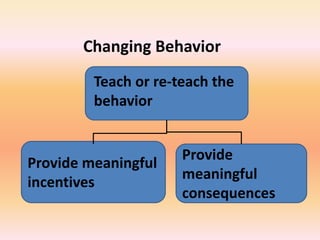
This document discusses positive behavioral interventions and perspectives in education. It provides examples of how to change behaviors by teaching expected behaviors, modeling them, and providing meaningful incentives and consequences. Positive behavioral interventions are planned to prevent problem behaviors from occurring or escalating by understanding what triggers them and modifying those triggers. Examples of interventions include preventative cueing, using "I" messages, and positive phrasing to describe expected behaviors rather than just prohibiting unwanted ones. Reinforcing positive behaviors with a ratio of at least 4:1 compared to negative behaviors is also important.