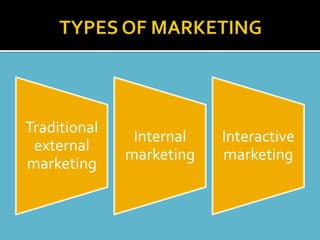
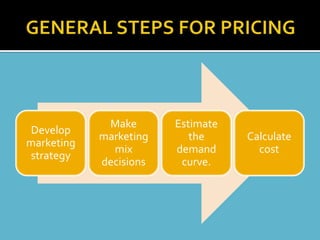
This document discusses banking and marketing in the banking sector. It begins by defining banks as financial institutions that deal with money and credit. It then outlines the different types of banks in India including central banks, public sector banks, private sector banks, and cooperative banks. It also discusses the key functions of banks like issuing bank notes, processing payments, lending money, and providing other financial services. The document then covers bank marketing, defining it as satisfying customer needs more effectively than competitors. It discusses market segmentation in the banking sector and various marketing strategies employed by banks including the traditional marketing mix and internal and interactive marketing approaches.