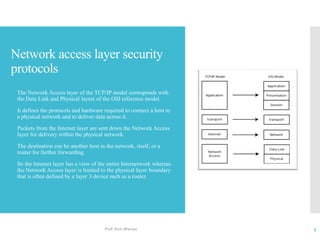
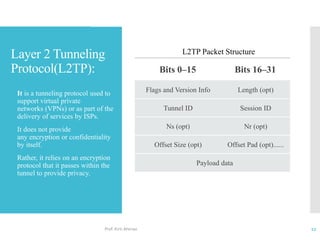
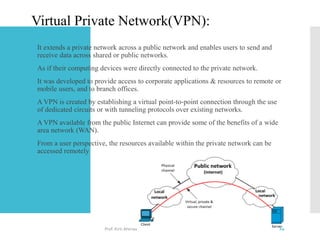
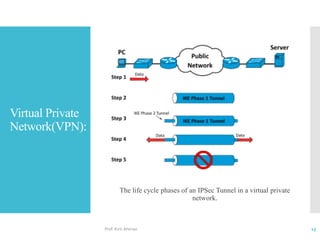
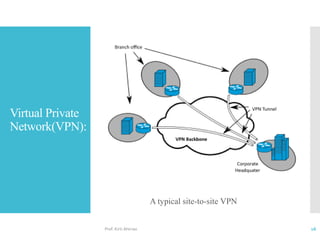
The document discusses network access layer security protocols, highlighting essential technologies such as Layer 2 Forwarding (L2F), Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP), and Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP). It explains their functions in networking, including tunneling, encryption, and creating Virtual Private Networks (VPNs). Additionally, it provides an overview of various physical network protocols and their roles within local and wide area networks.