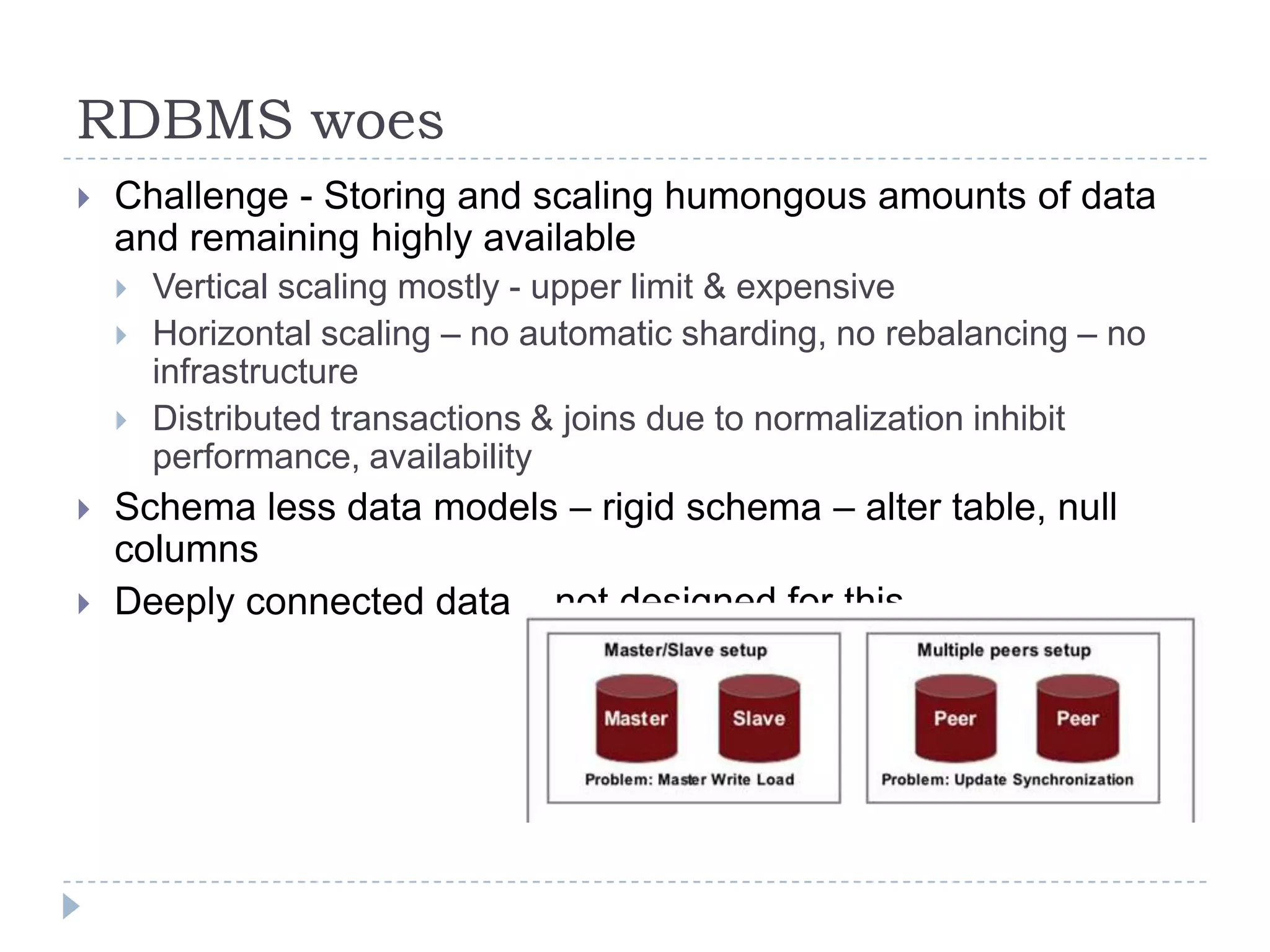
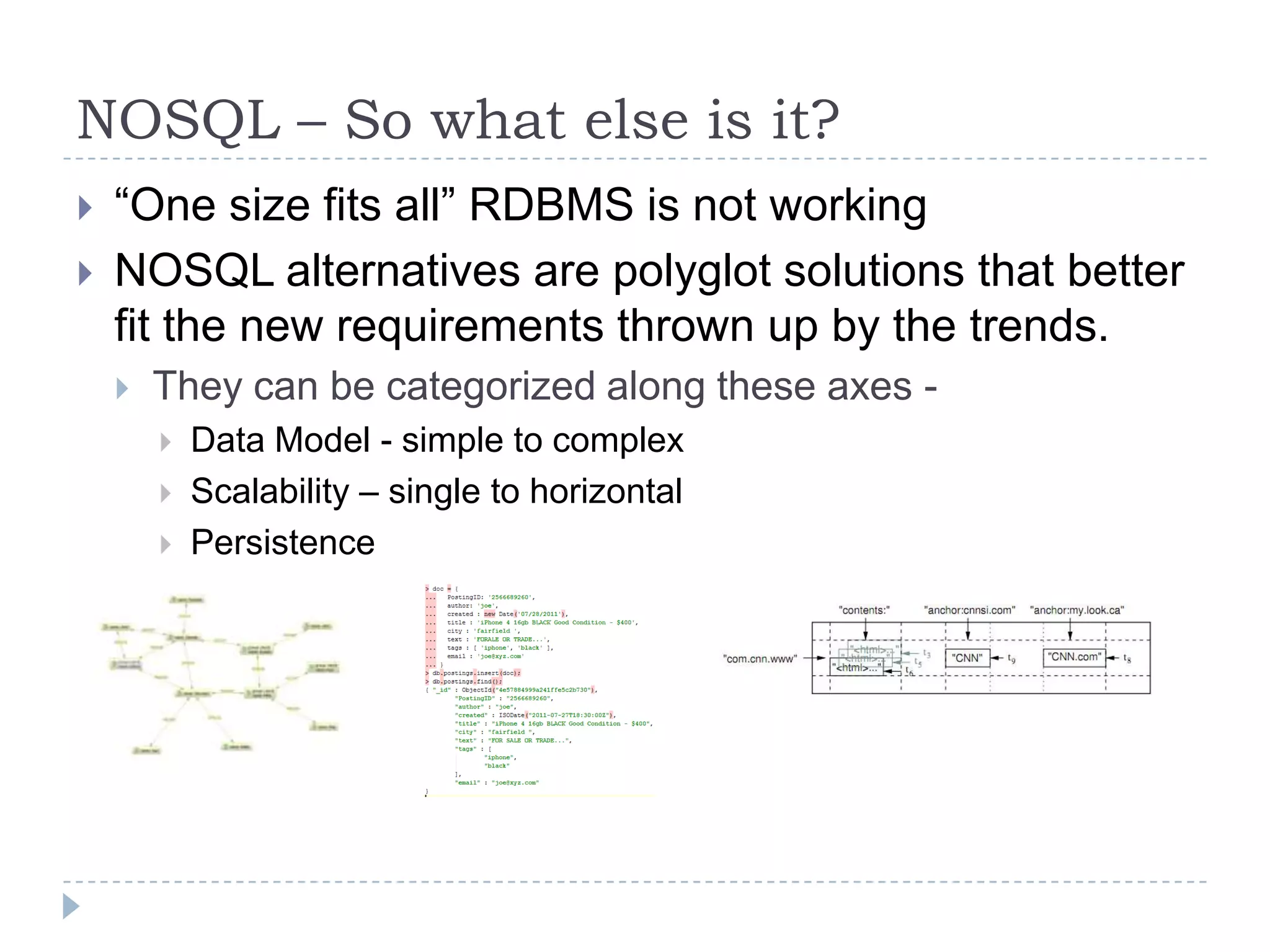
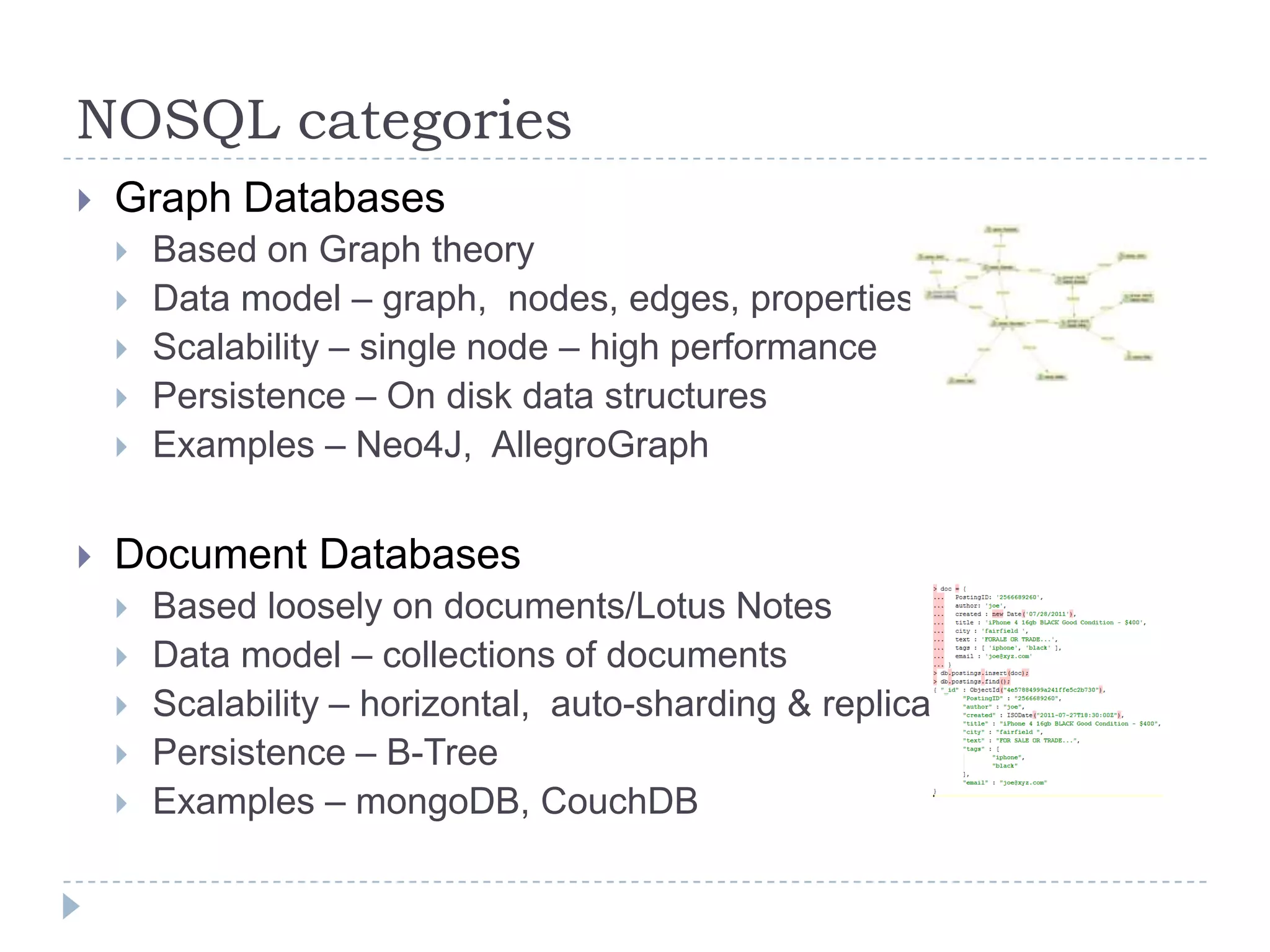
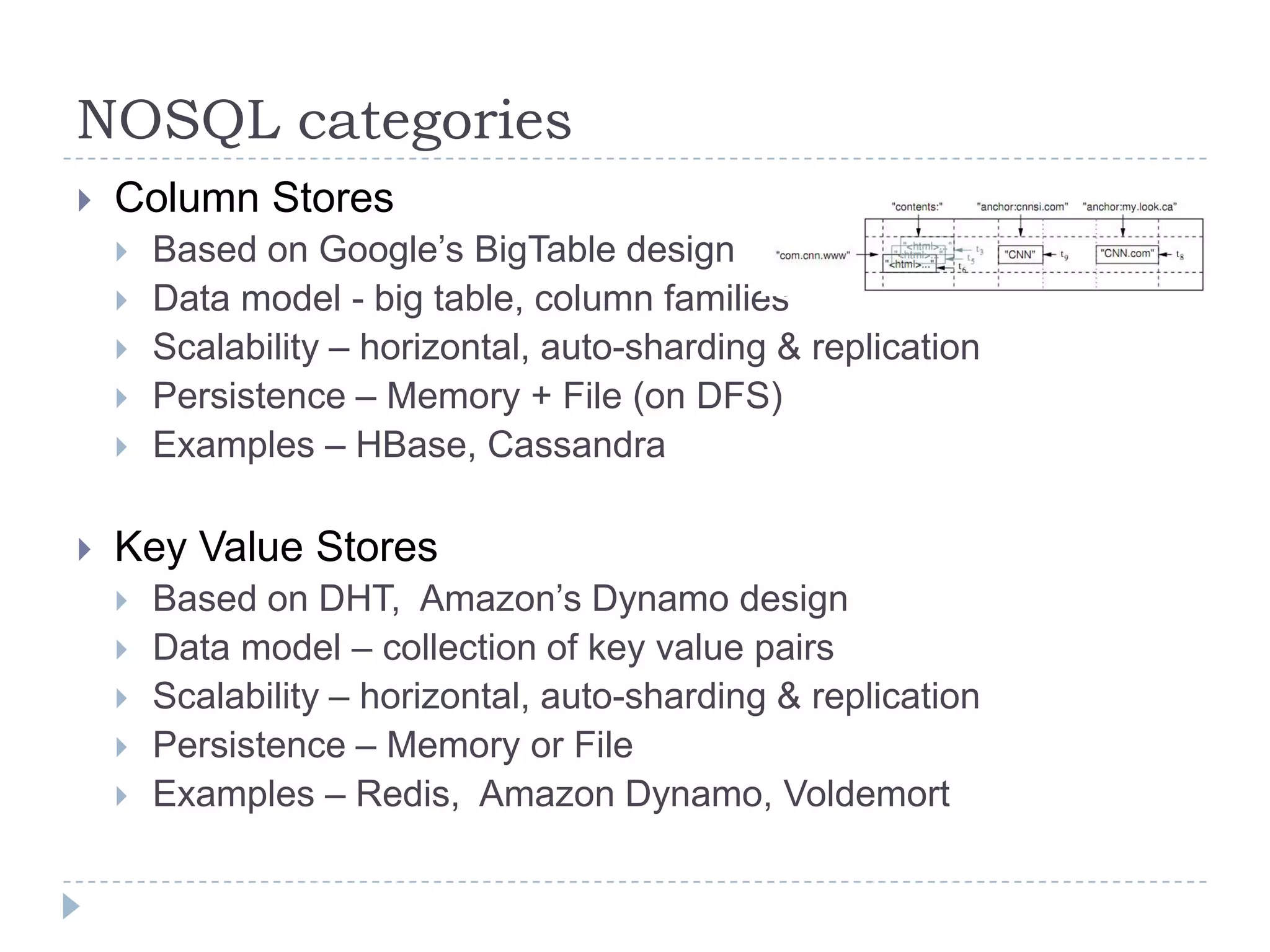
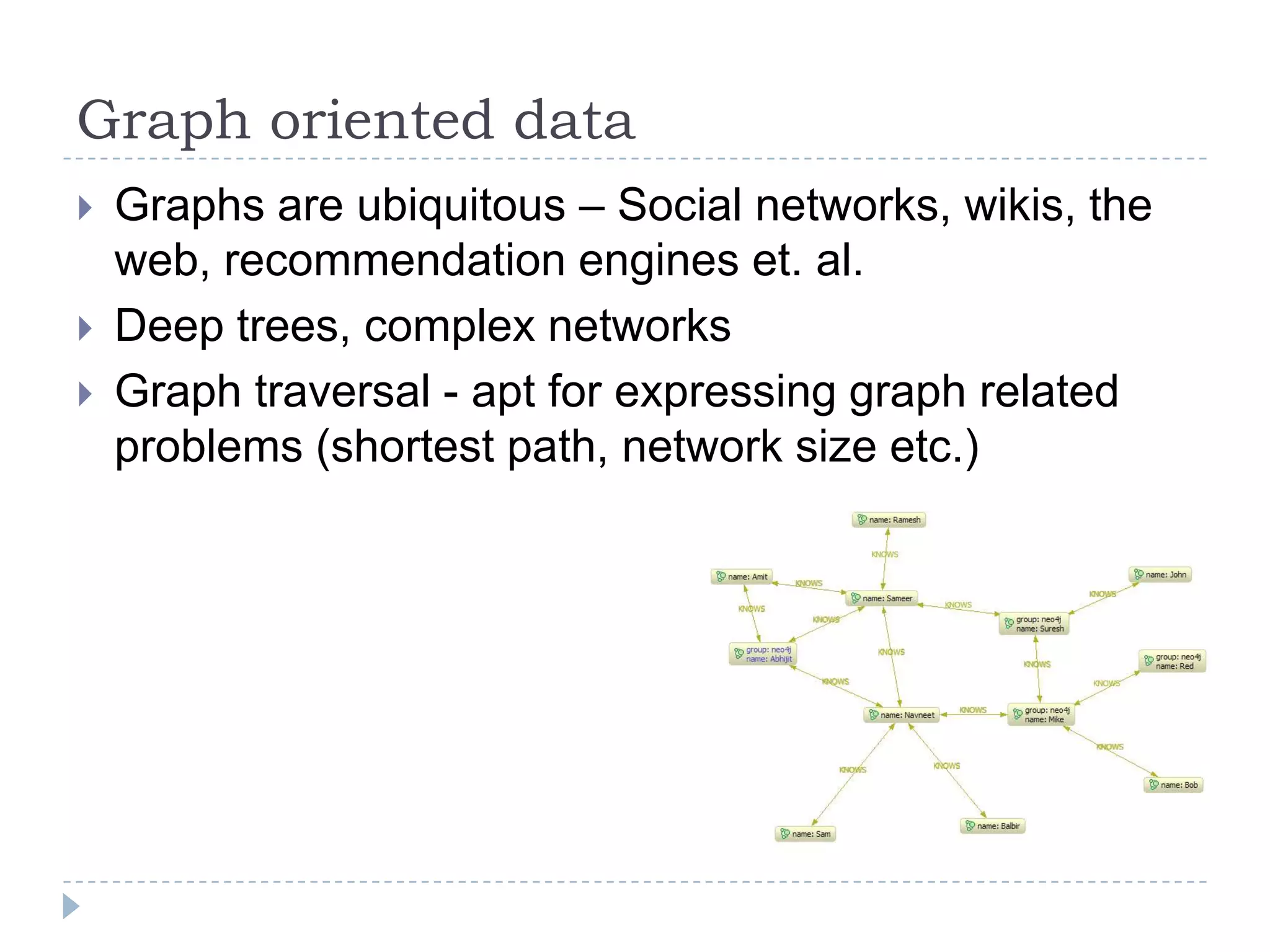
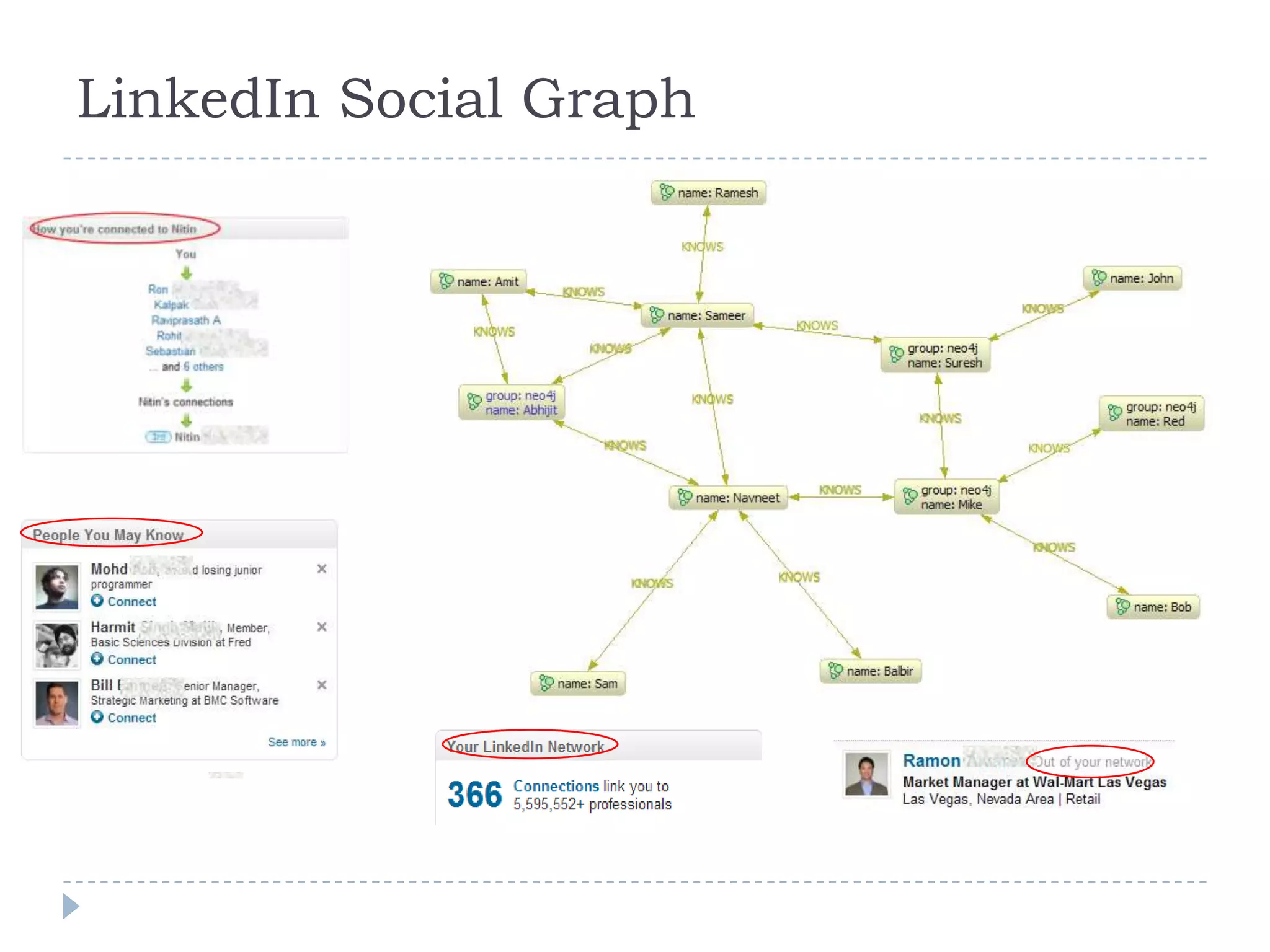
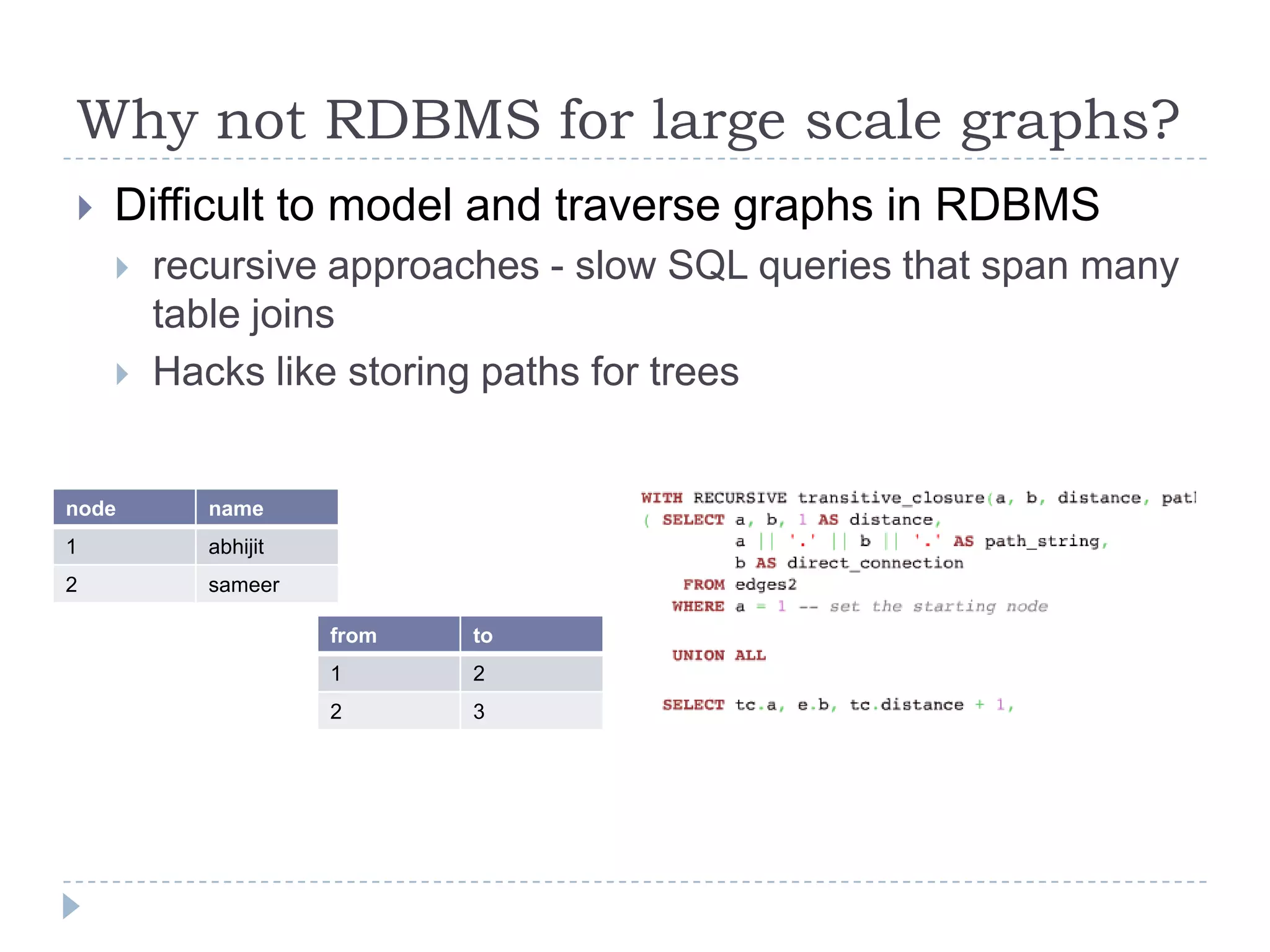
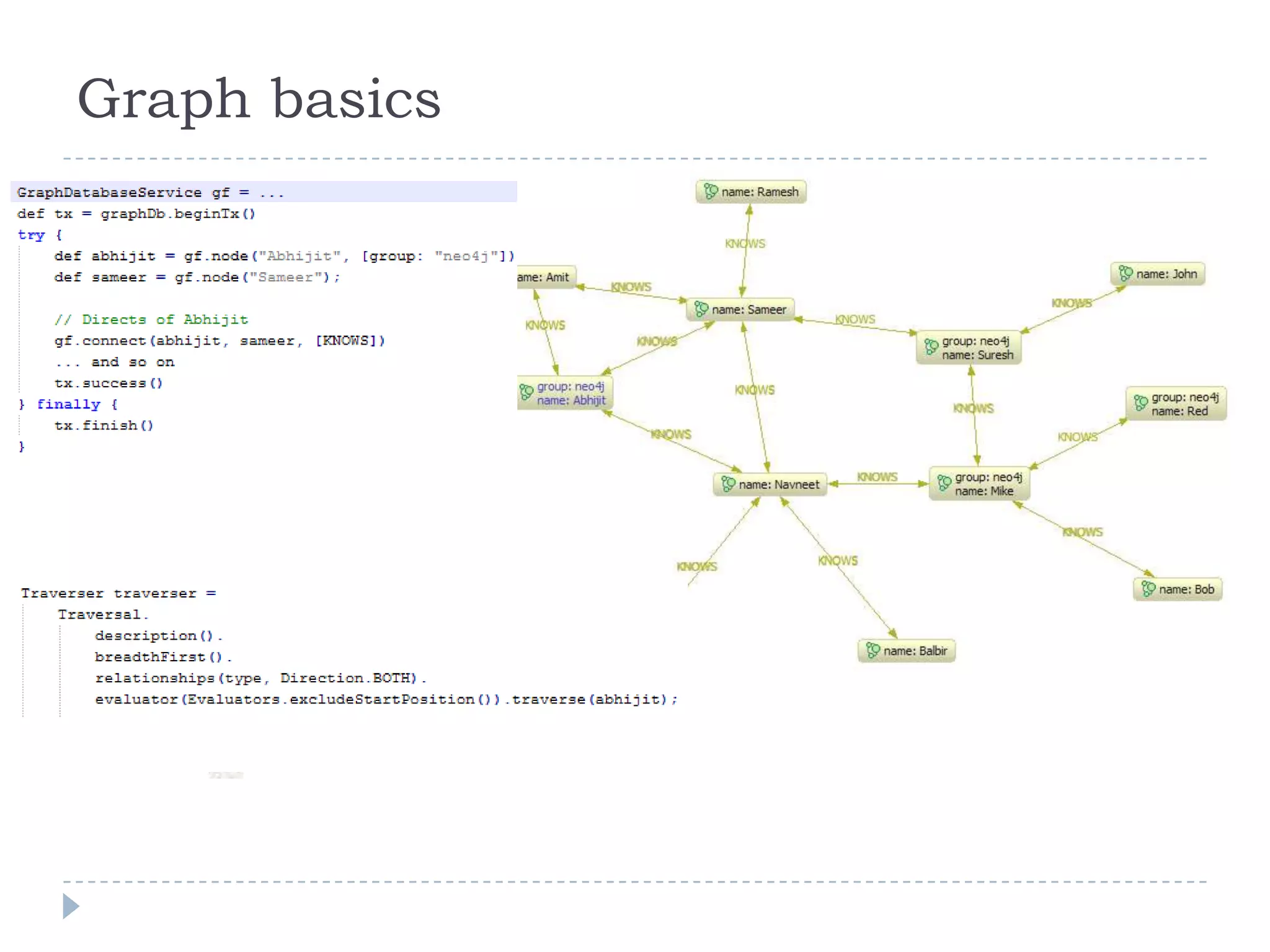
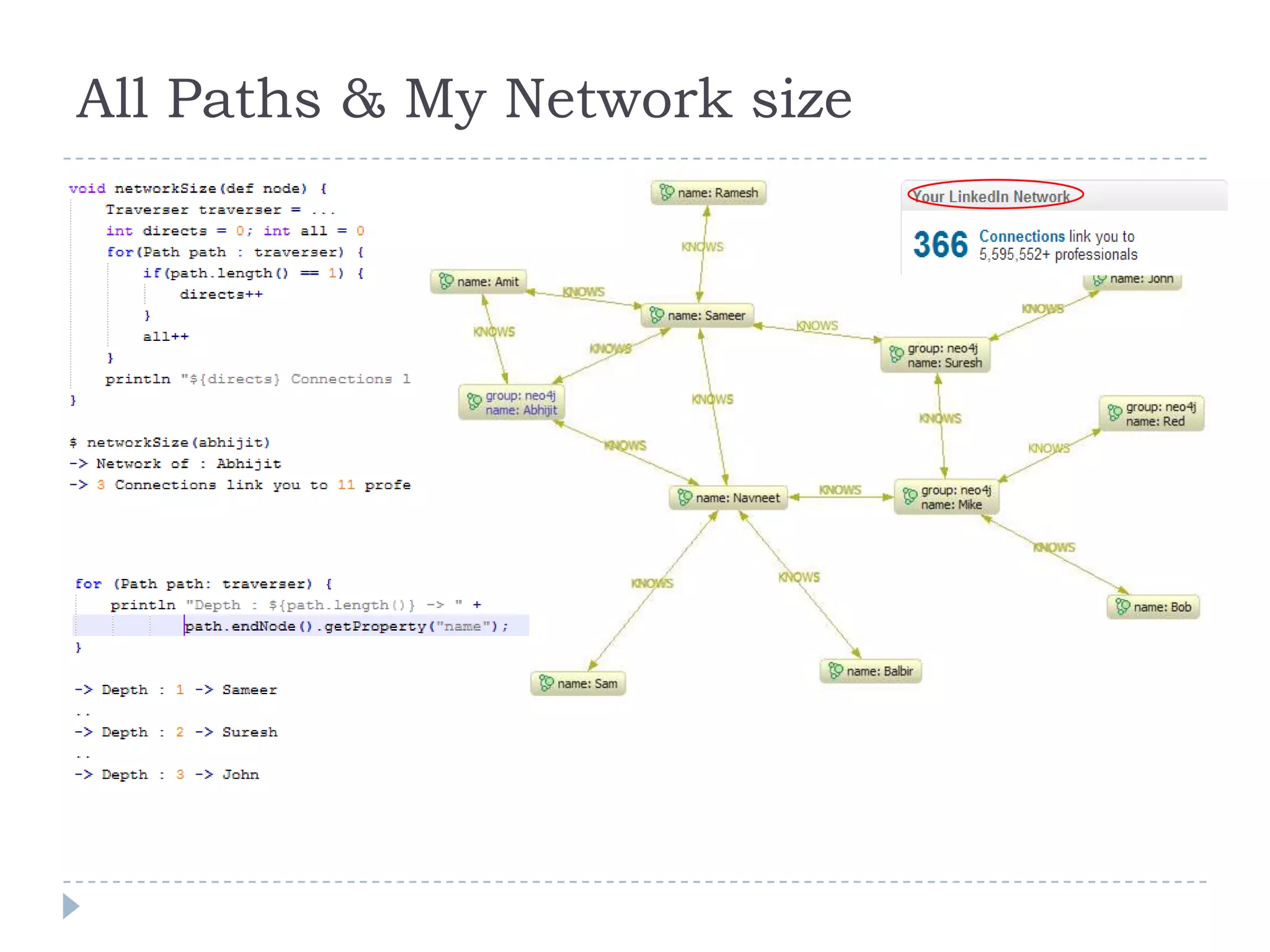
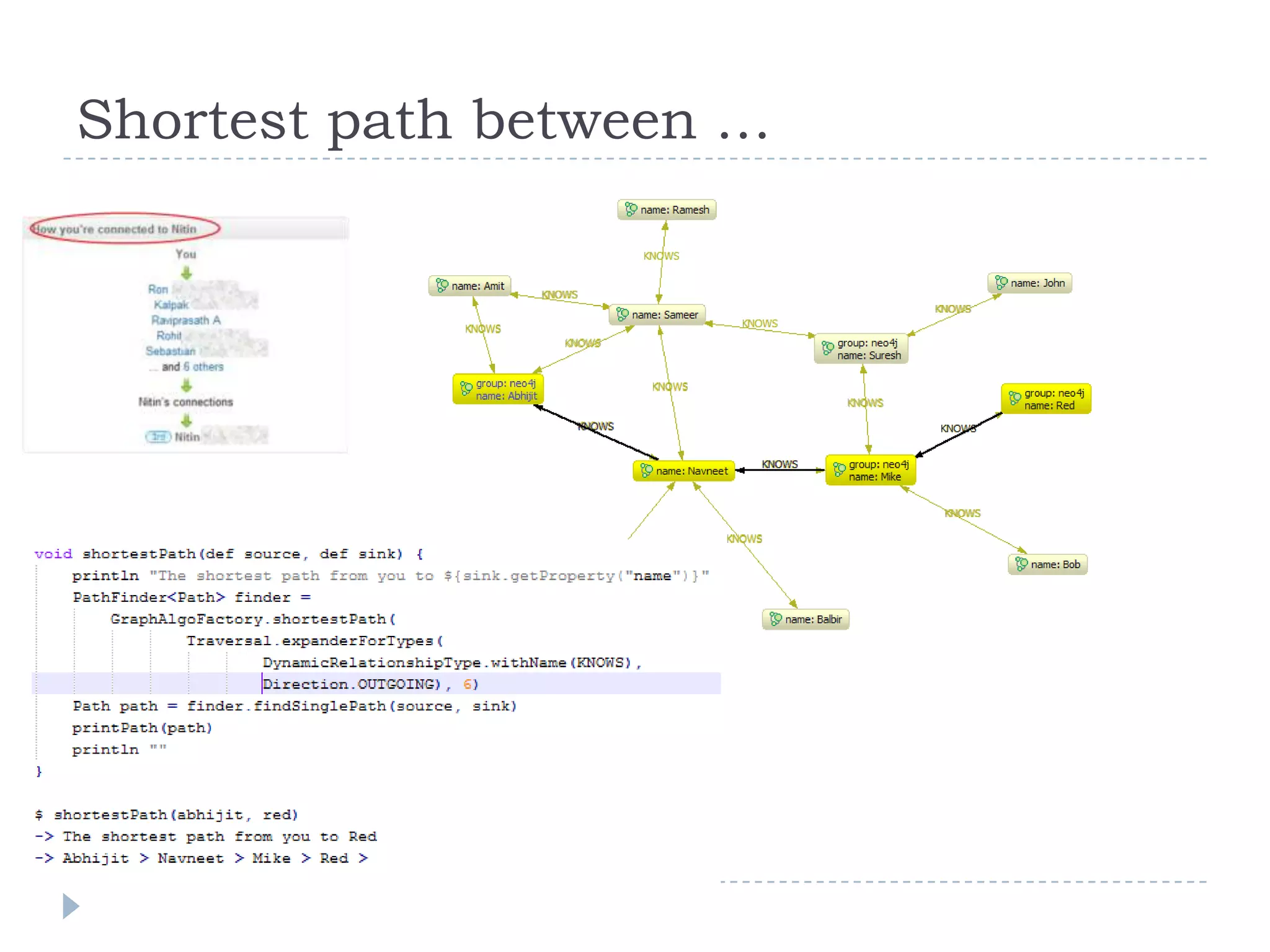
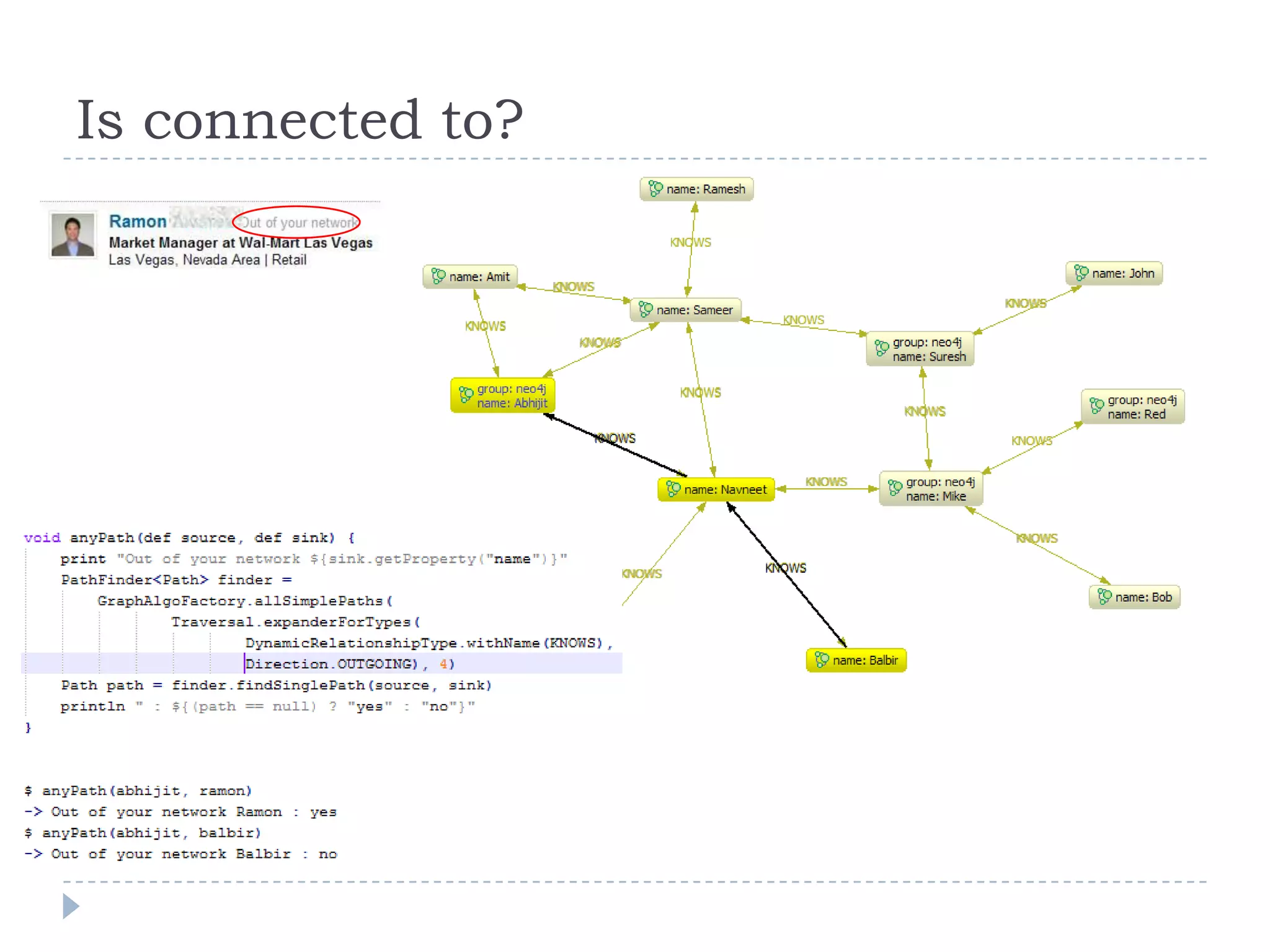
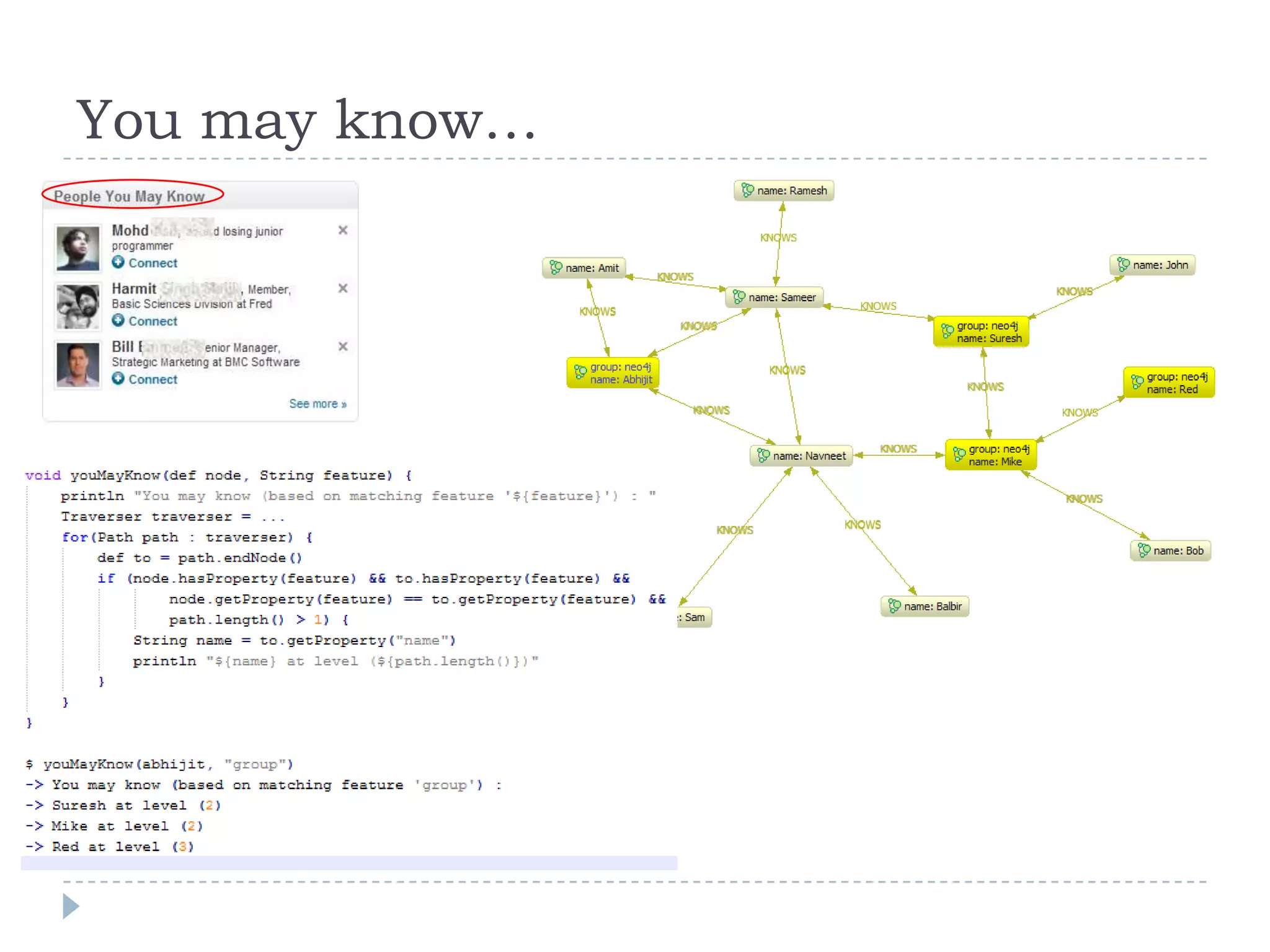
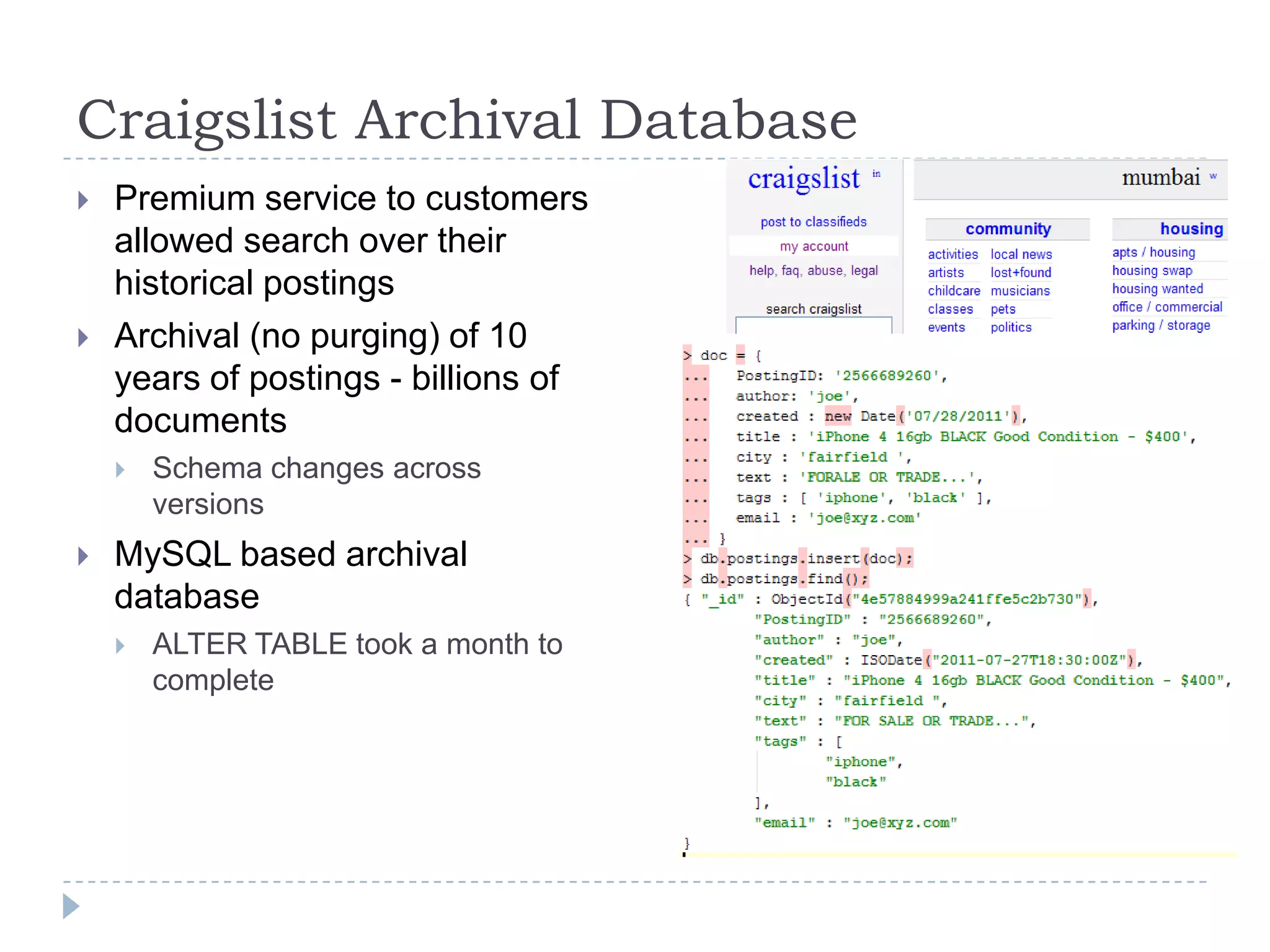
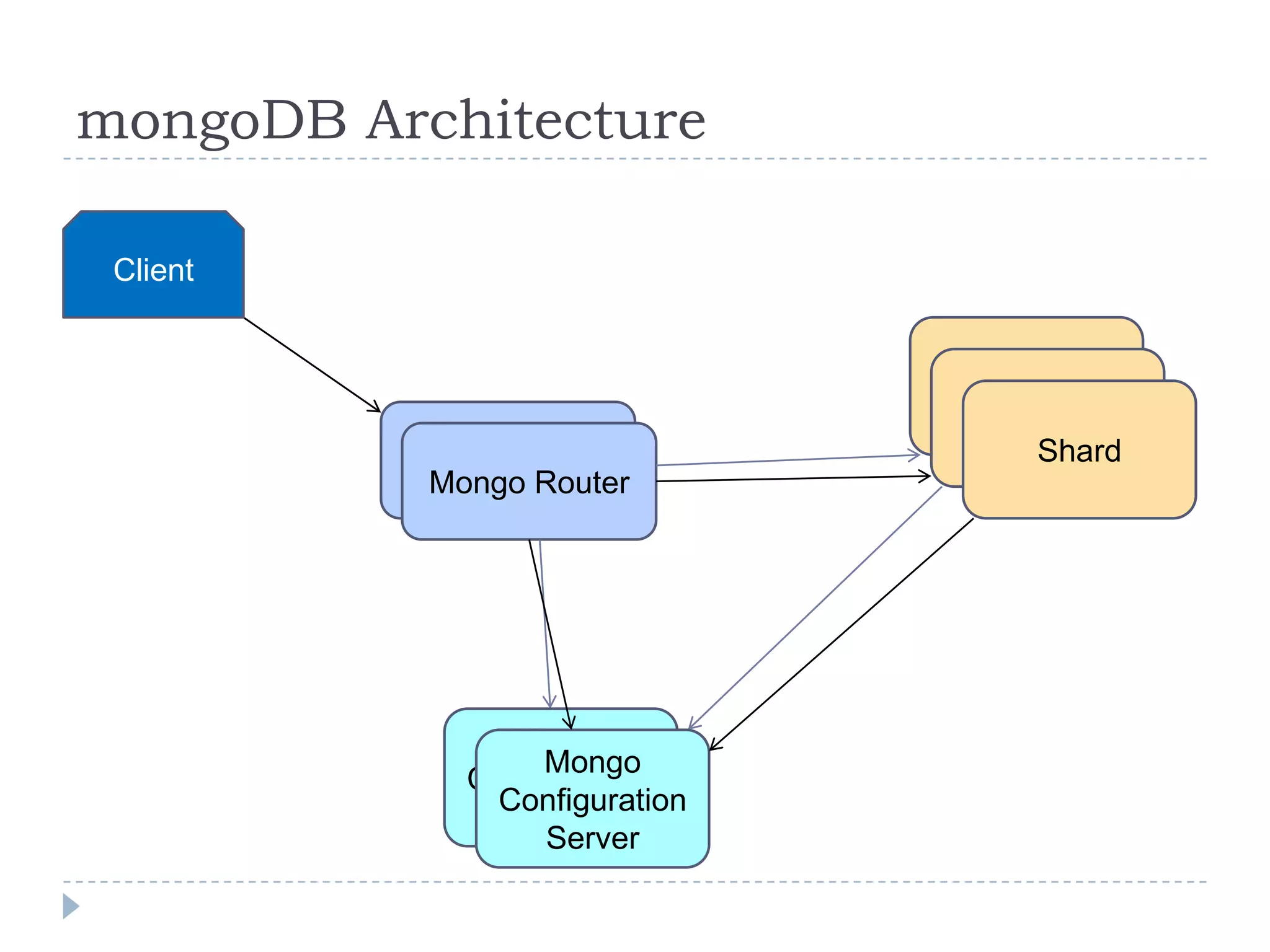
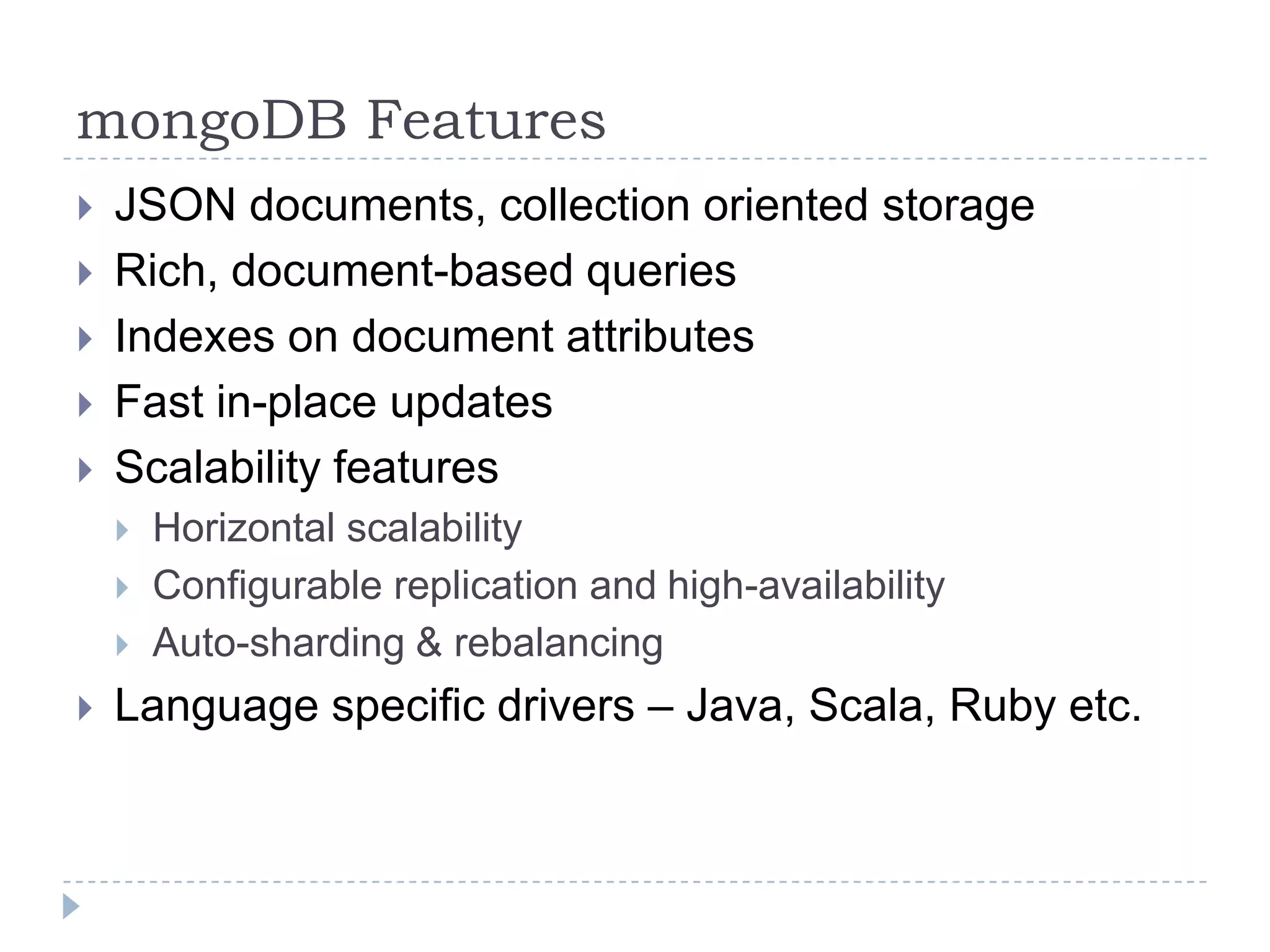
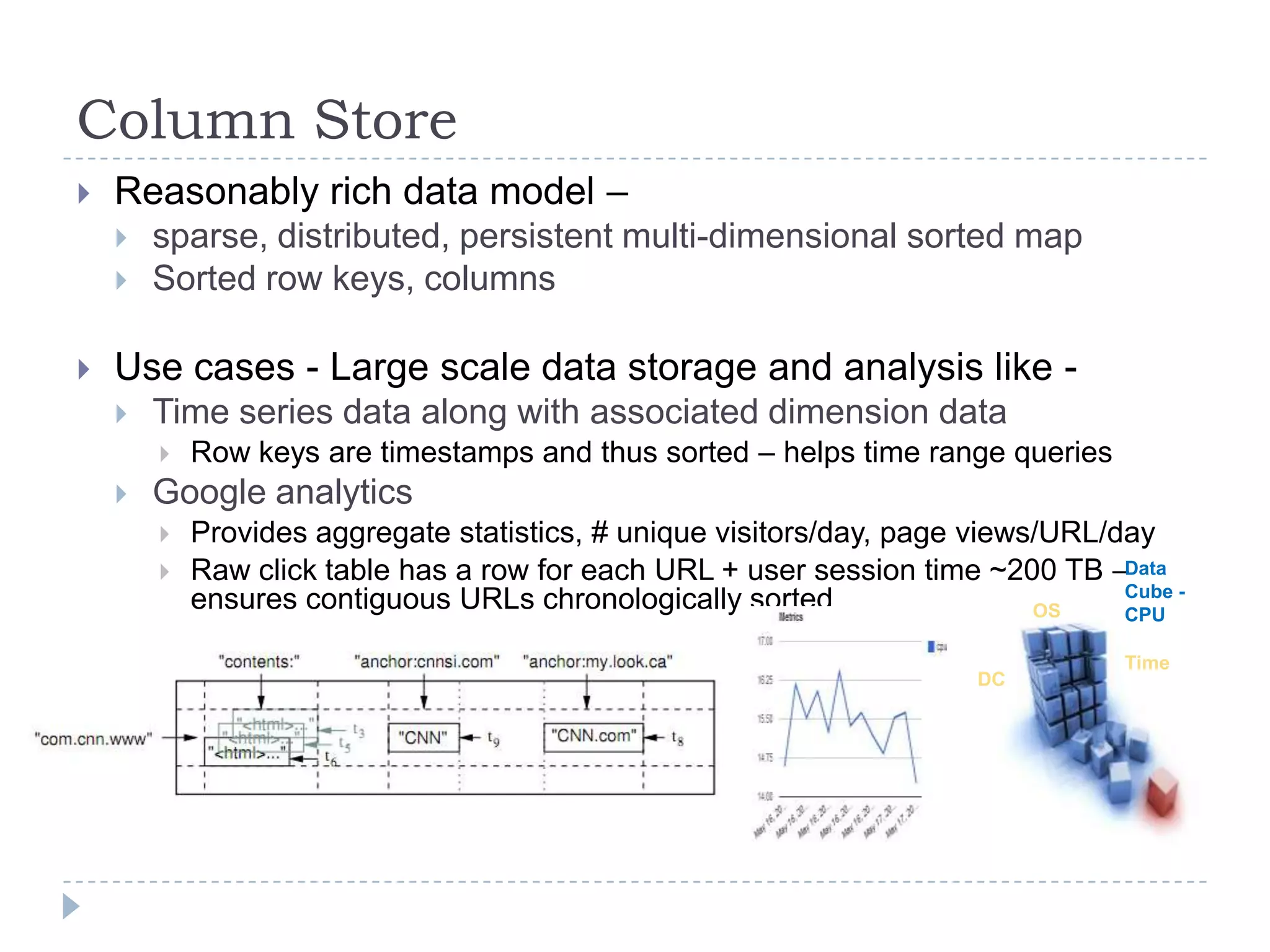
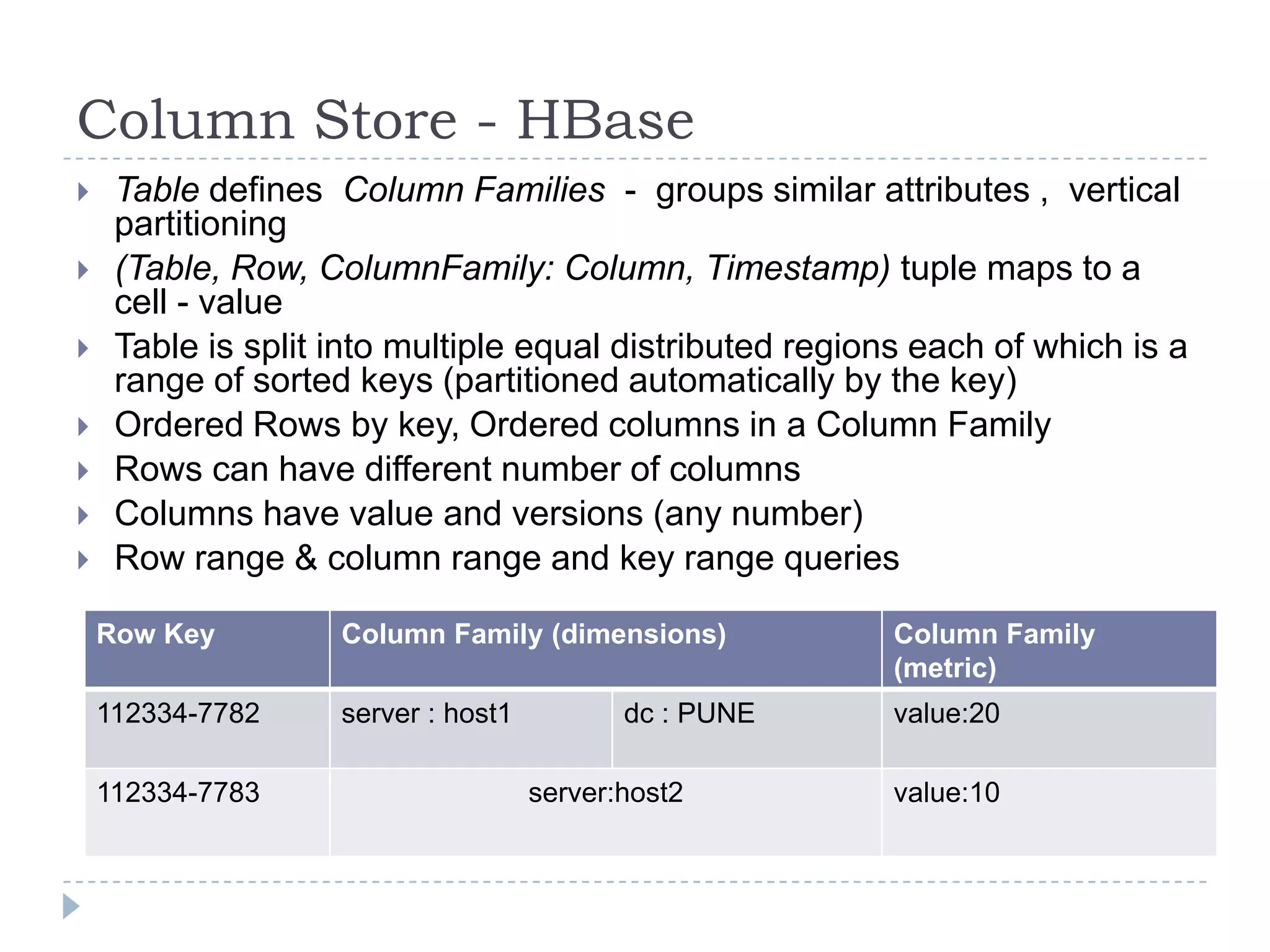
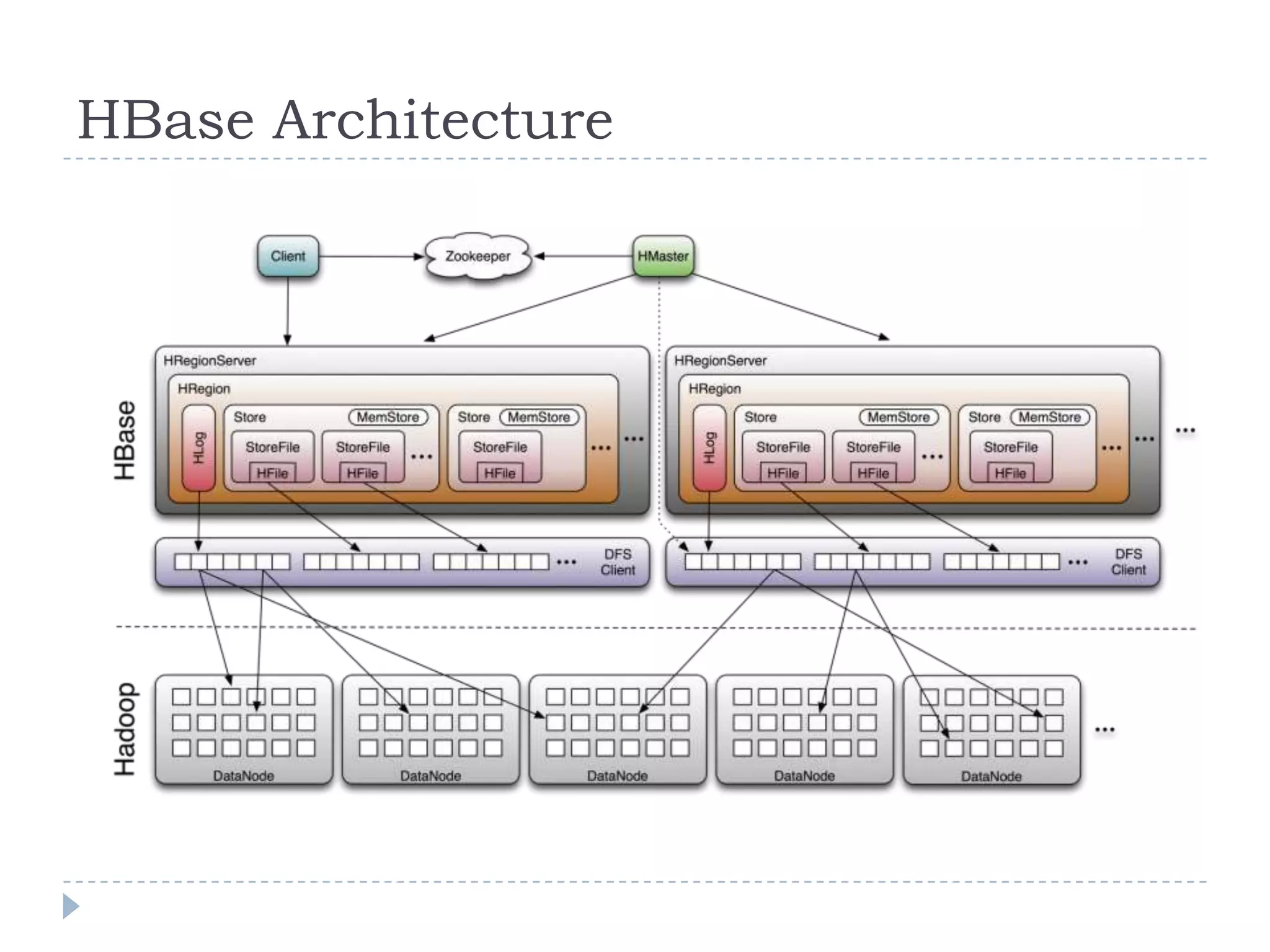
The document discusses trends in big data and the rising importance of NoSQL databases. It covers the growth in data sizes, connectedness of data, and performance needs of modern applications. Relational databases struggle with these trends. NoSQL databases provide alternatives with flexible data models, horizontal scalability, and availability over consistency. The document categorizes NoSQL databases as graph databases, document databases, column stores, and key-value stores, providing examples and use cases for each type.