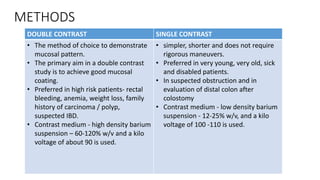
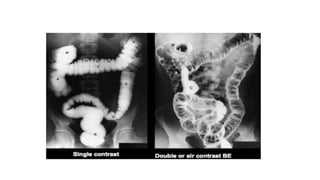
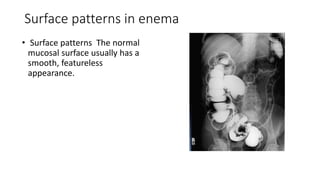
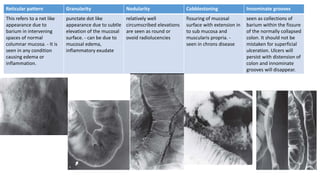
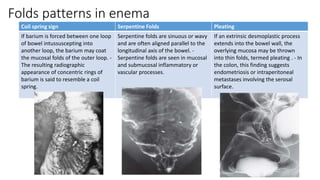
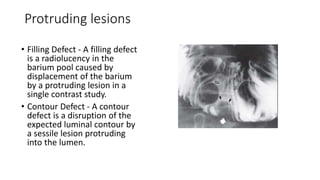
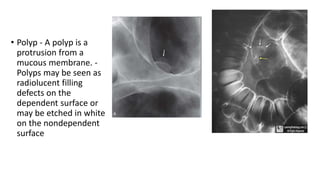
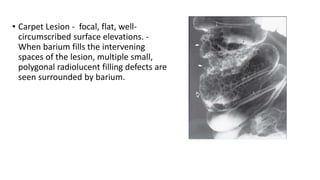
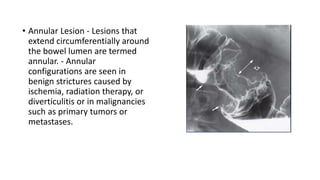
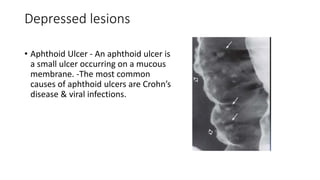
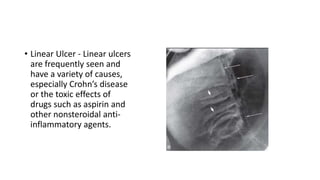
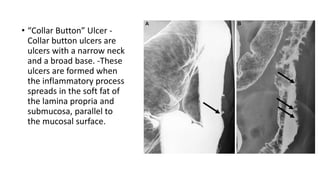
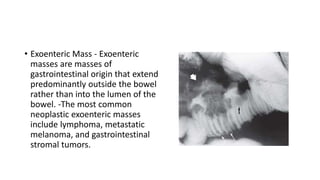
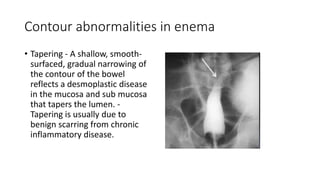
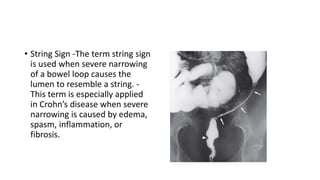
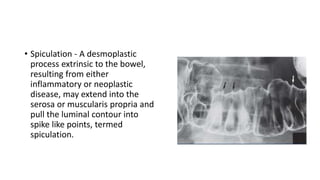
Barium enema is a radiographic procedure used to examine the large bowel. It involves inserting barium sulfate into the rectum to coat the colon walls. There are two main techniques - double contrast uses both barium and air to better visualize the mucosal surface, while single contrast uses only barium. It is used to screen for and evaluate colon cancer, inflammatory bowel disease, and other conditions. Key steps in the procedure and patient preparation are outlined. Normal and abnormal findings seen on barium enema are described, including surface patterns, folds, protruding lesions like polyps, and depressed lesions like ulcers.