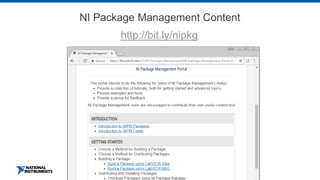
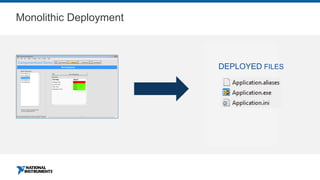
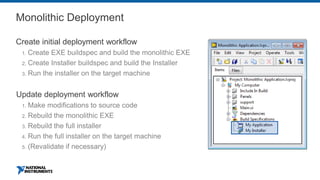
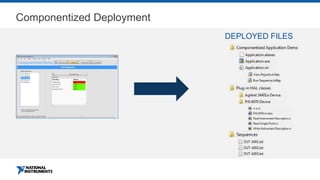
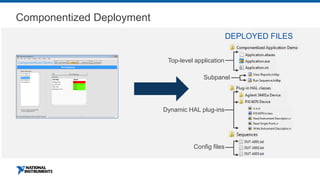
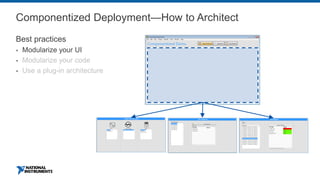
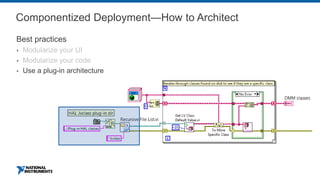
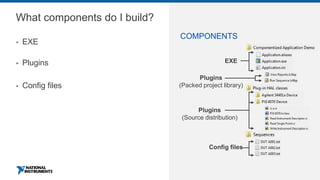
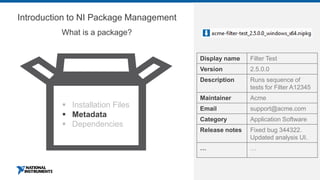
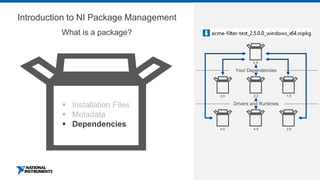
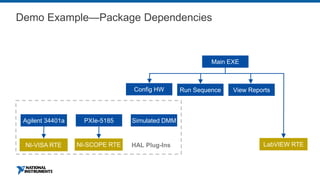
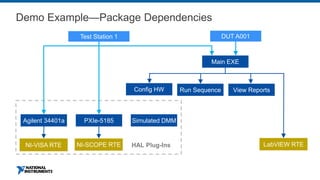
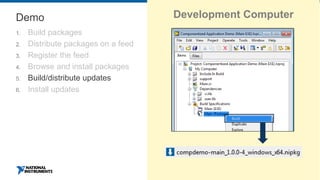
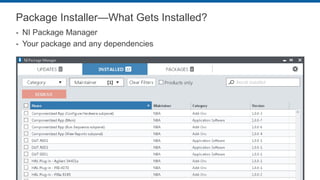
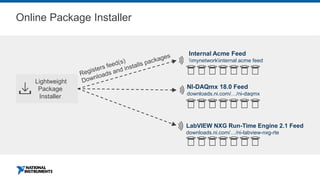
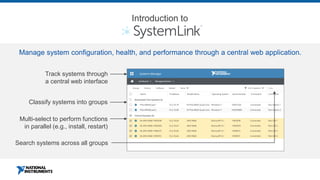
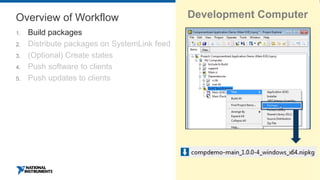
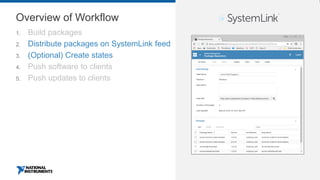
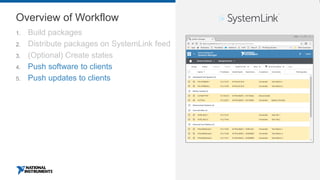
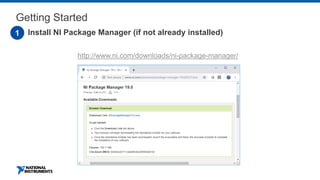
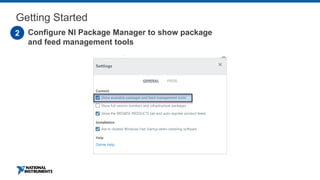
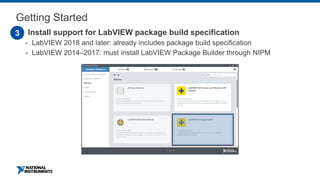
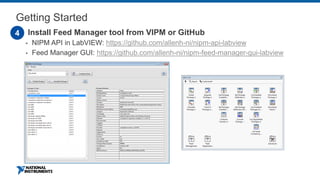
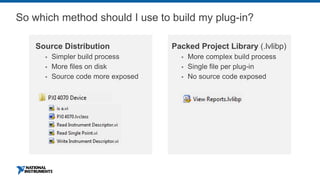
This document discusses best practices for distributing componentized LabVIEW applications. It covers how to architect a componentized application by modularizing the UI and code into reusable components like subpanels and plugins. It also describes how to build components as EXEs, source distributions, or packed project libraries. Finally, it discusses distribution methods like using NI Package Management to package the application and dependencies into installable packages that can be deployed and updated remotely.