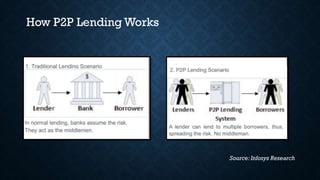
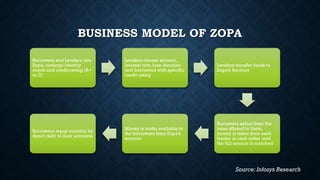
Peer-to-peer (P2P) lending platforms like Zopa and Prosper allow individuals to borrow and lend money without going through a traditional bank. Lenders choose loans to fund and set their own interest rates. Borrowers receive loan amounts and pay monthly payments directly to their lenders. P2P lending offers competitive rates for borrowers and high returns for lenders. However, risks include lack of regulation, no collateral from borrowers, and potential platform failures reducing confidence. For P2P lending to grow, increased awareness, regulation, and technology are needed to build trust and better screening while expanding into new loan categories could also help.
![BANKING WITHOUT BANKS
PEER-TO-PEER LENDING
Group 1
Aakash Kulkarni [MGBSEP13IBWM001]
Aishwarye Pandey [MGBSEP13CMM028]
Kanika Bansal [MGBSEP13CMM039]
Nishant Menda [MGBSEP13IBWM017]
Ritika Shetty [MGBSEP13CMM047]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bankingwithoutbanksgroup1-140305032859-phpapp02/85/Banking-without-banks-group-1-1-320.jpg)