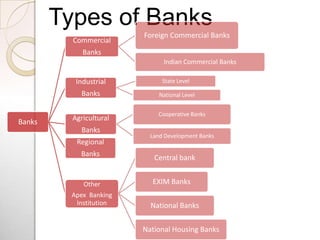
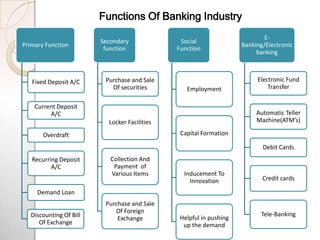
A bank is an institution that accepts deposits and makes loans. It allows customers to deposit money into accounts and withdraw funds via cheque or debit card. There are various types of banks that serve different sectors such as commercial, investment, and retail. Banks offer services like savings and checking accounts, loans, credit and debit cards, online and mobile banking to facilitate financial transactions.