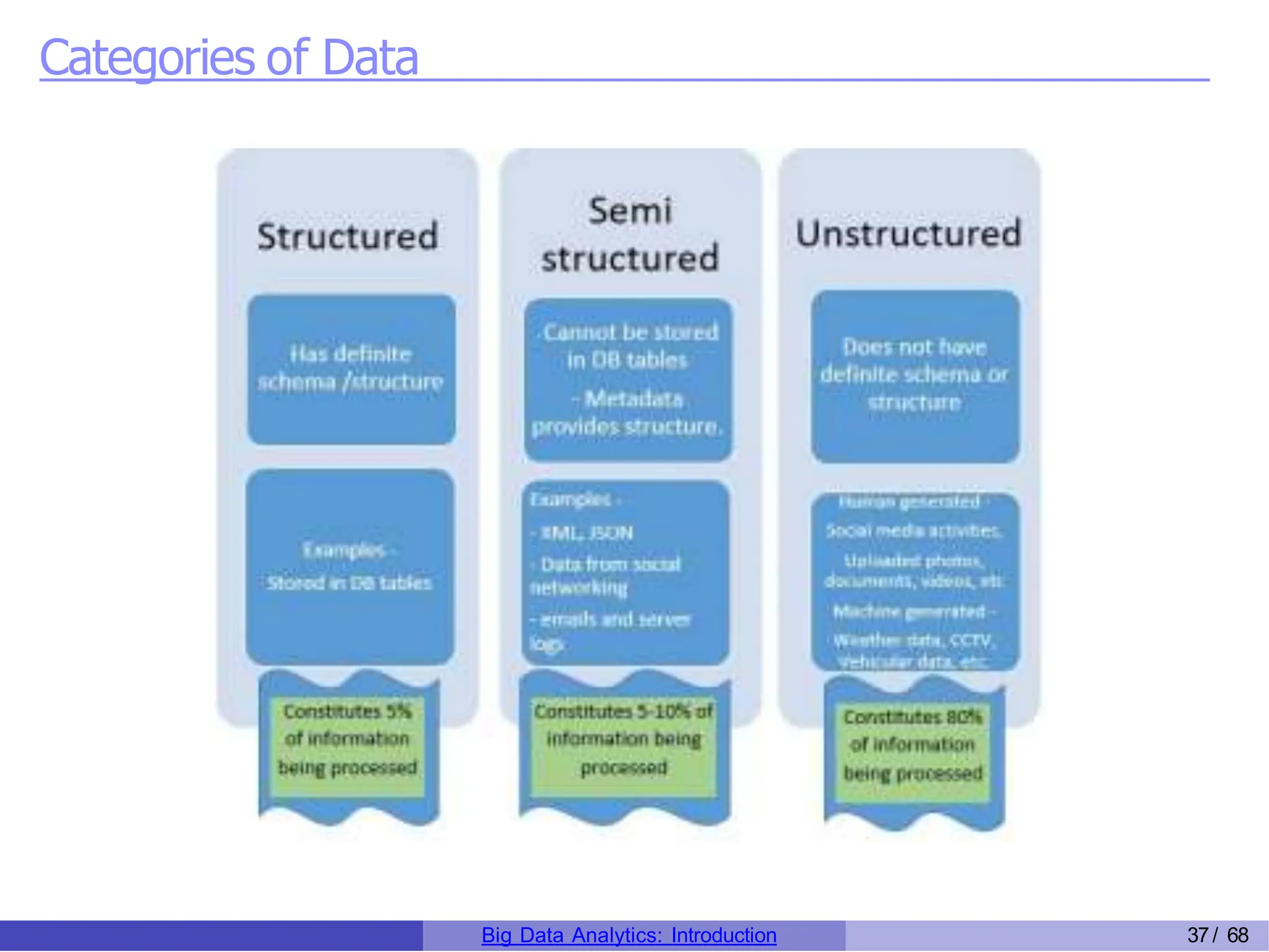
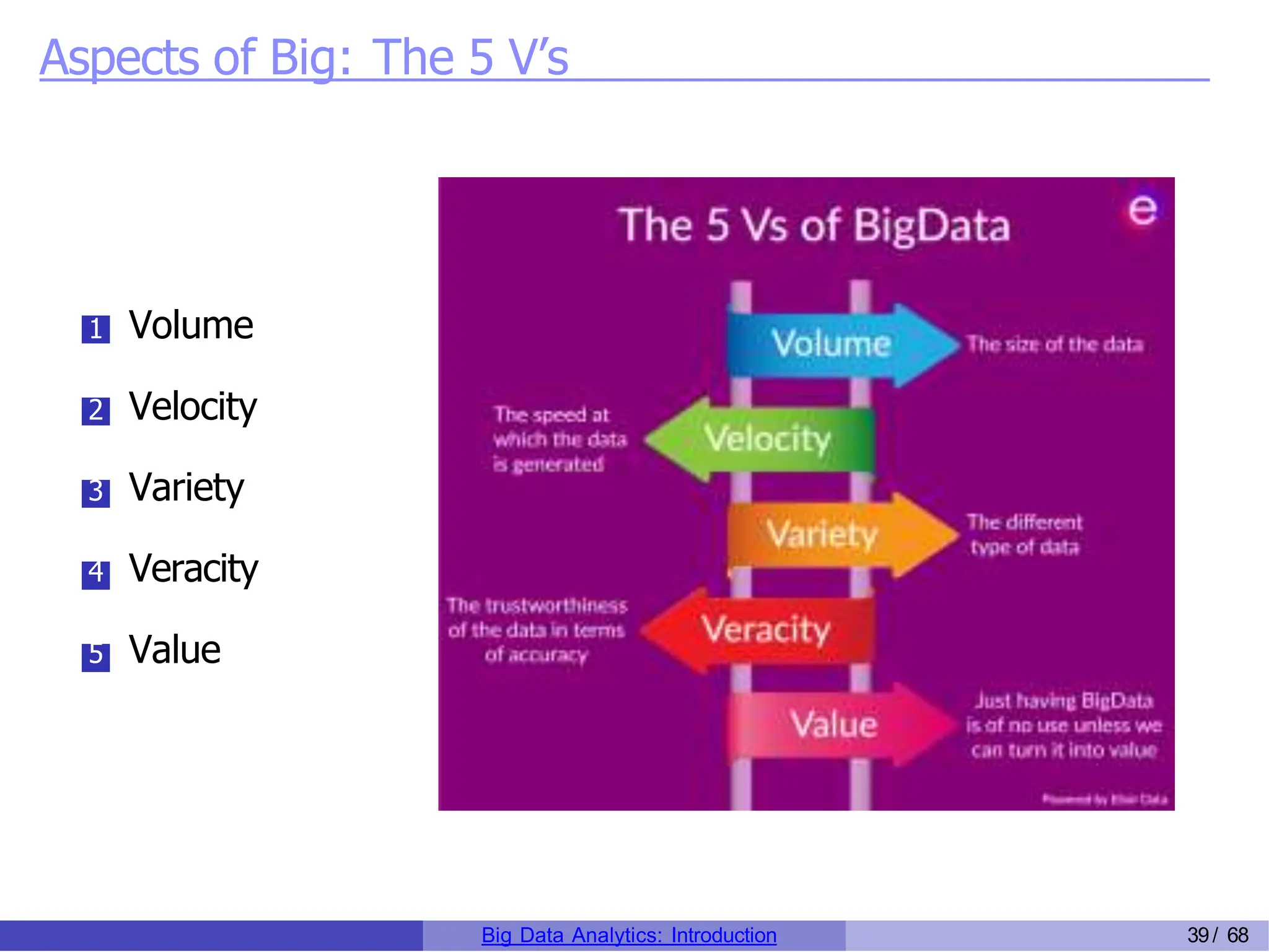
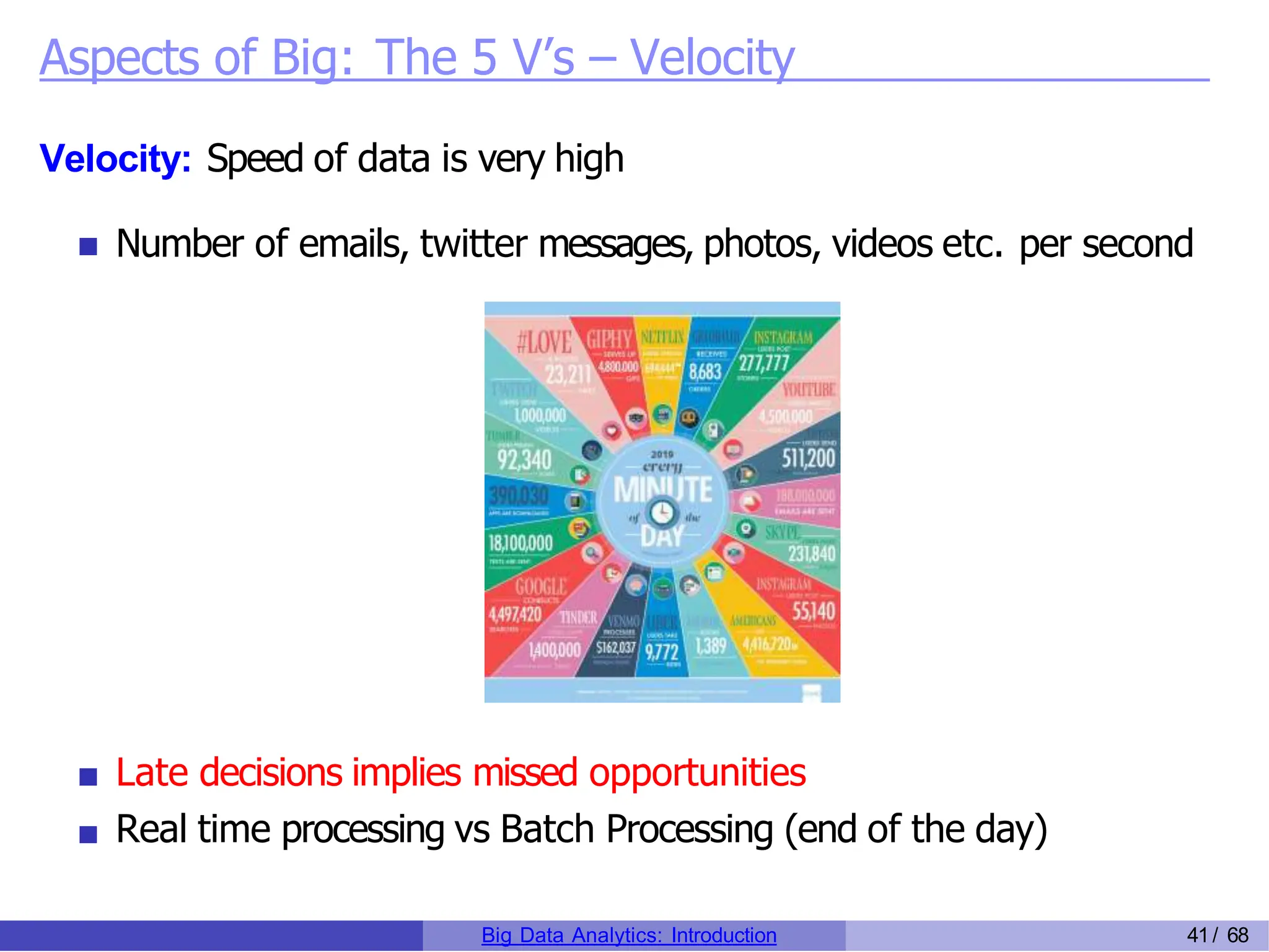
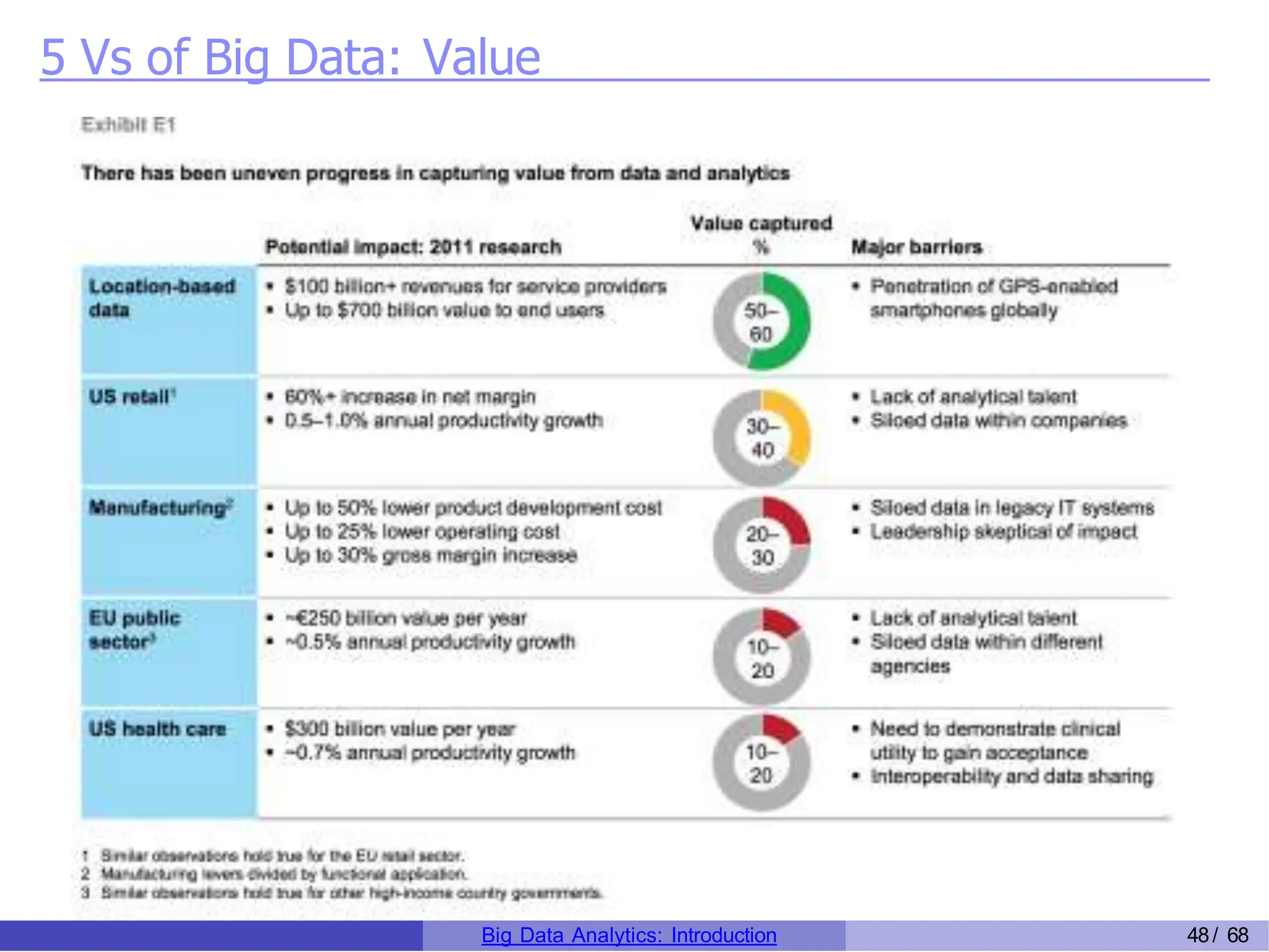
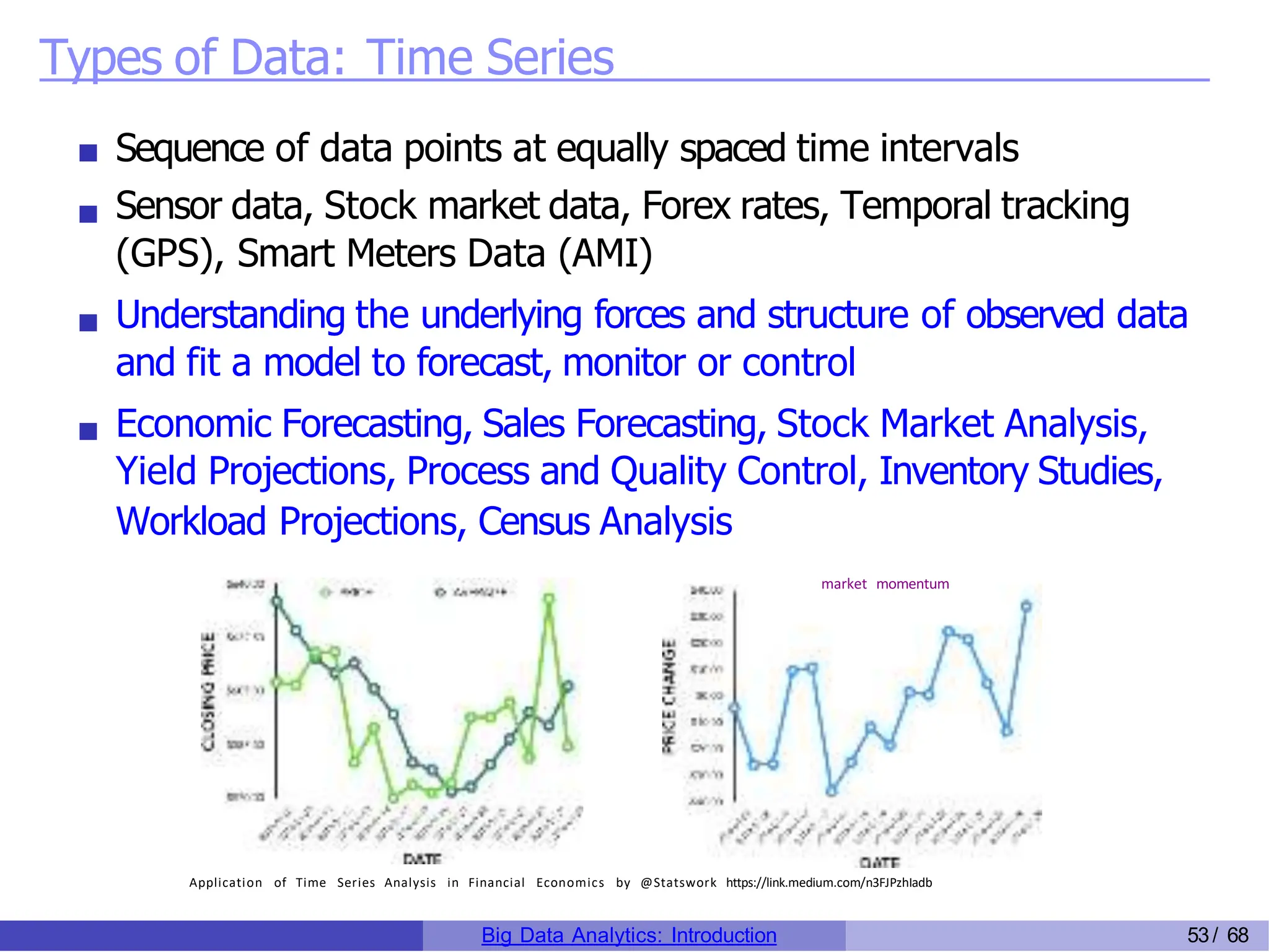
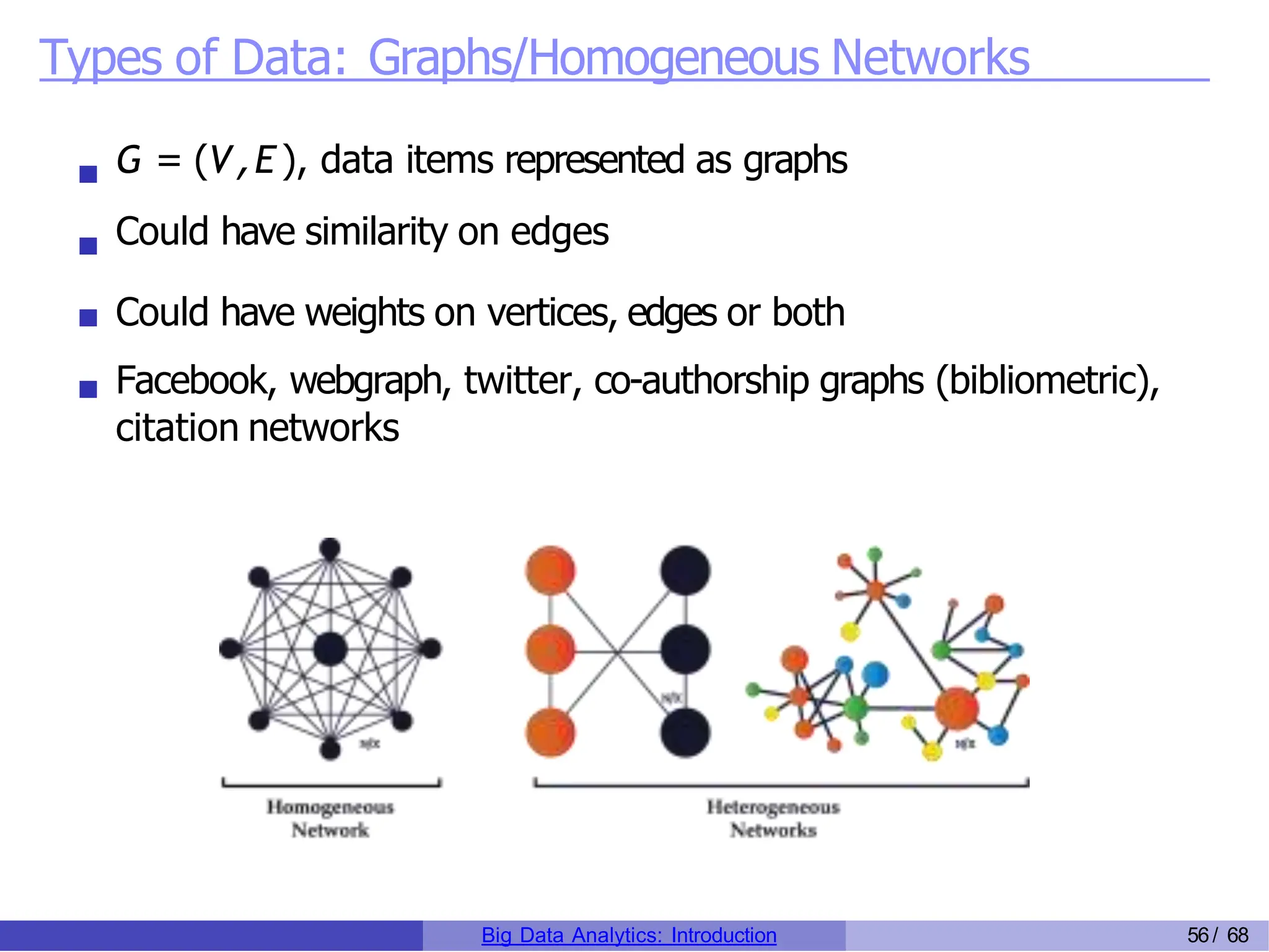
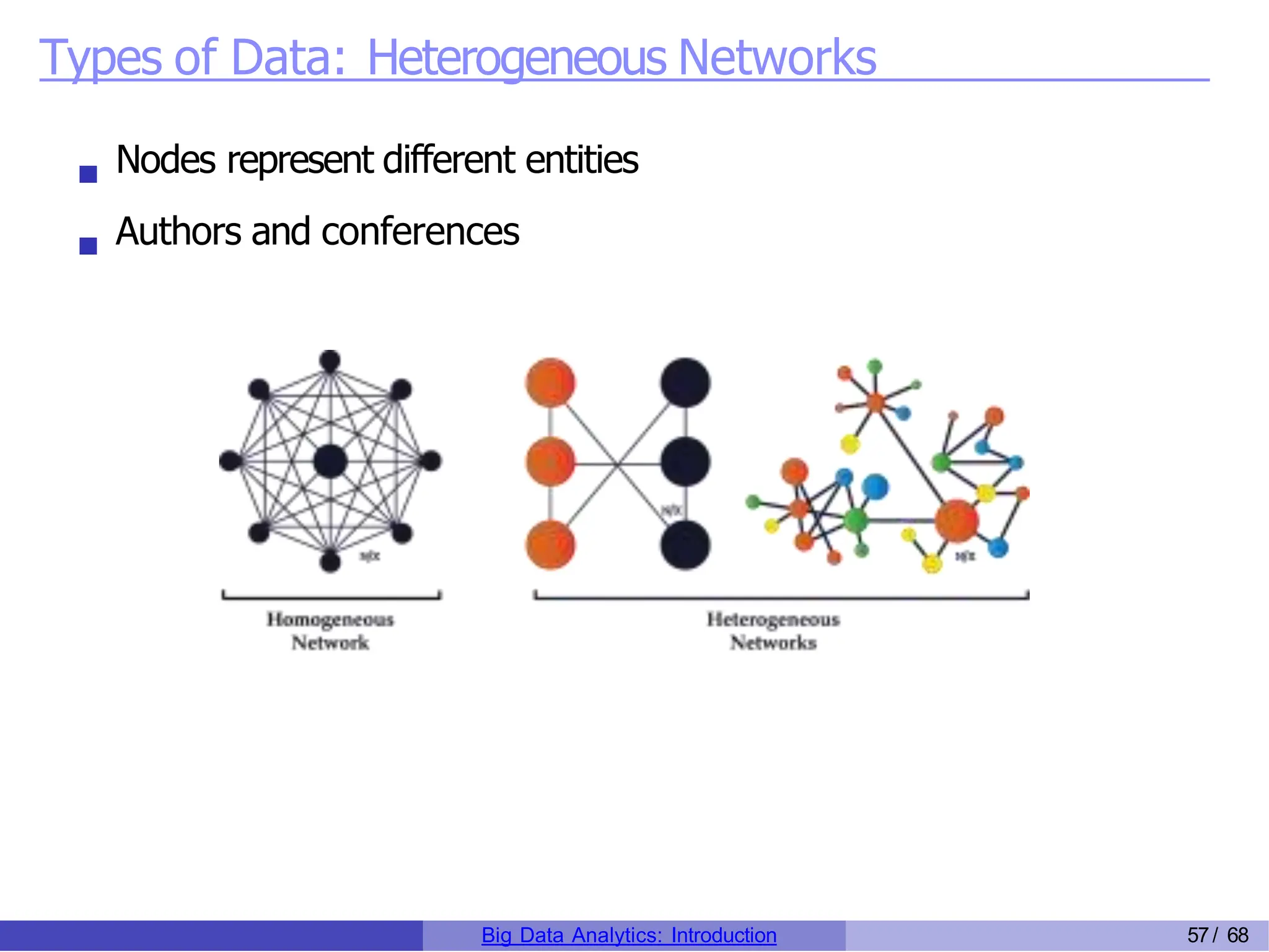
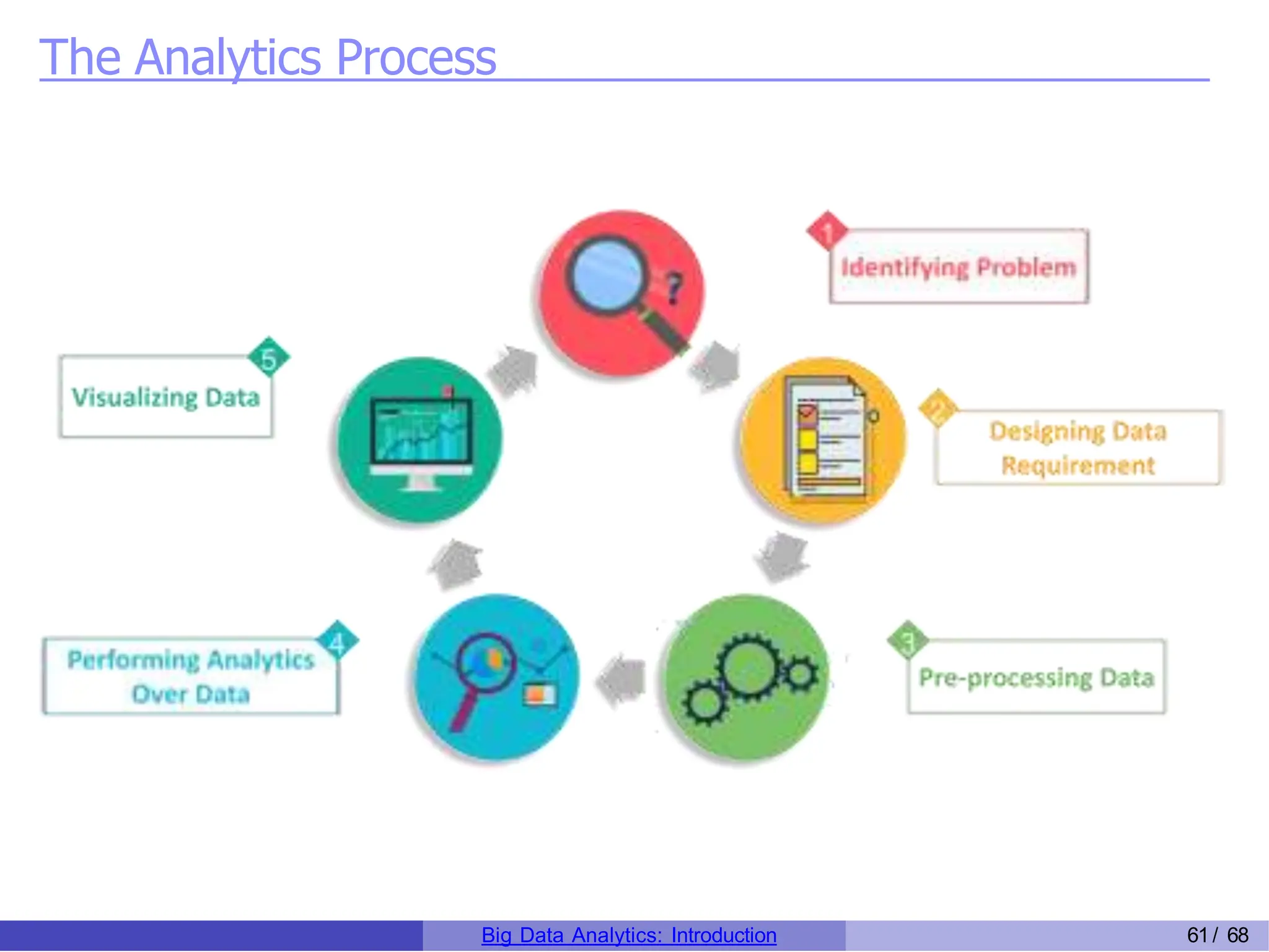
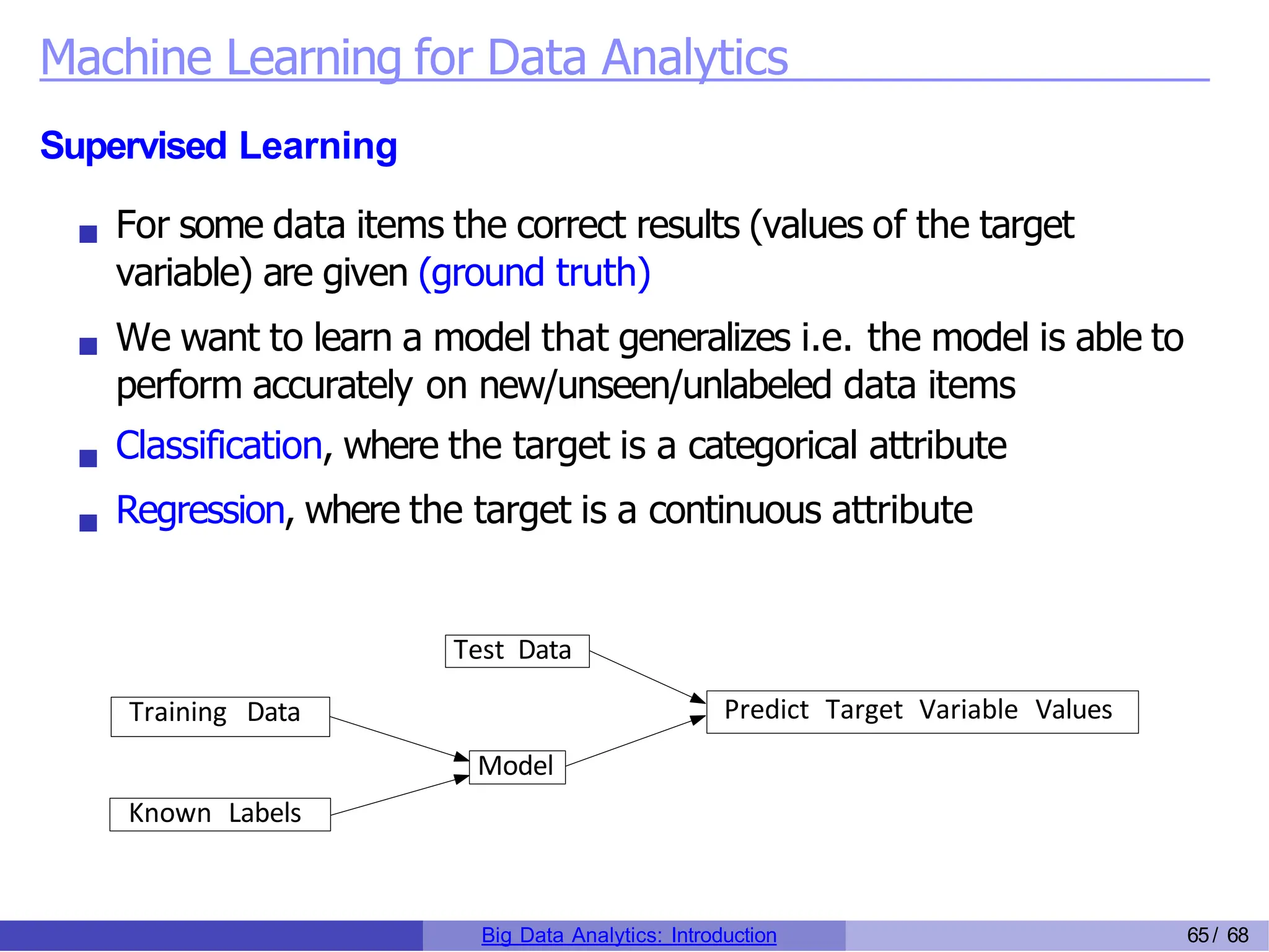
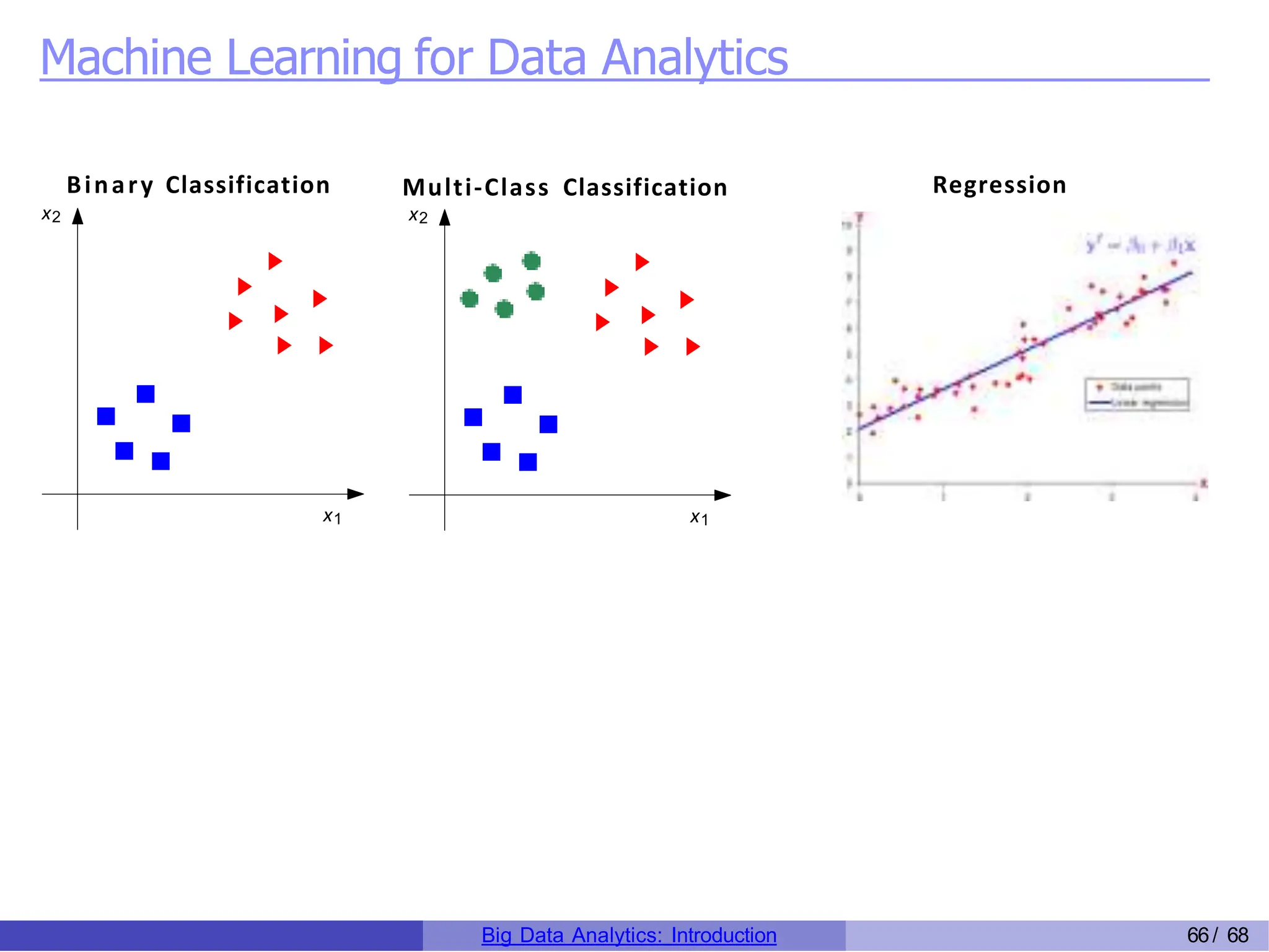
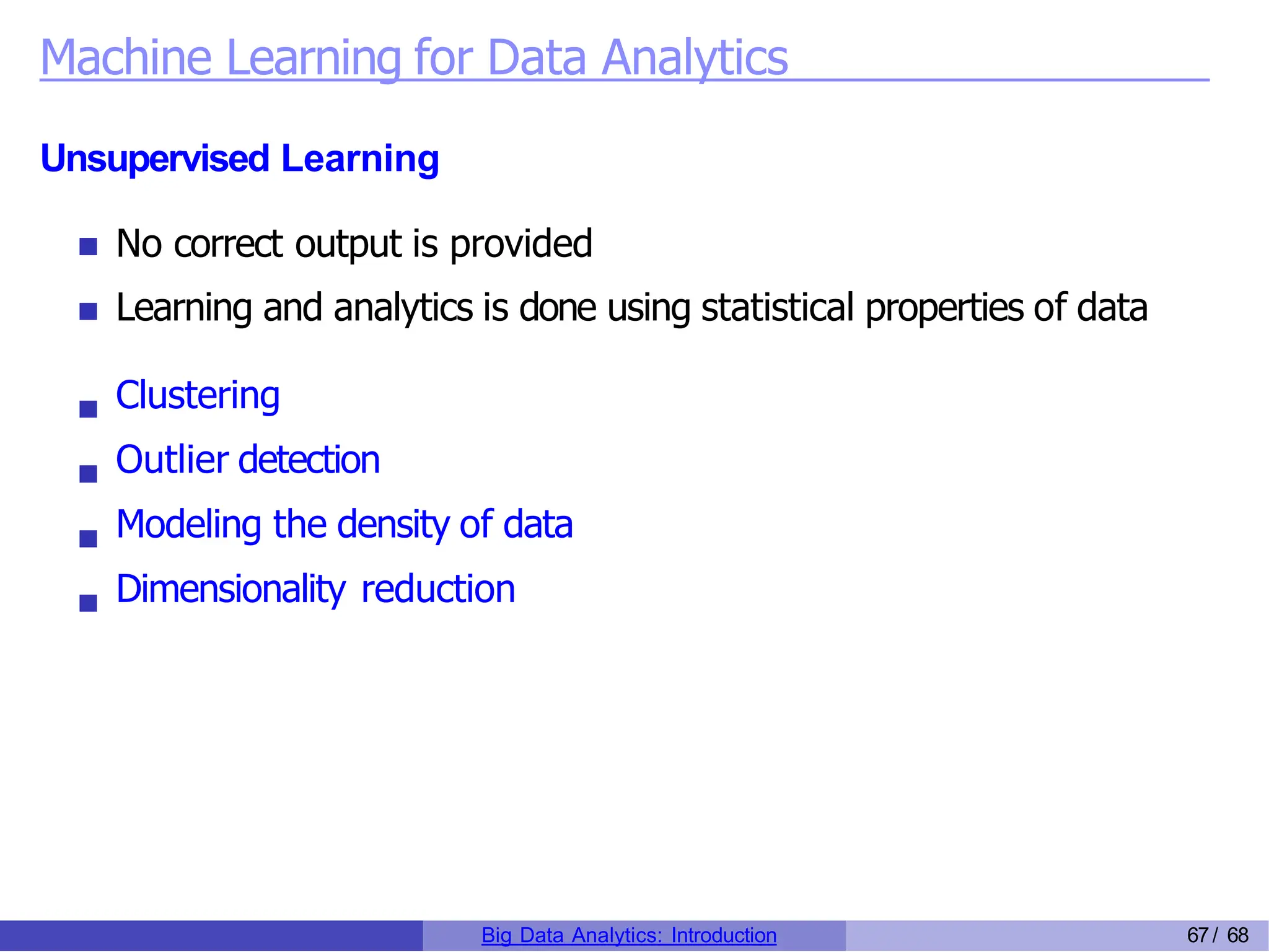
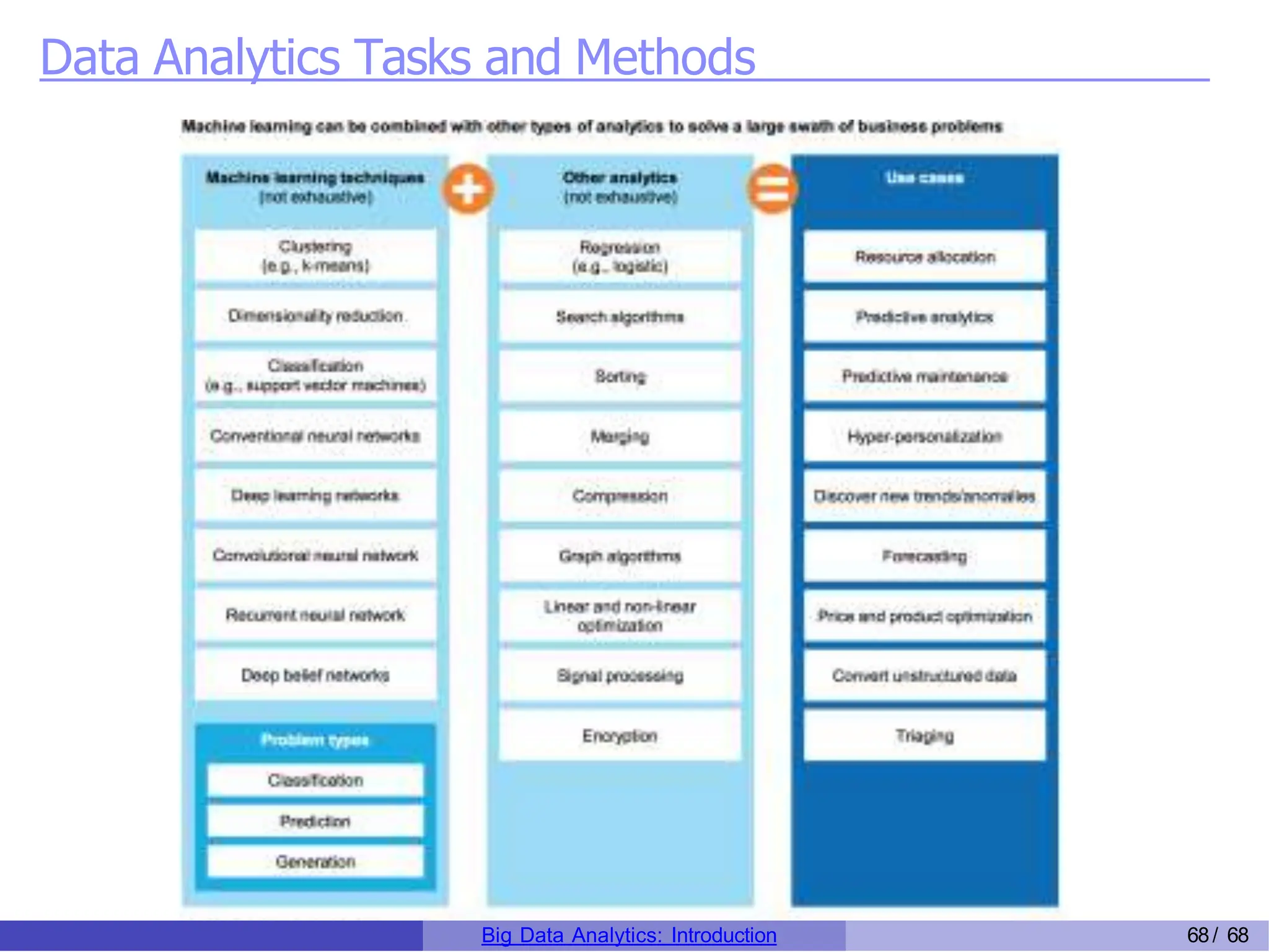
The document provides an overview of big data analytics, including its rapid growth, significance across industries, and the types of data and analytics processes involved. Key aspects include the definition of big data, its five V's (volume, velocity, variety, veracity, and value), and various applications in sectors such as retail, banking, healthcare, and government. It also outlines the analytics process and different data types utilized in analytics, emphasizing the importance of data-driven decision-making in modern organizations.