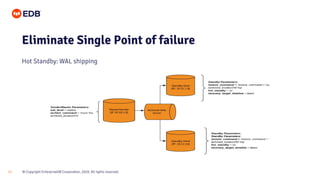
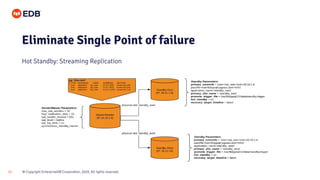
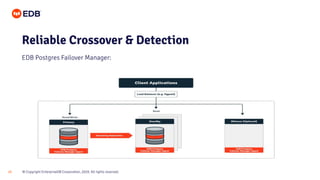
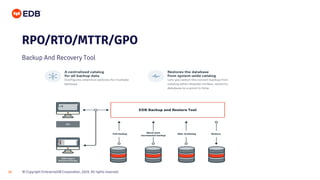
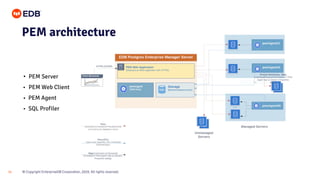
The document is a beginner's guide presented by EDB on high availability for PostgreSQL, covering fundamental concepts, recovery objectives, and strategies to achieve high availability, such as replication methods and monitoring tools. It discusses key metrics like Recovery Point Objective (RPO) and Recovery Time Objective (RTO), and emphasizes eliminating single points of failure through methods like streaming and logical replication. Additionally, it introduces the EDB Postgres Failover Manager and Postgres Enterprise Manager as tools for managing and monitoring high availability systems.