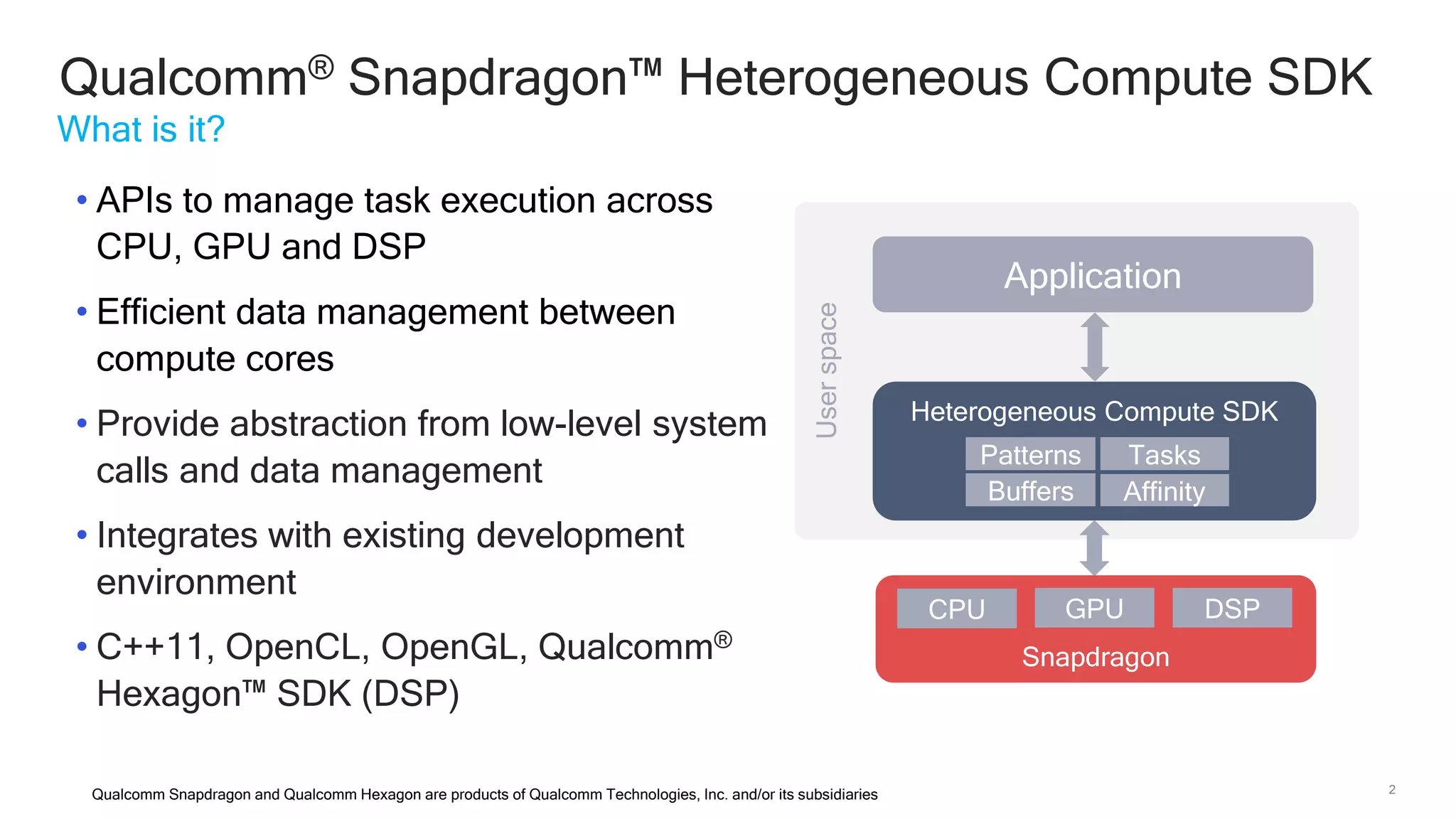
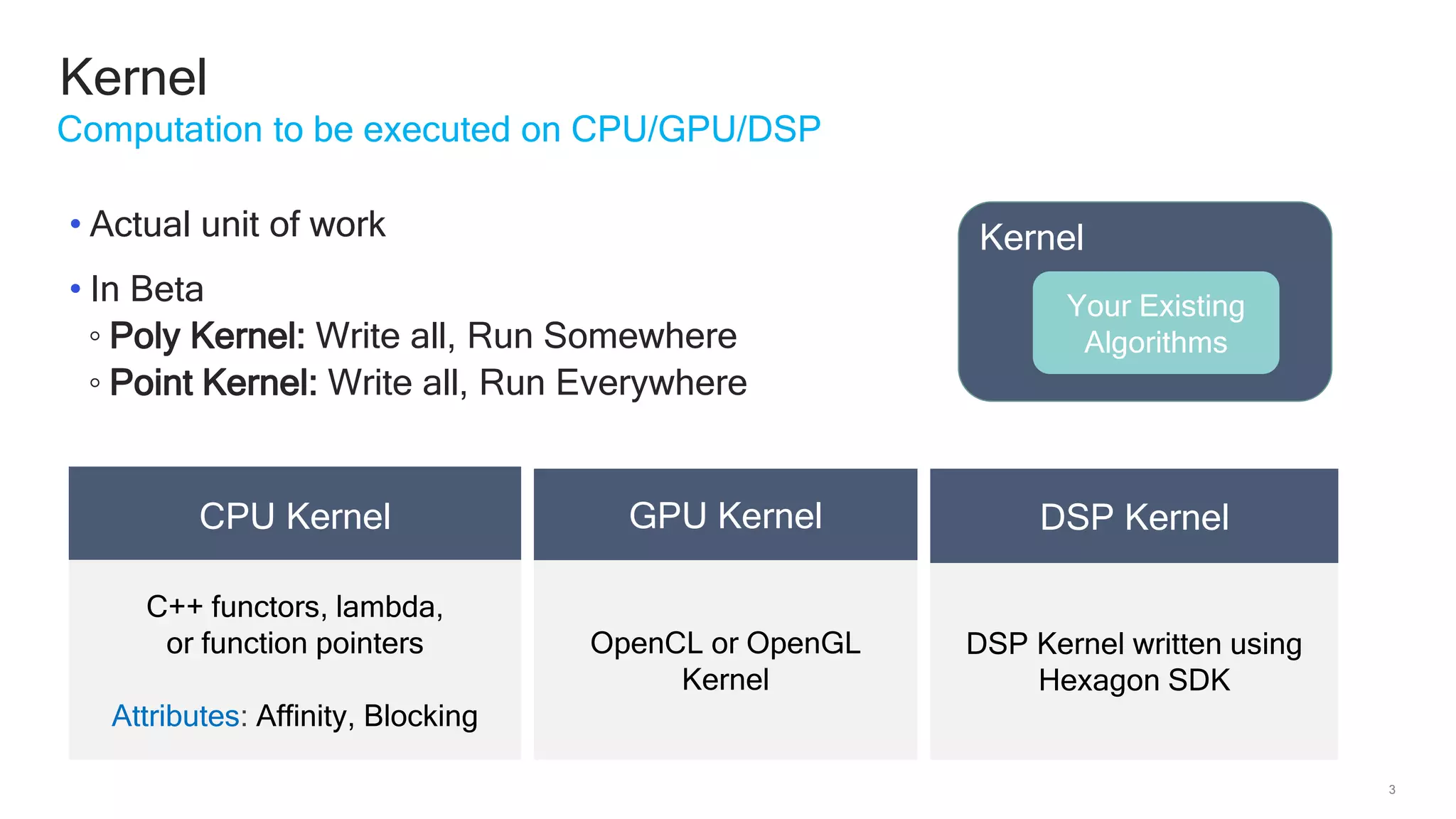
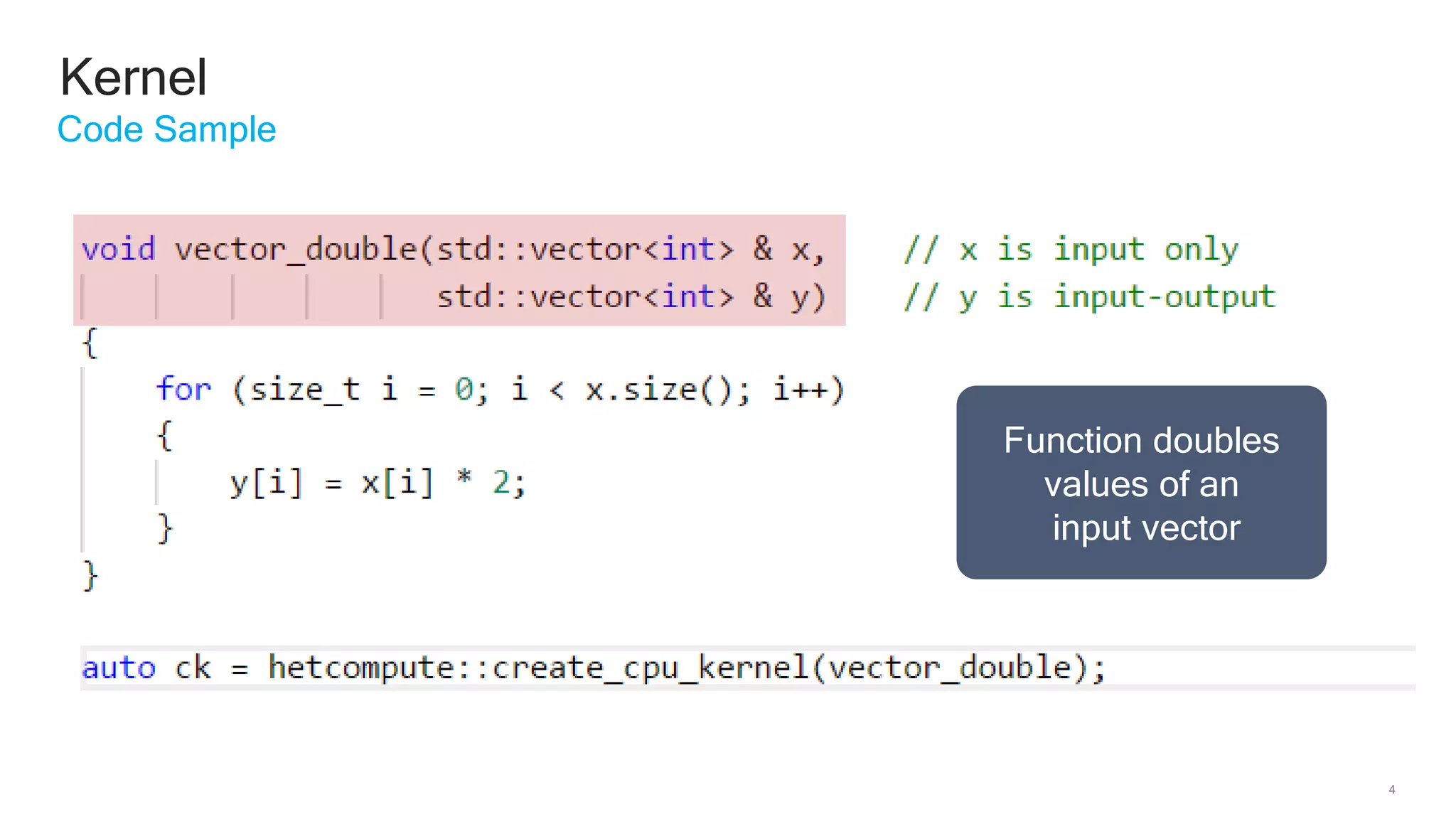
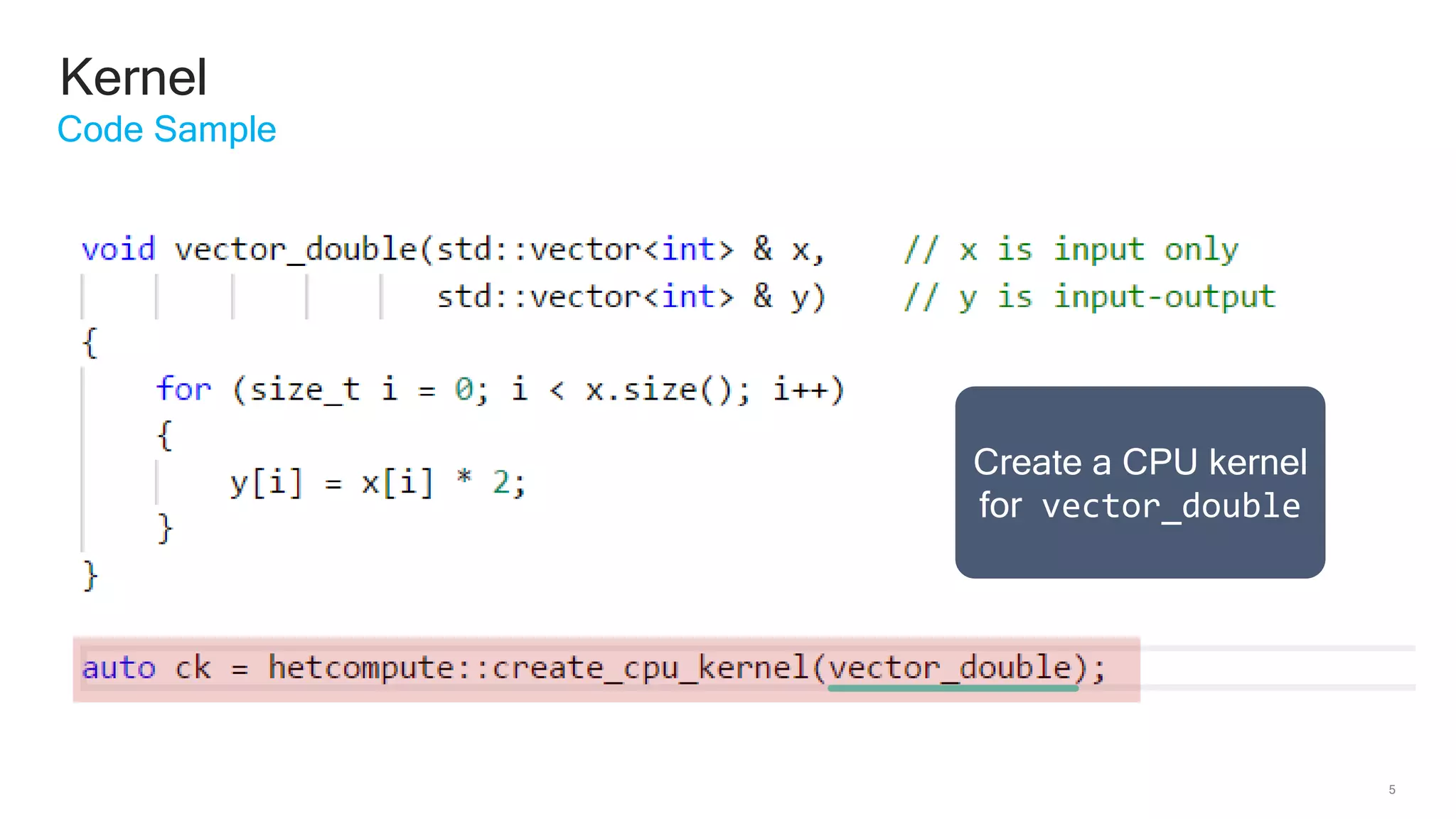
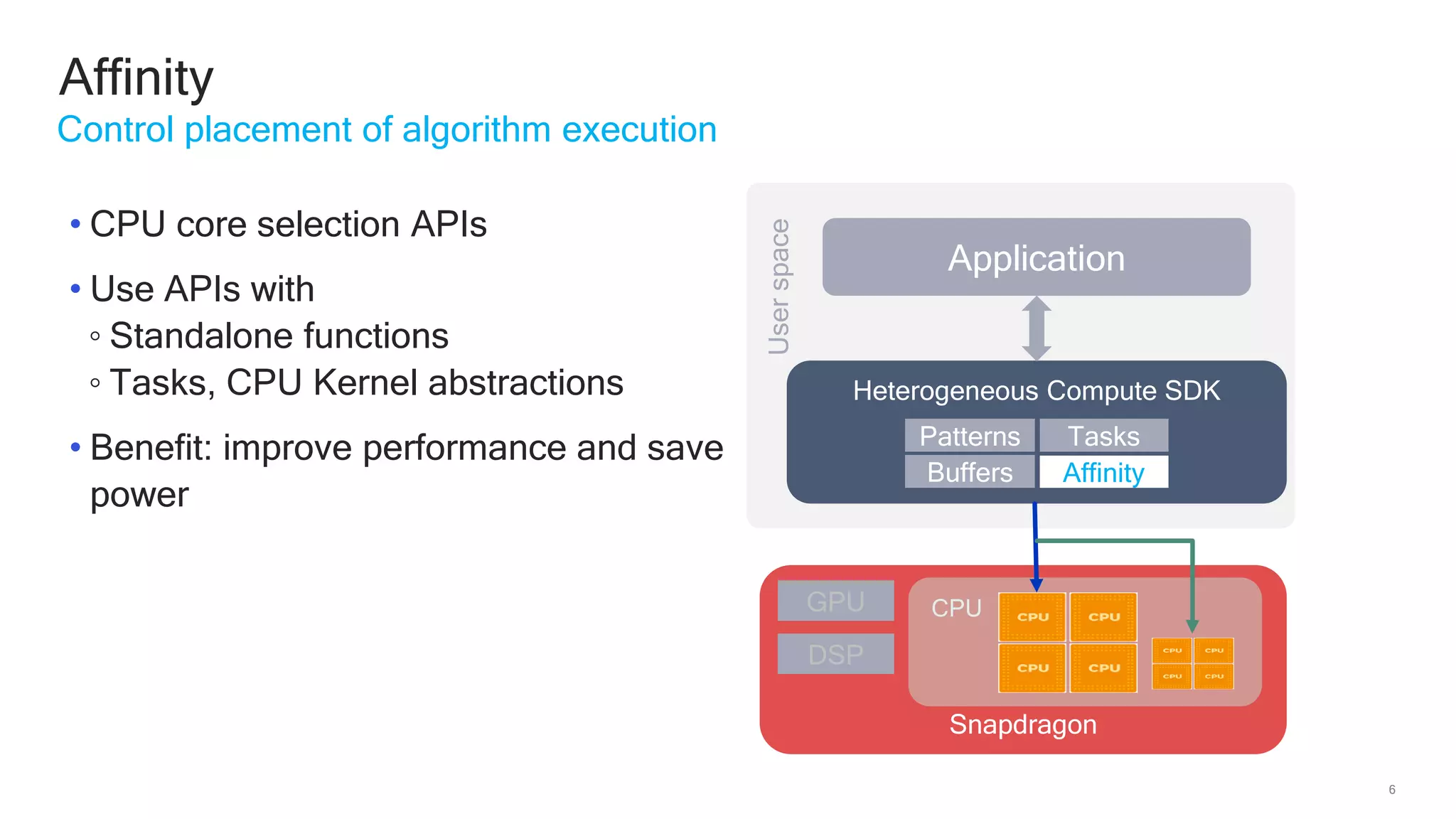
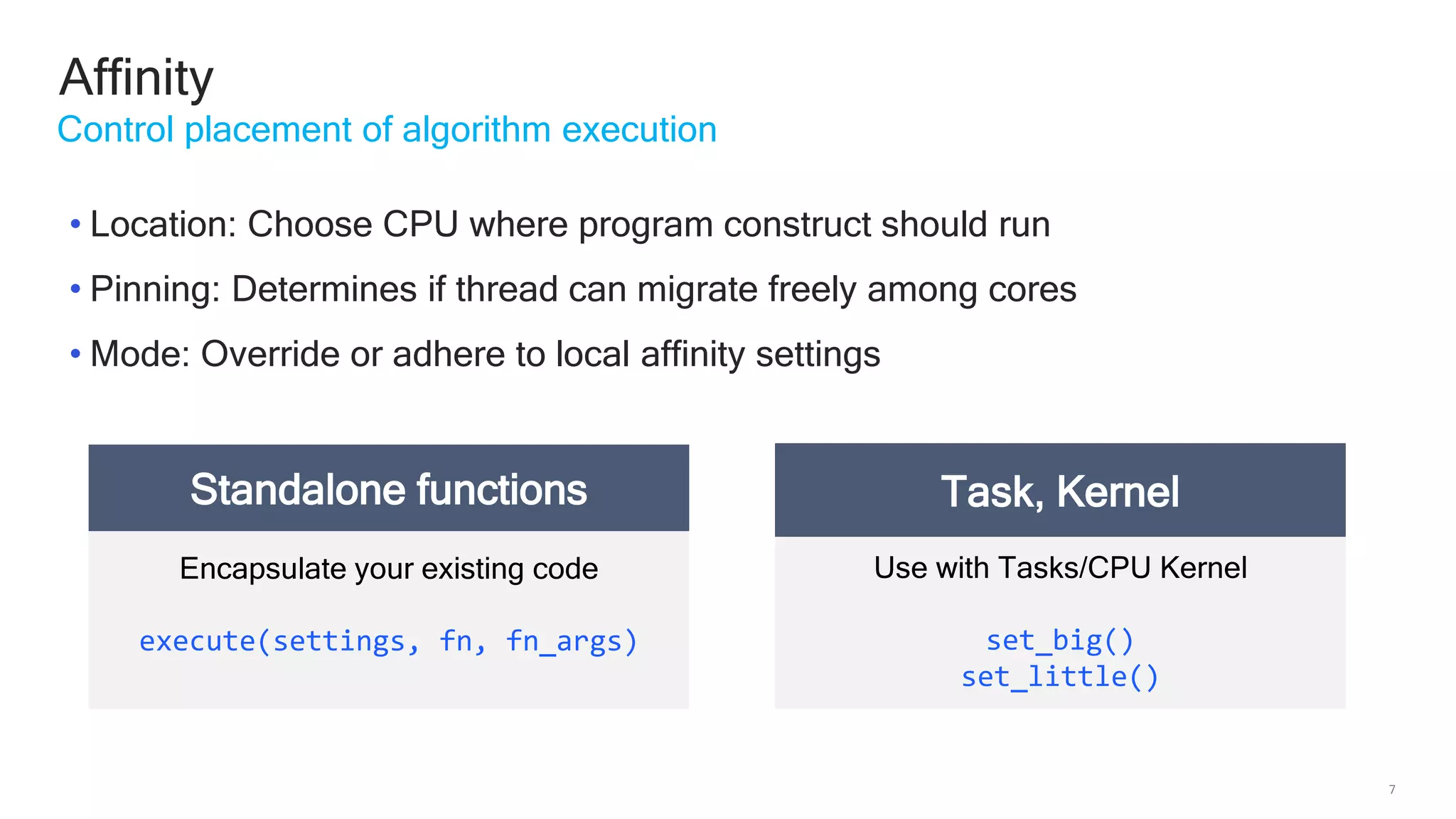
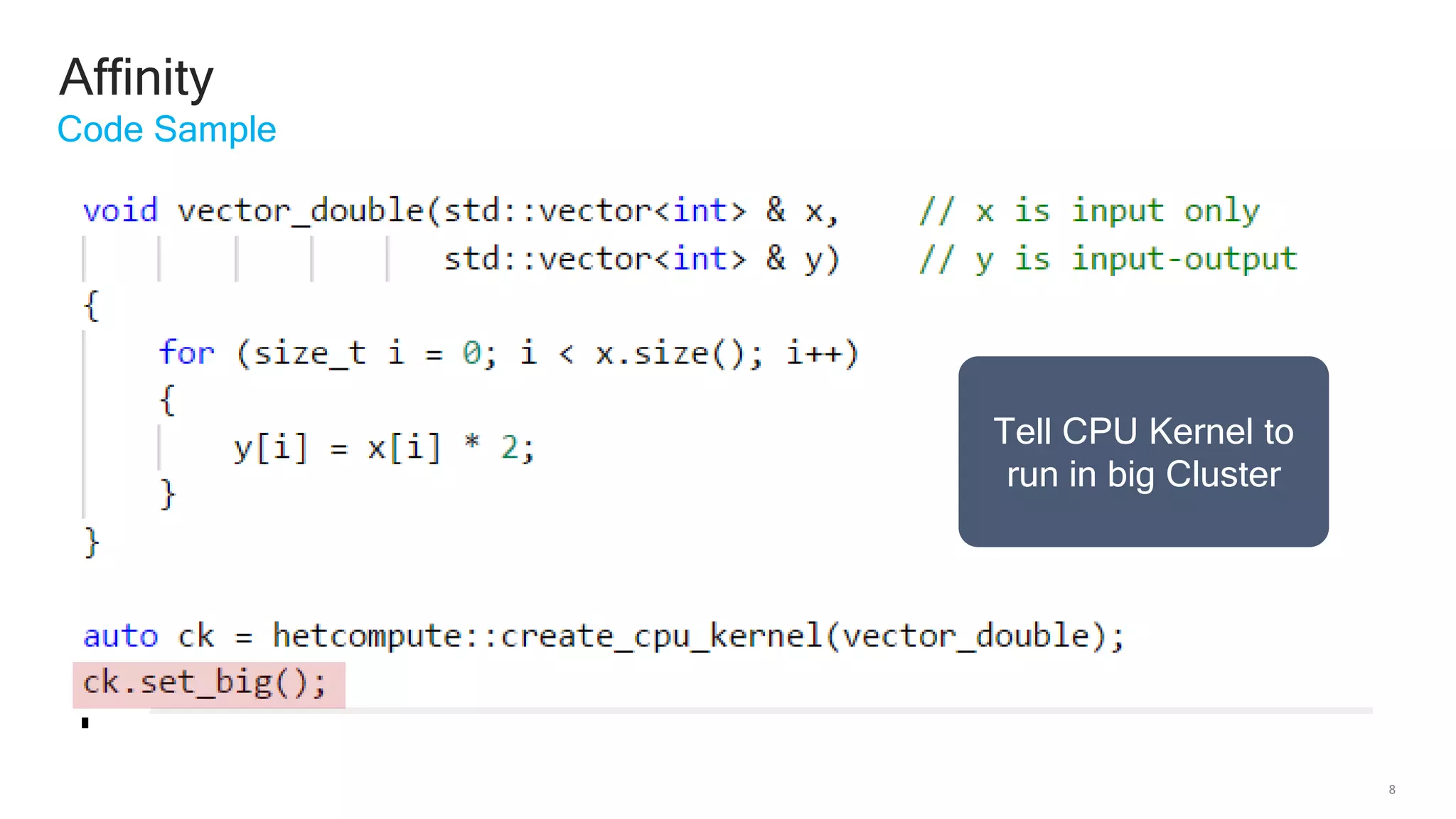
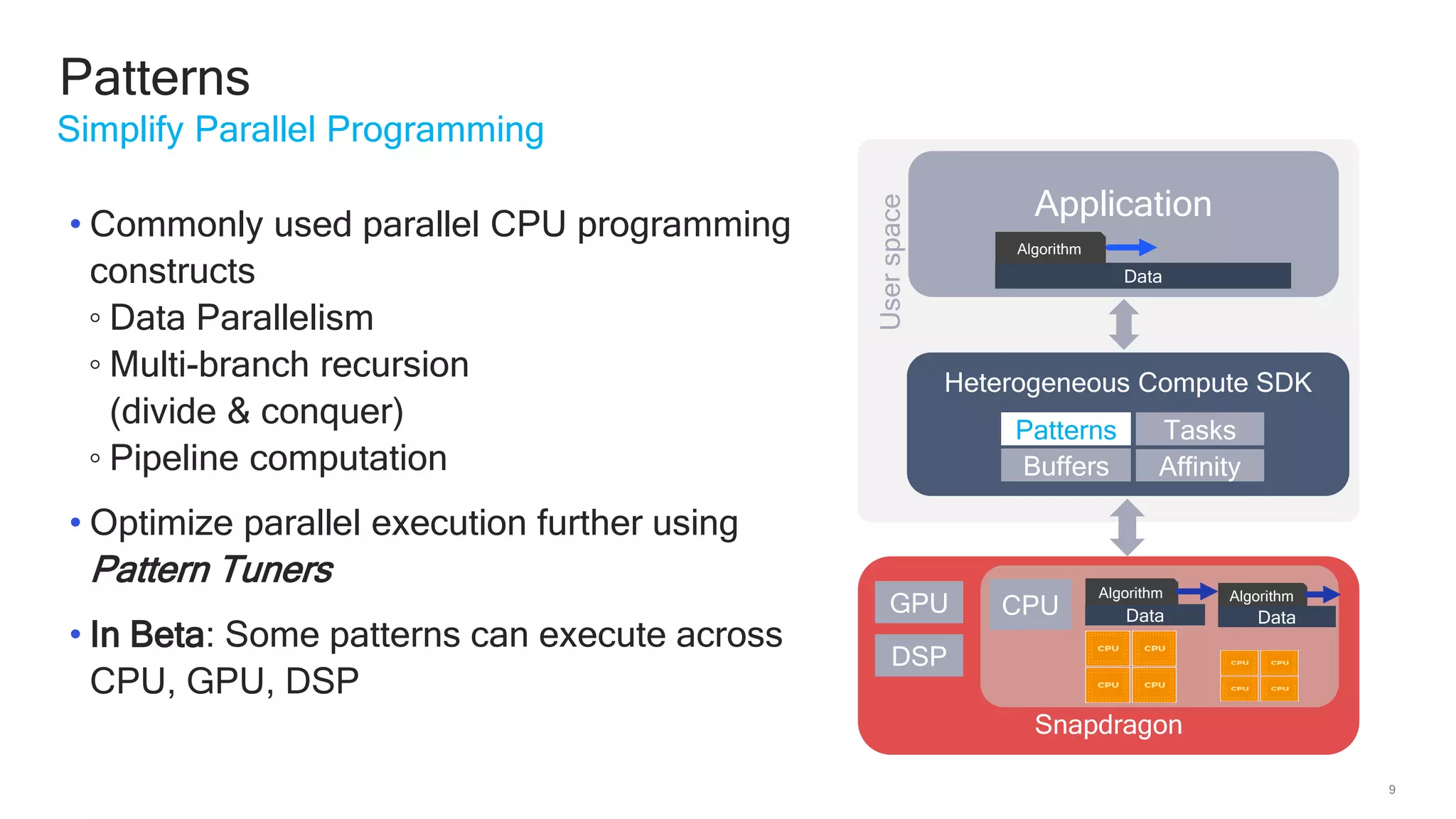
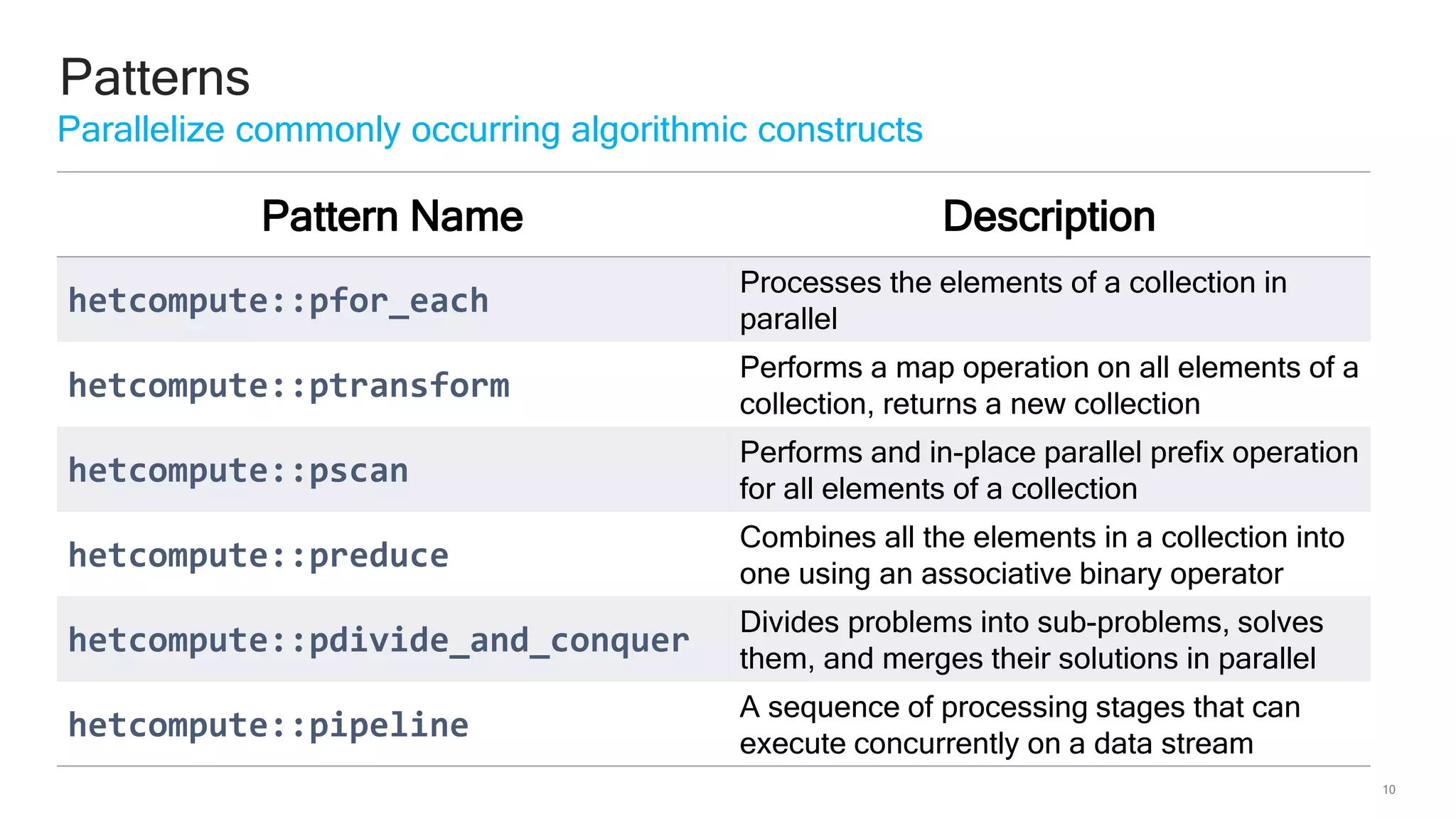
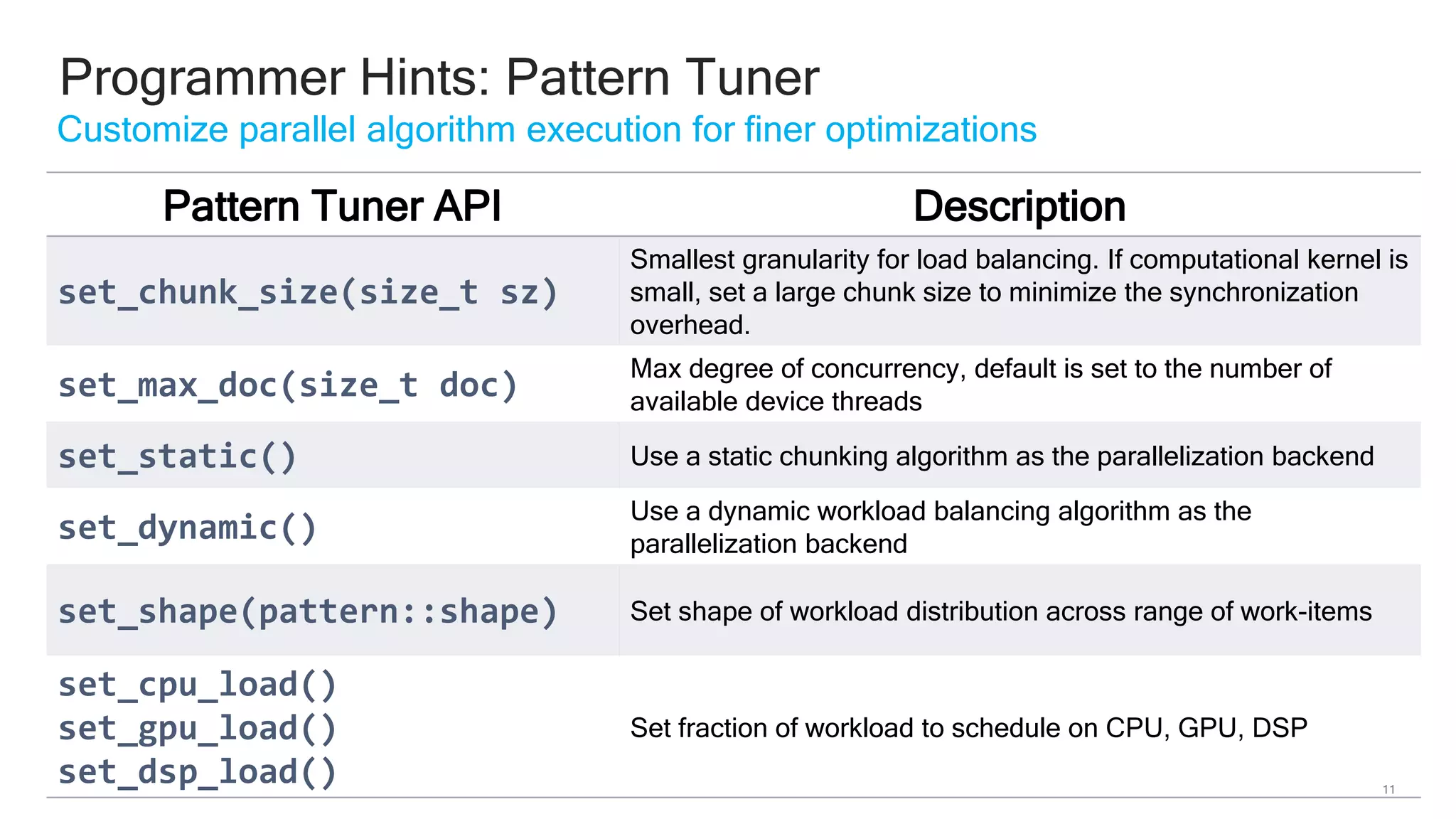
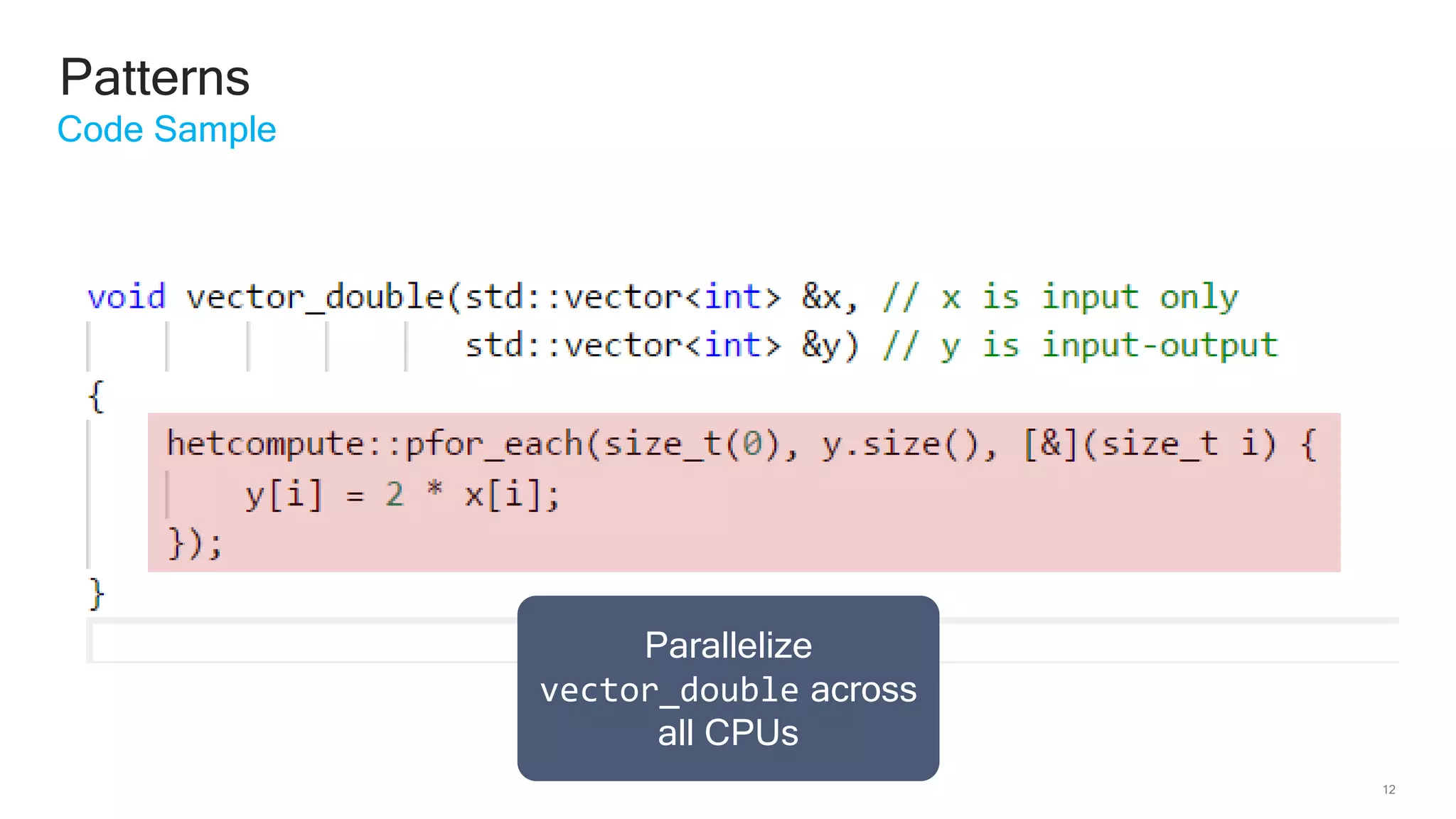
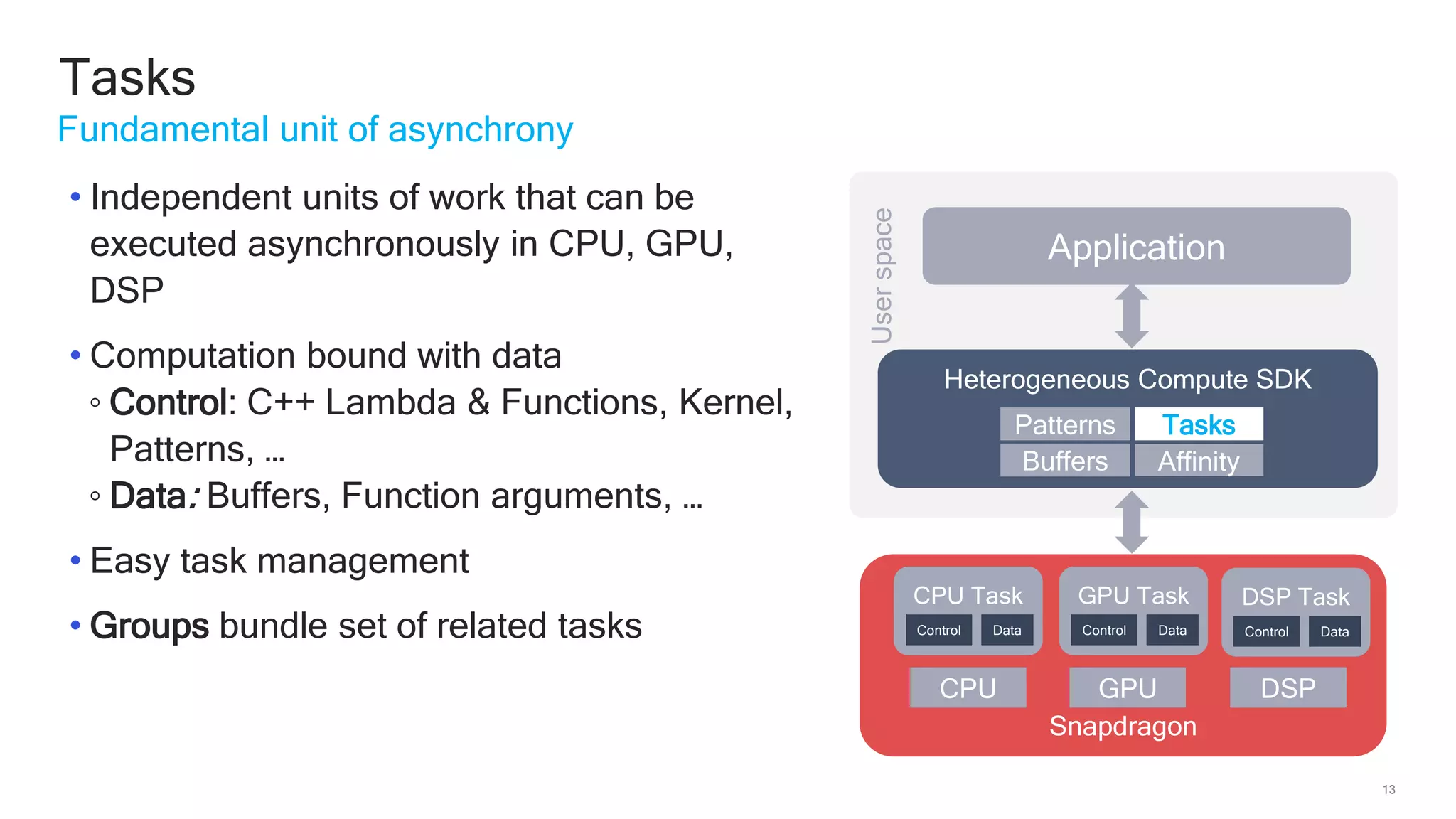
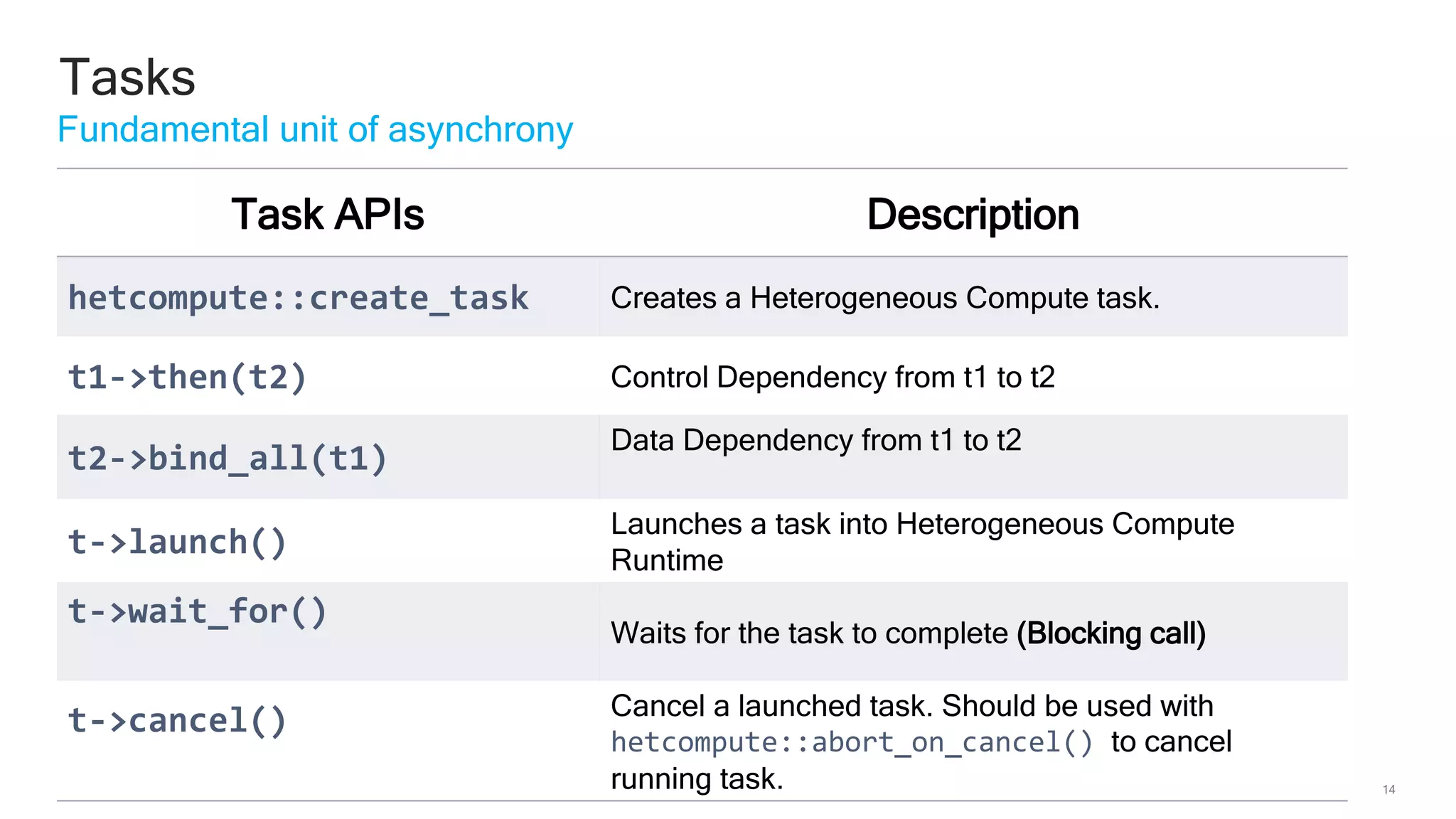
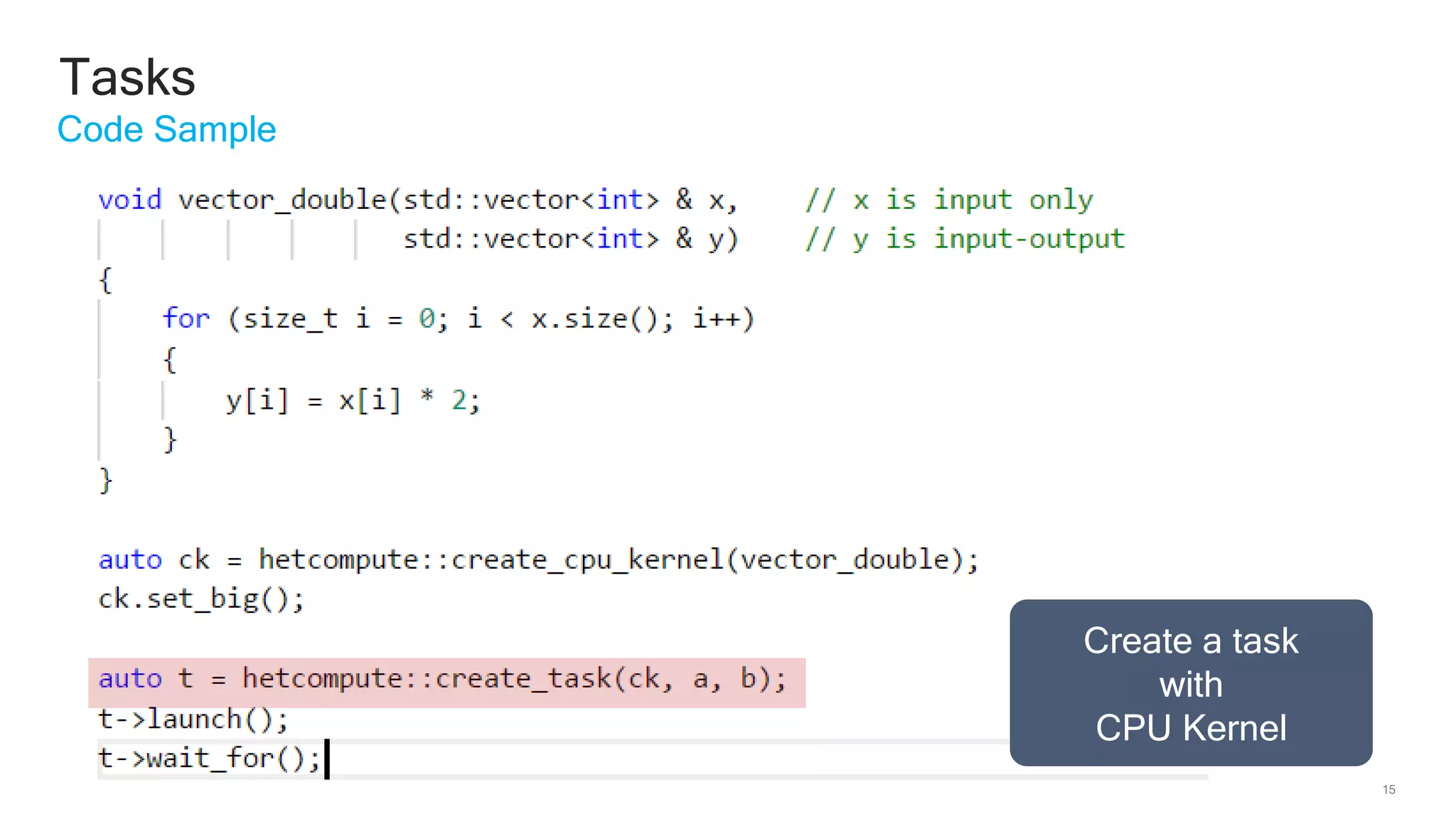
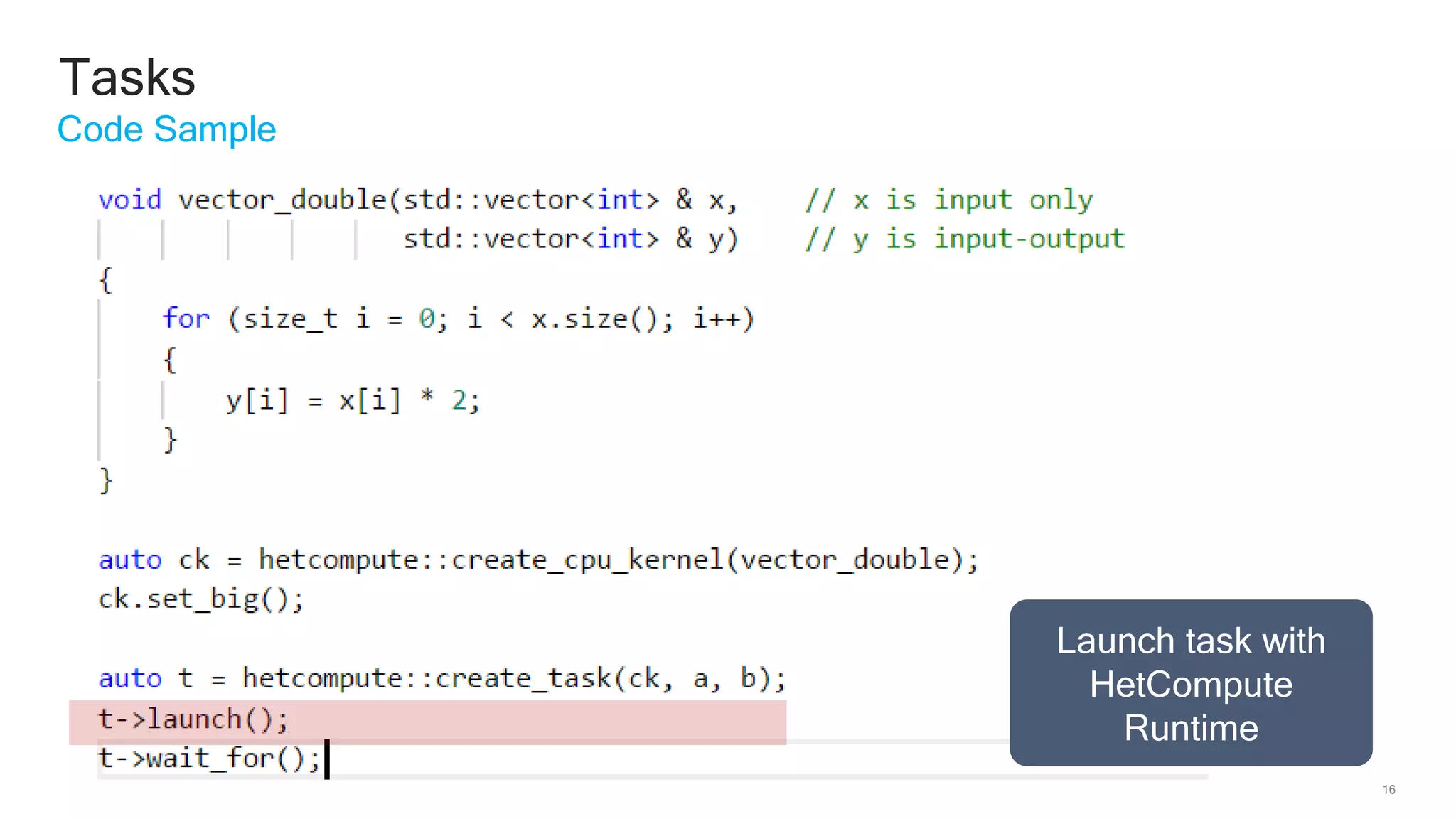
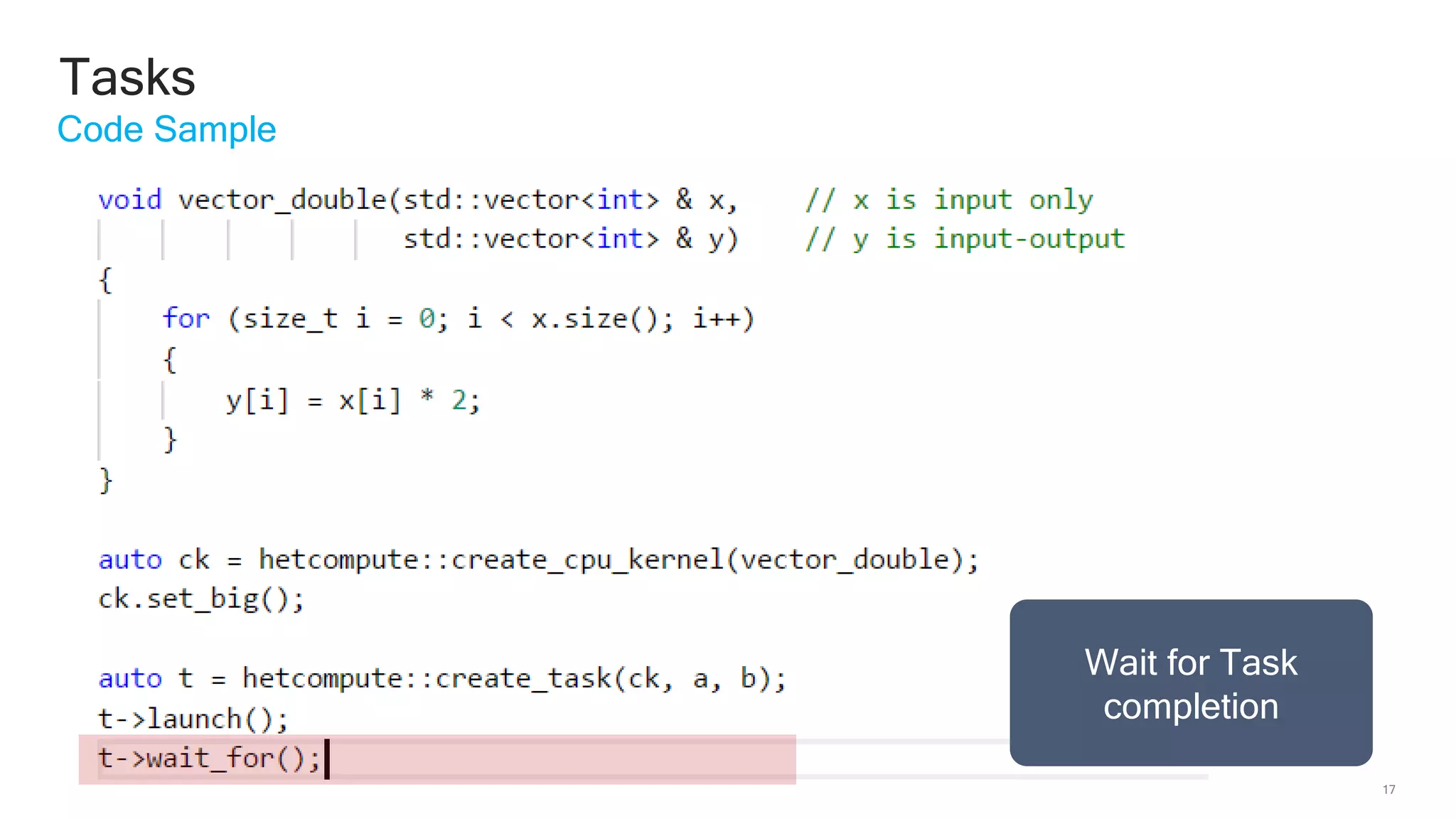
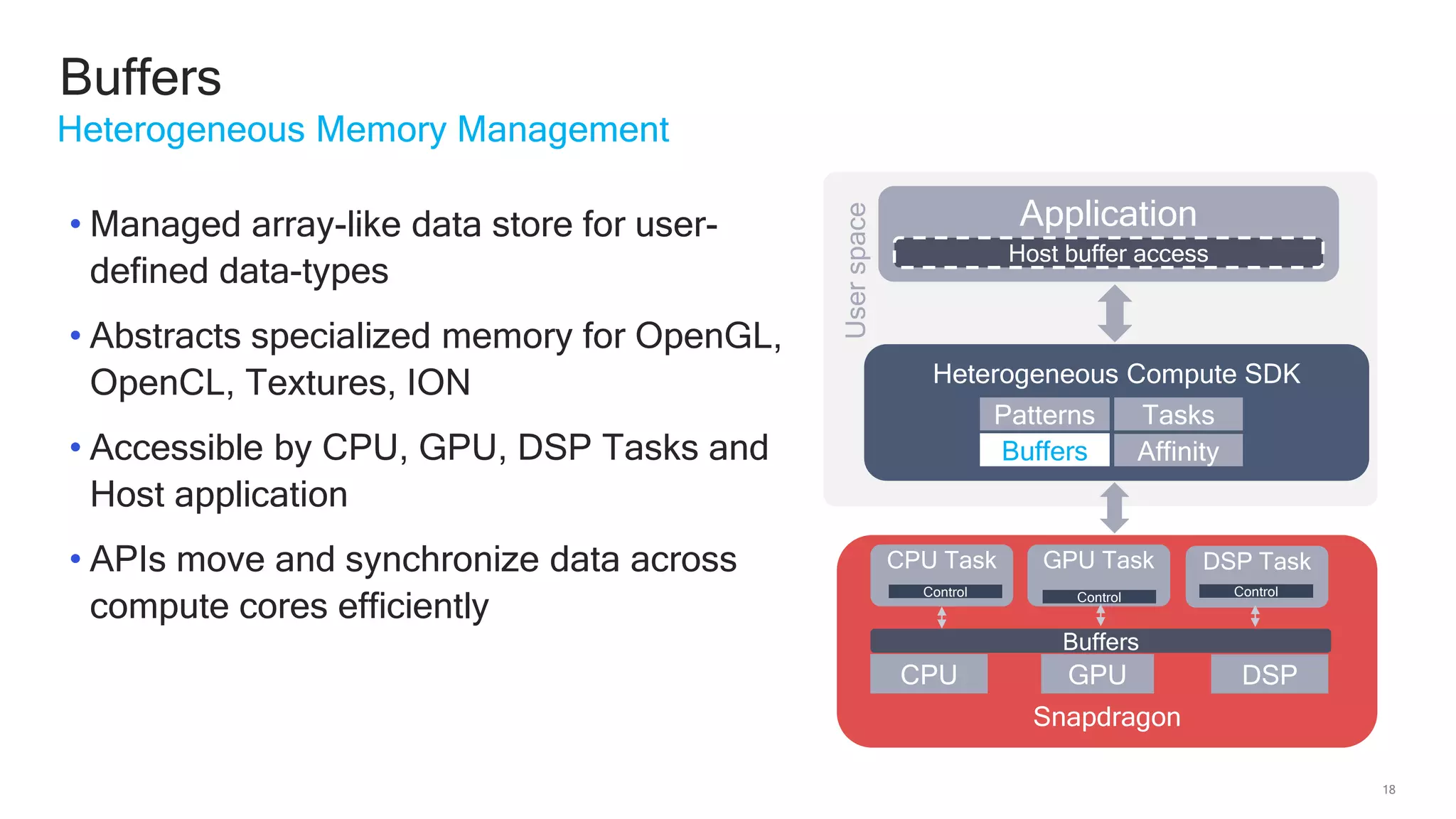
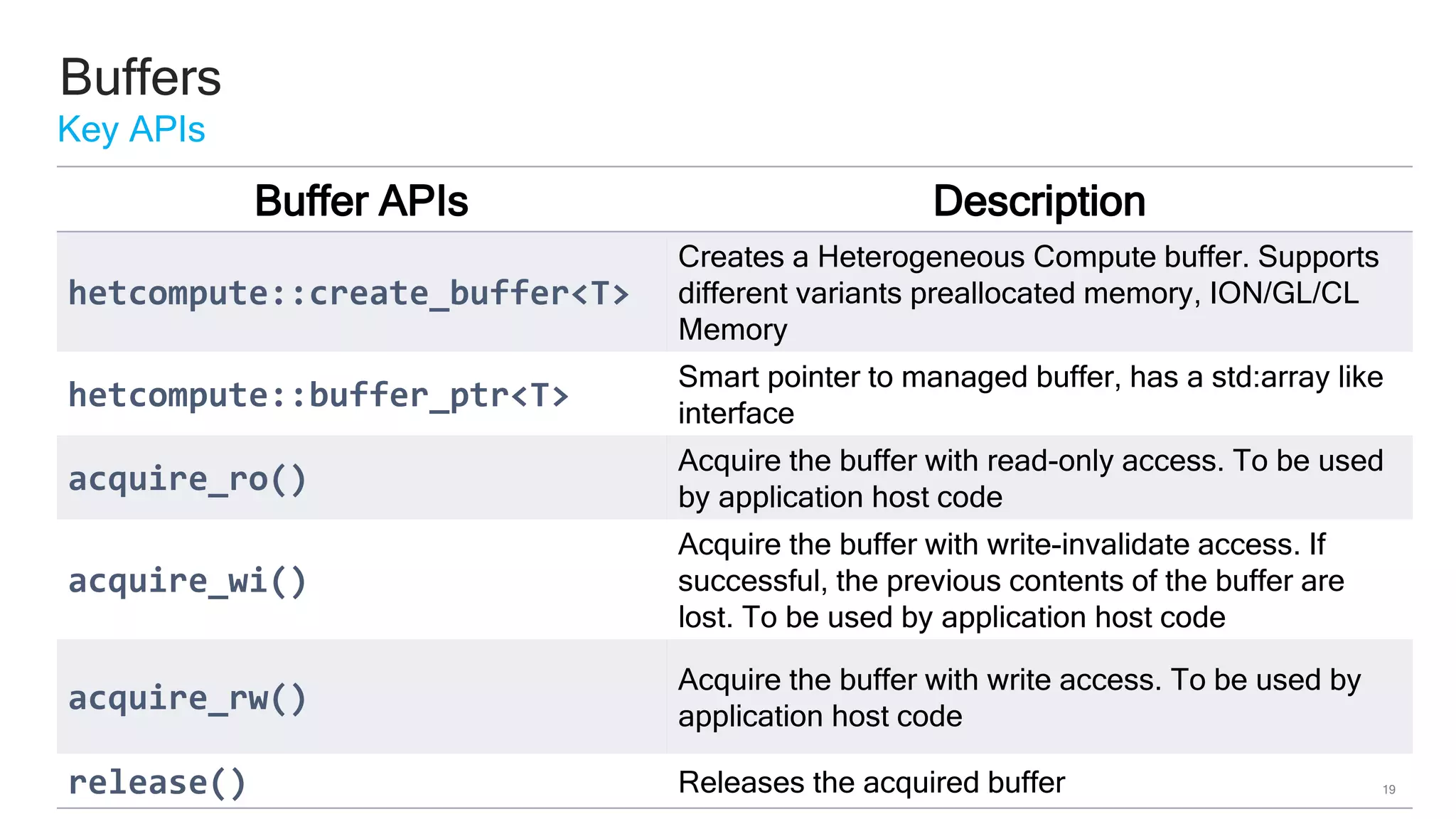
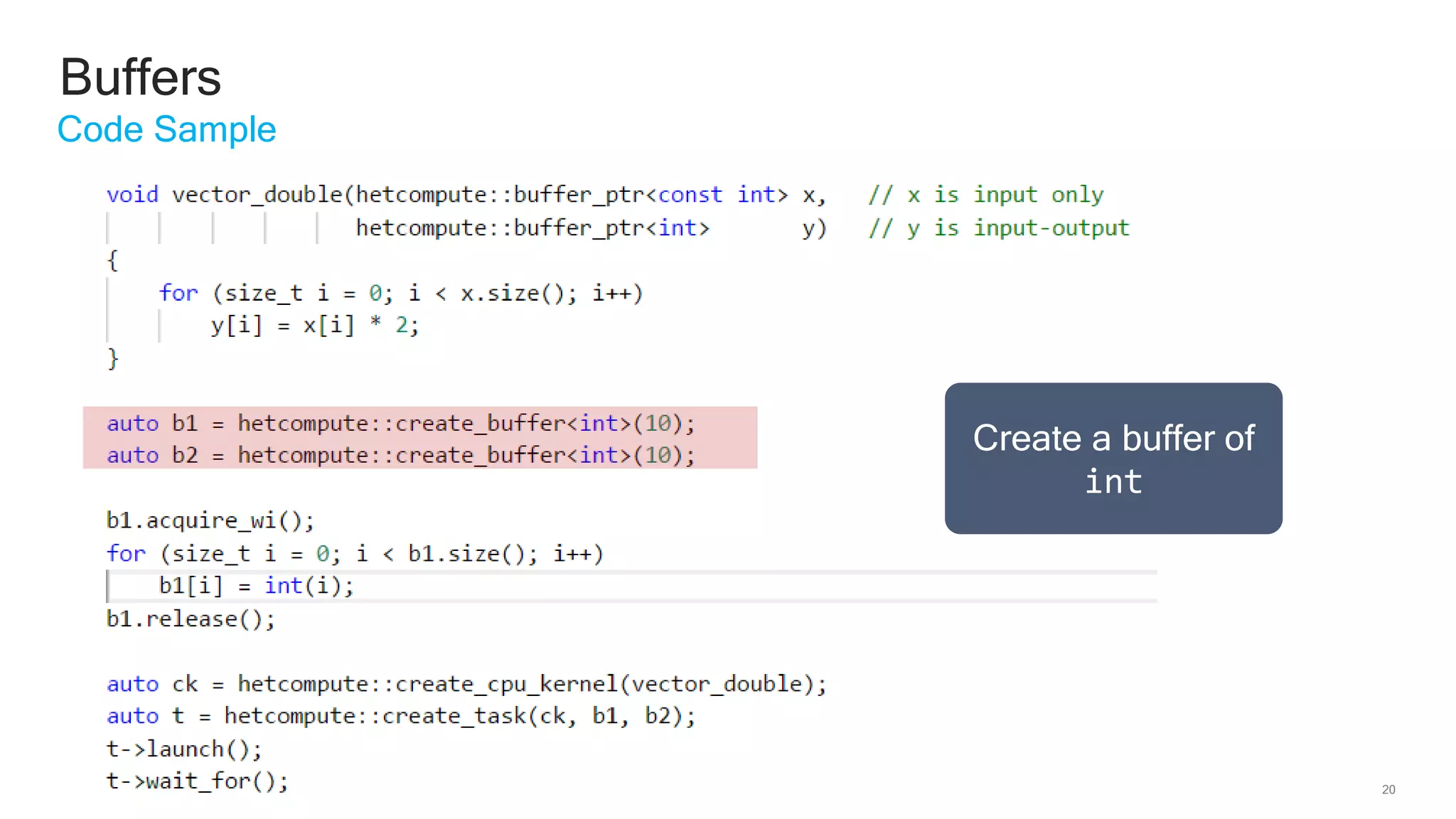
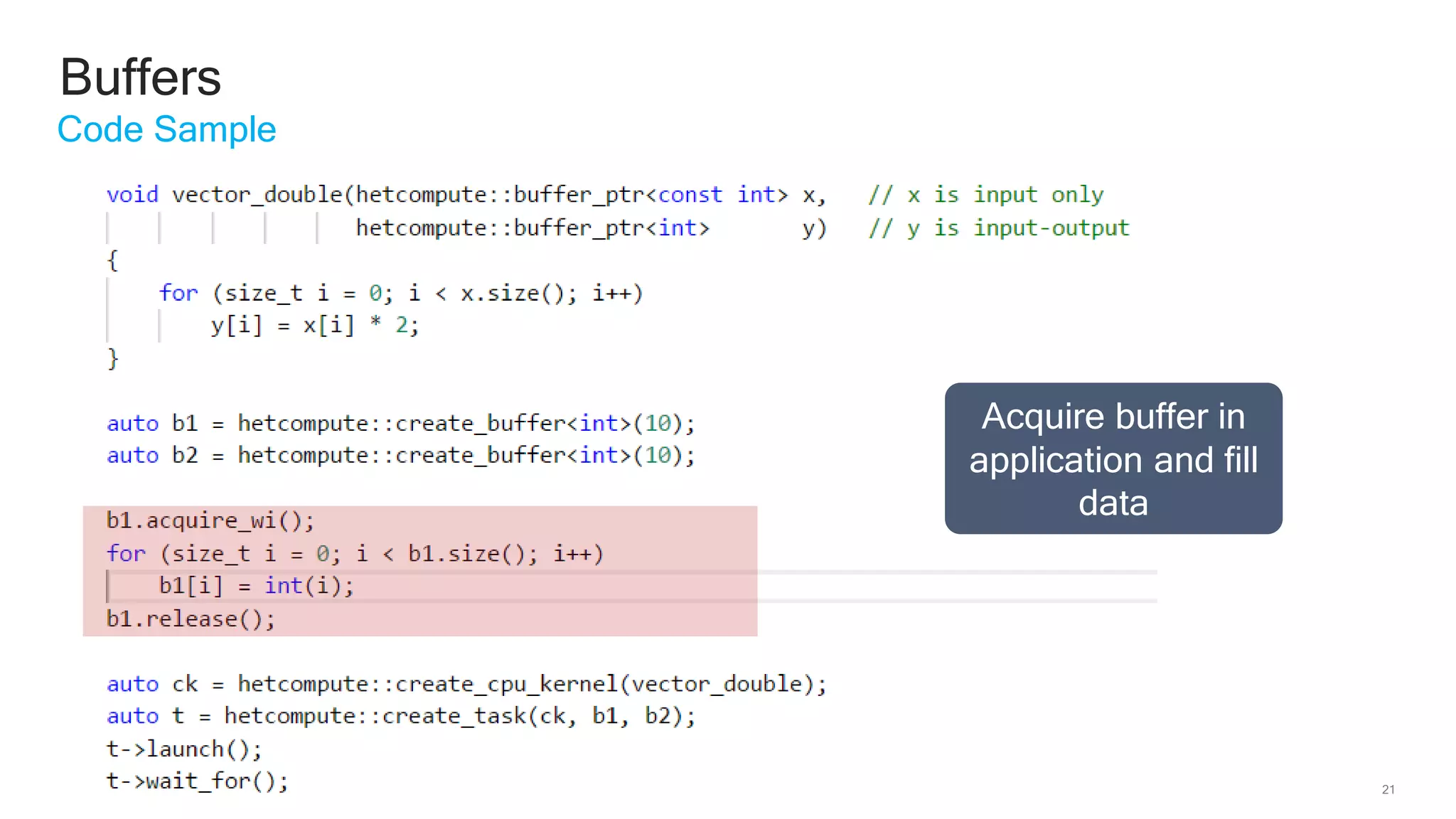
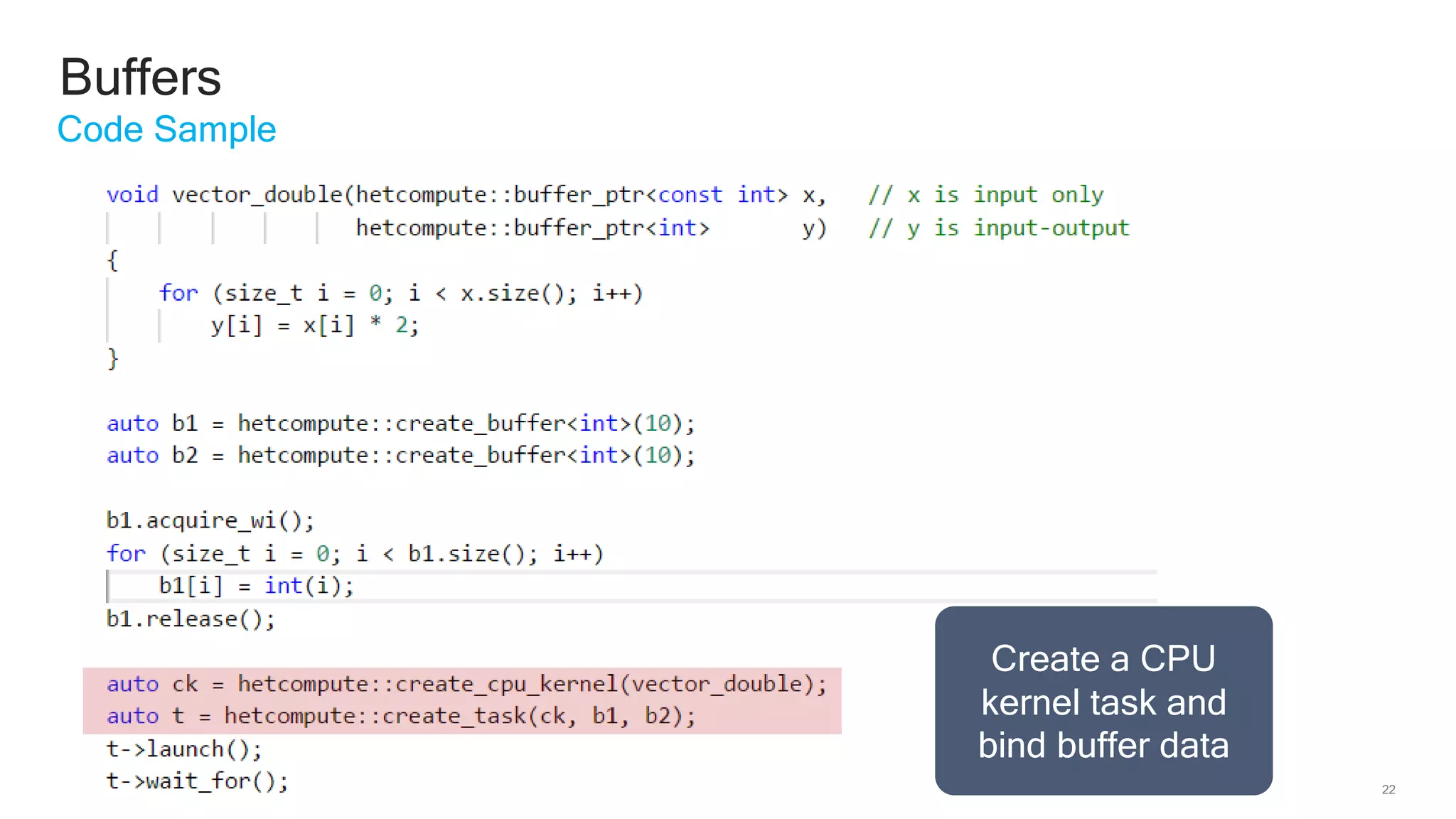
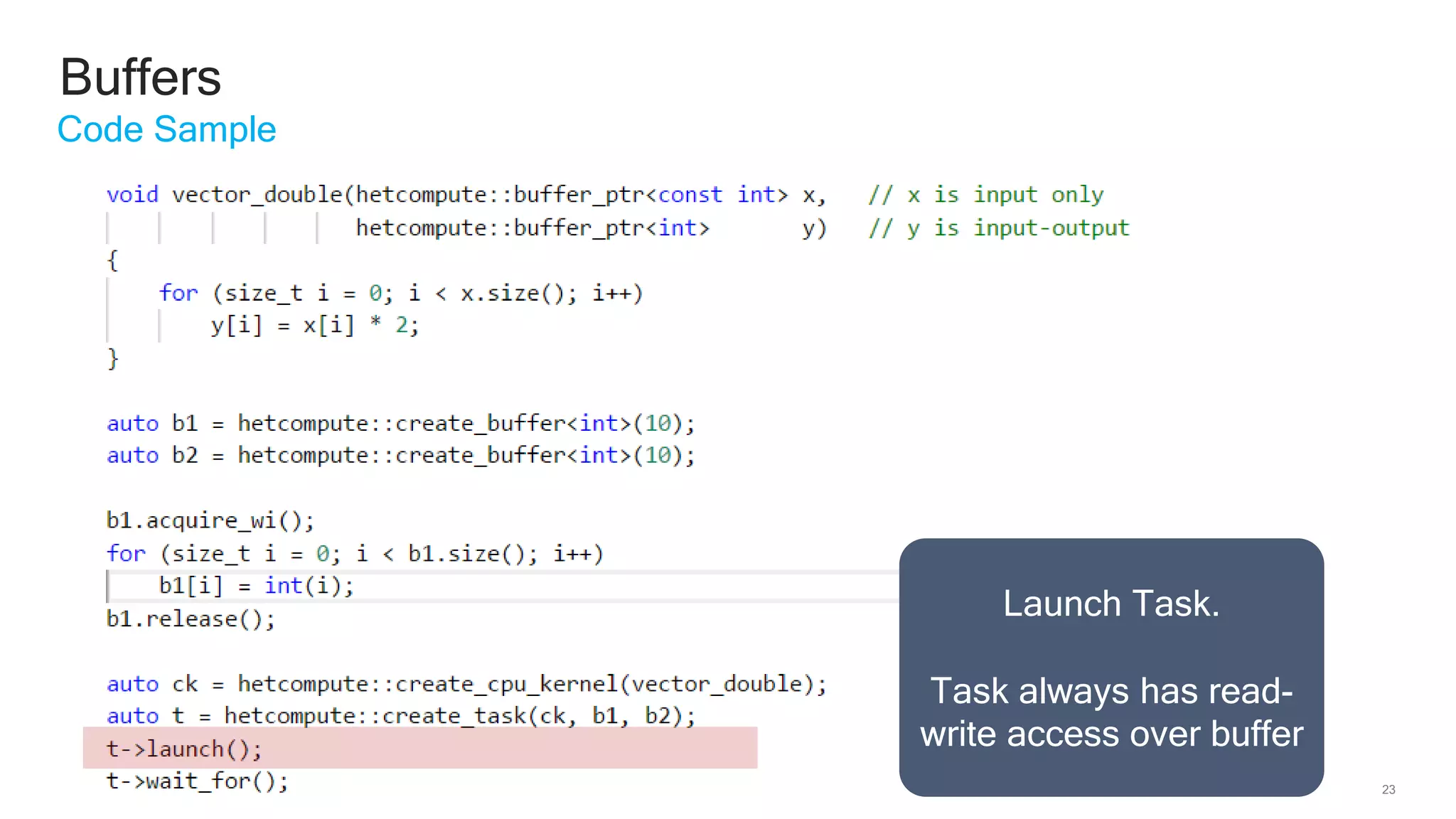
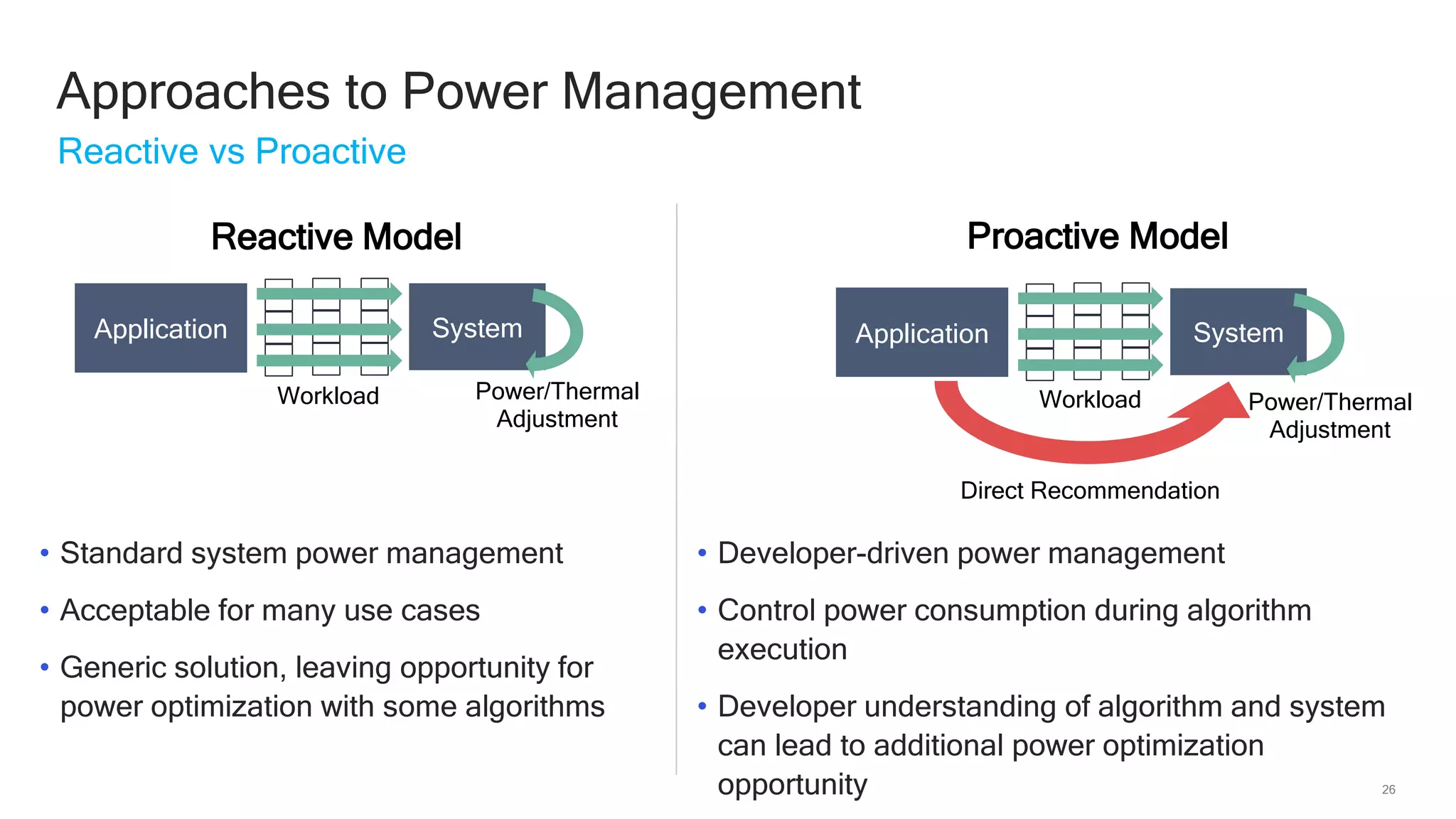
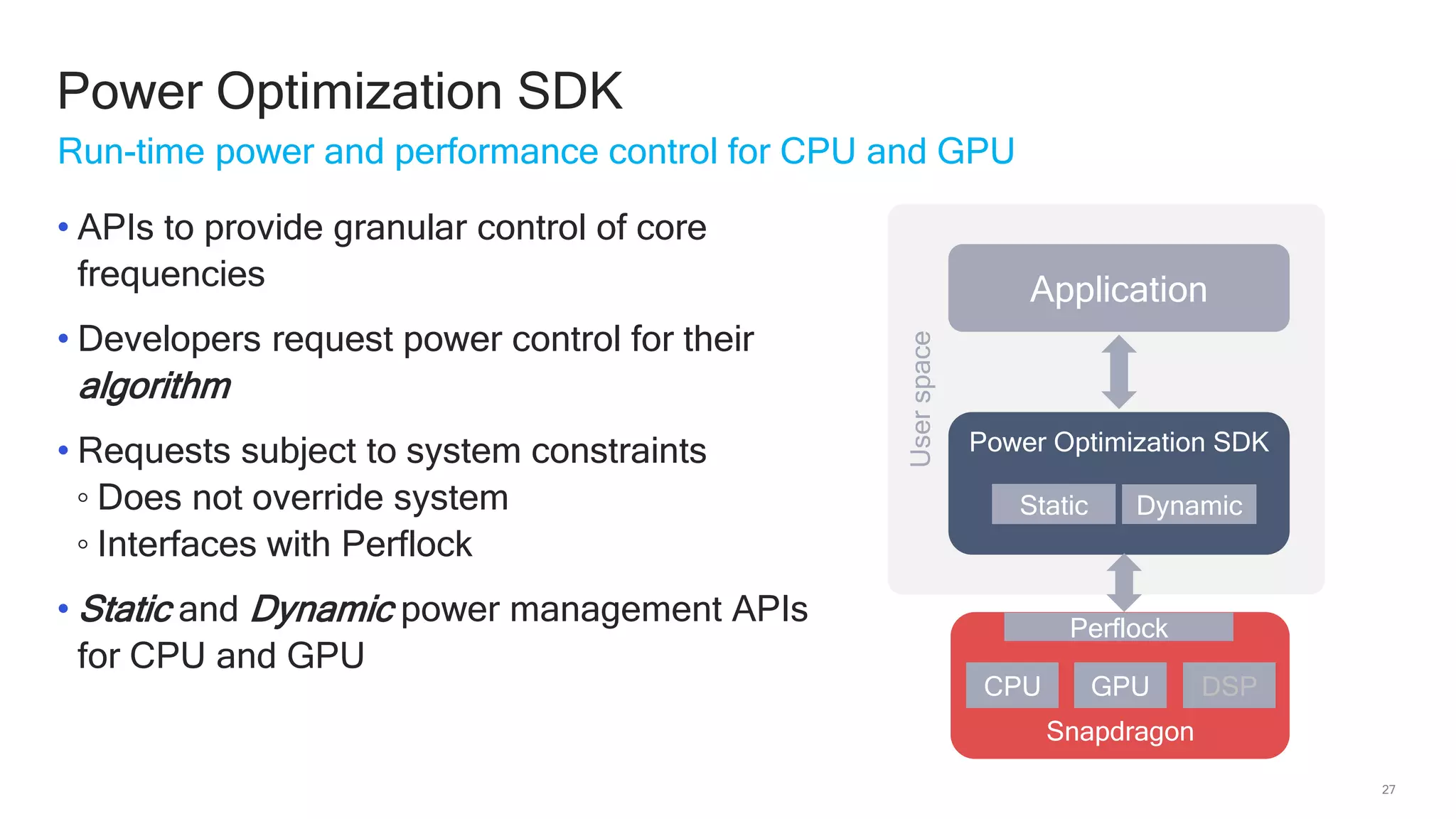
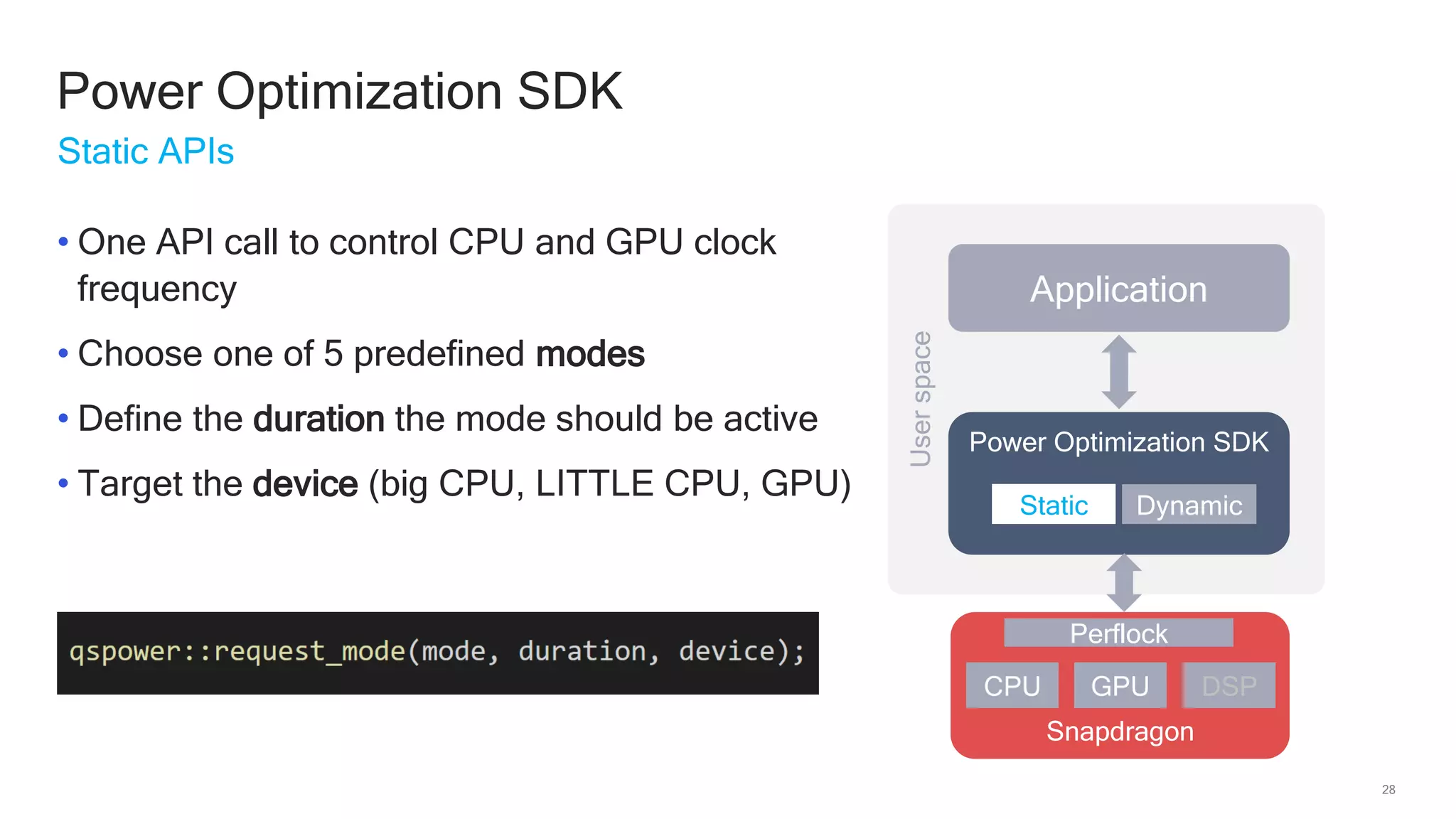
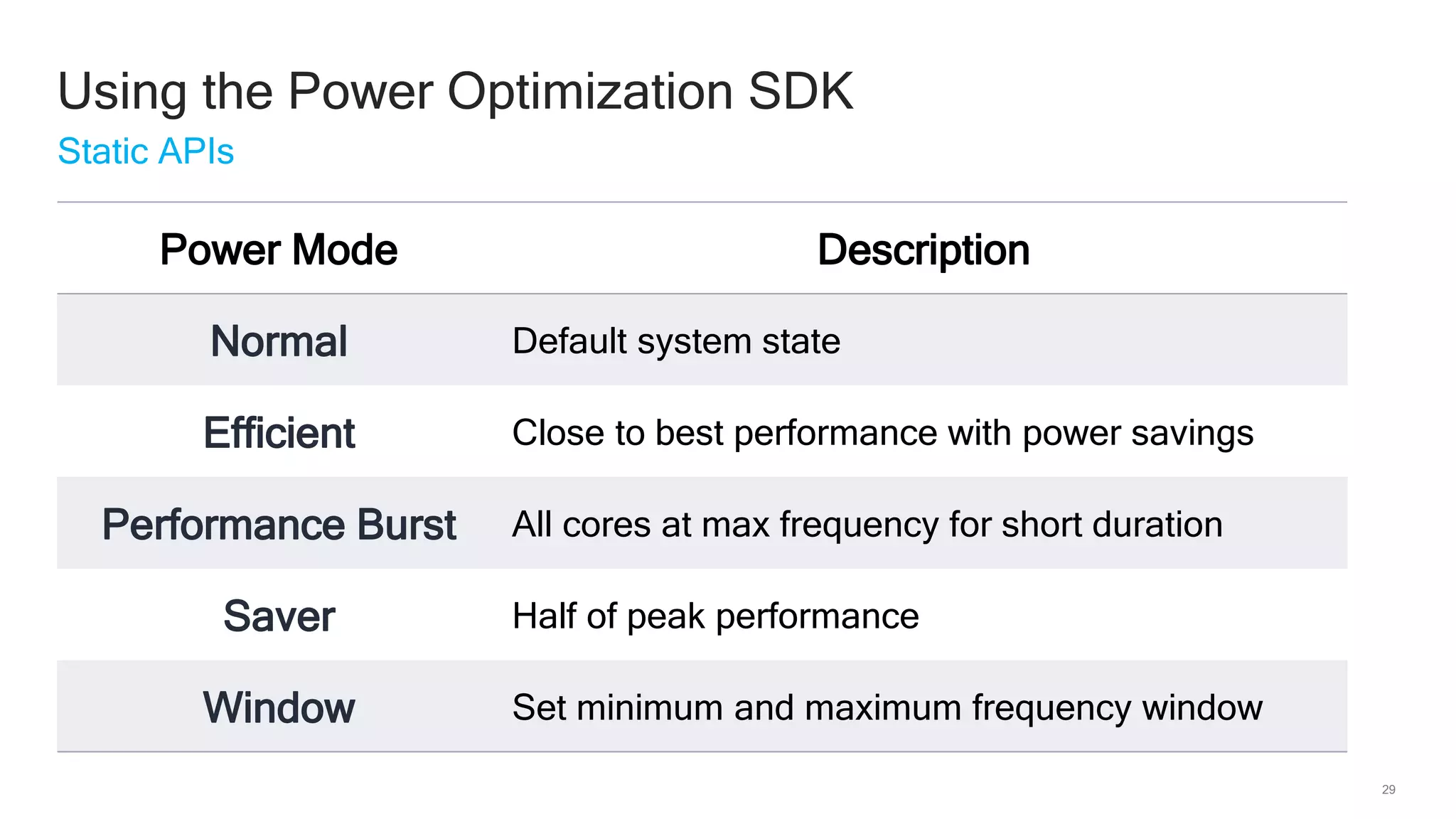
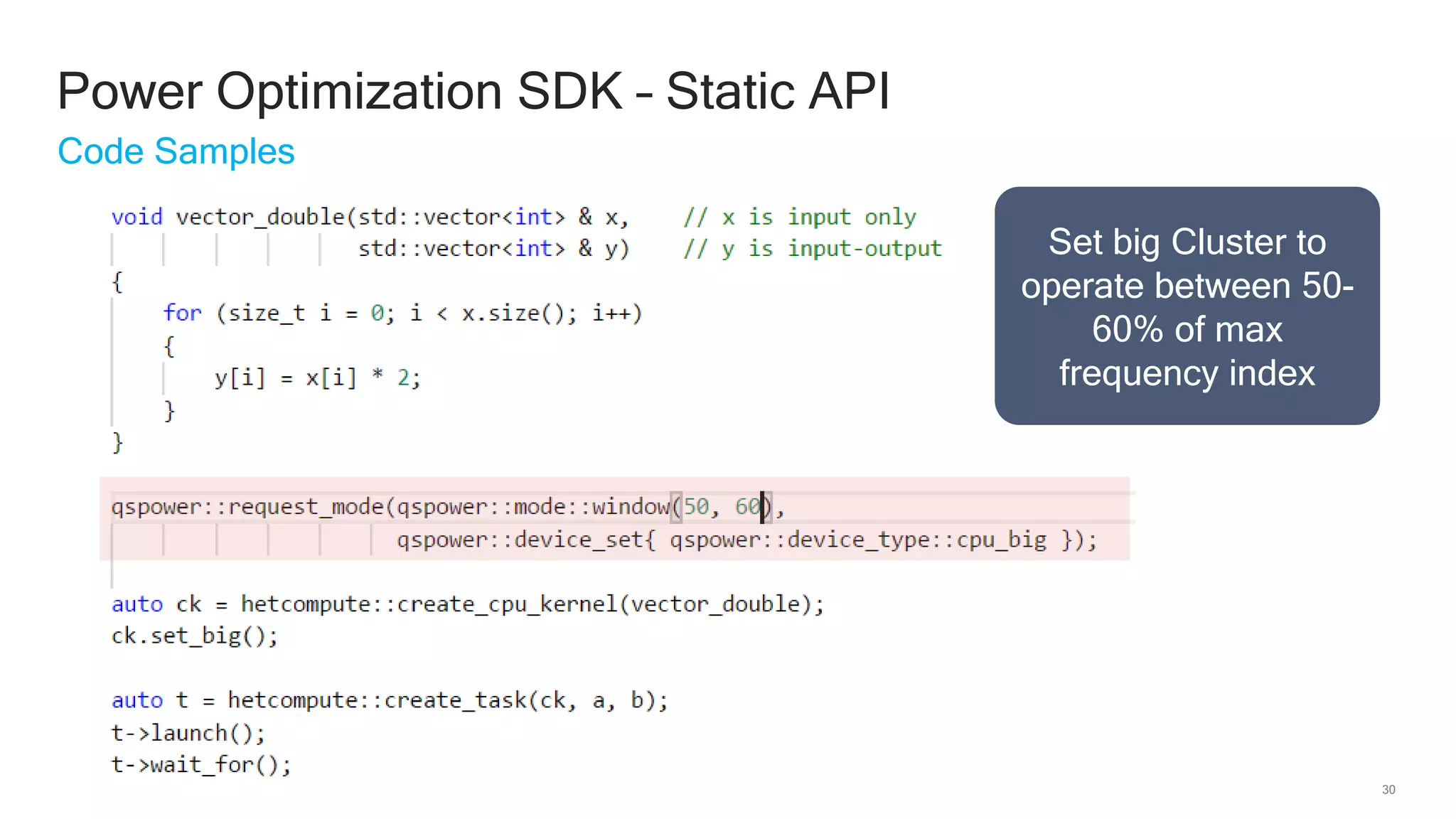
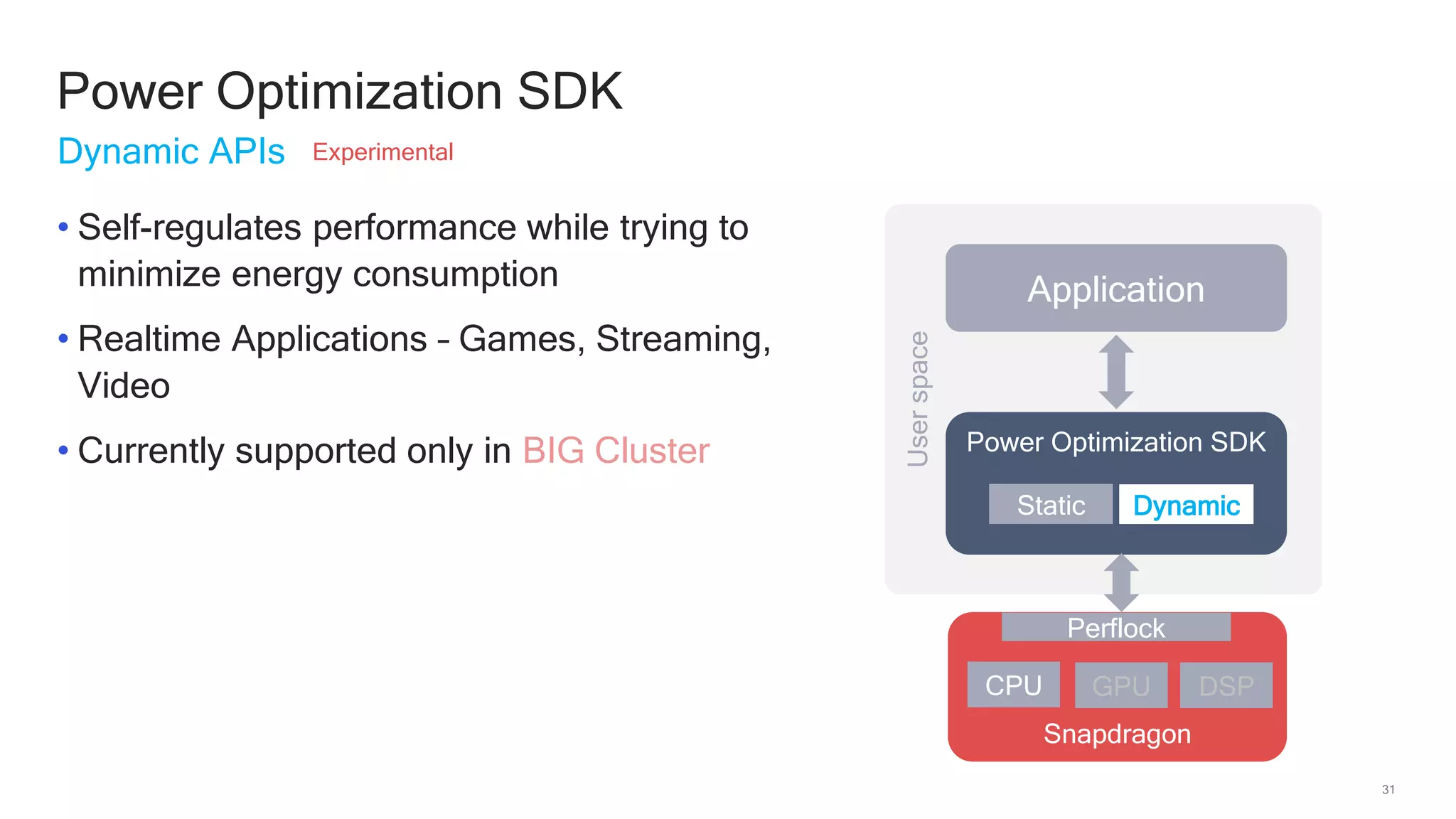
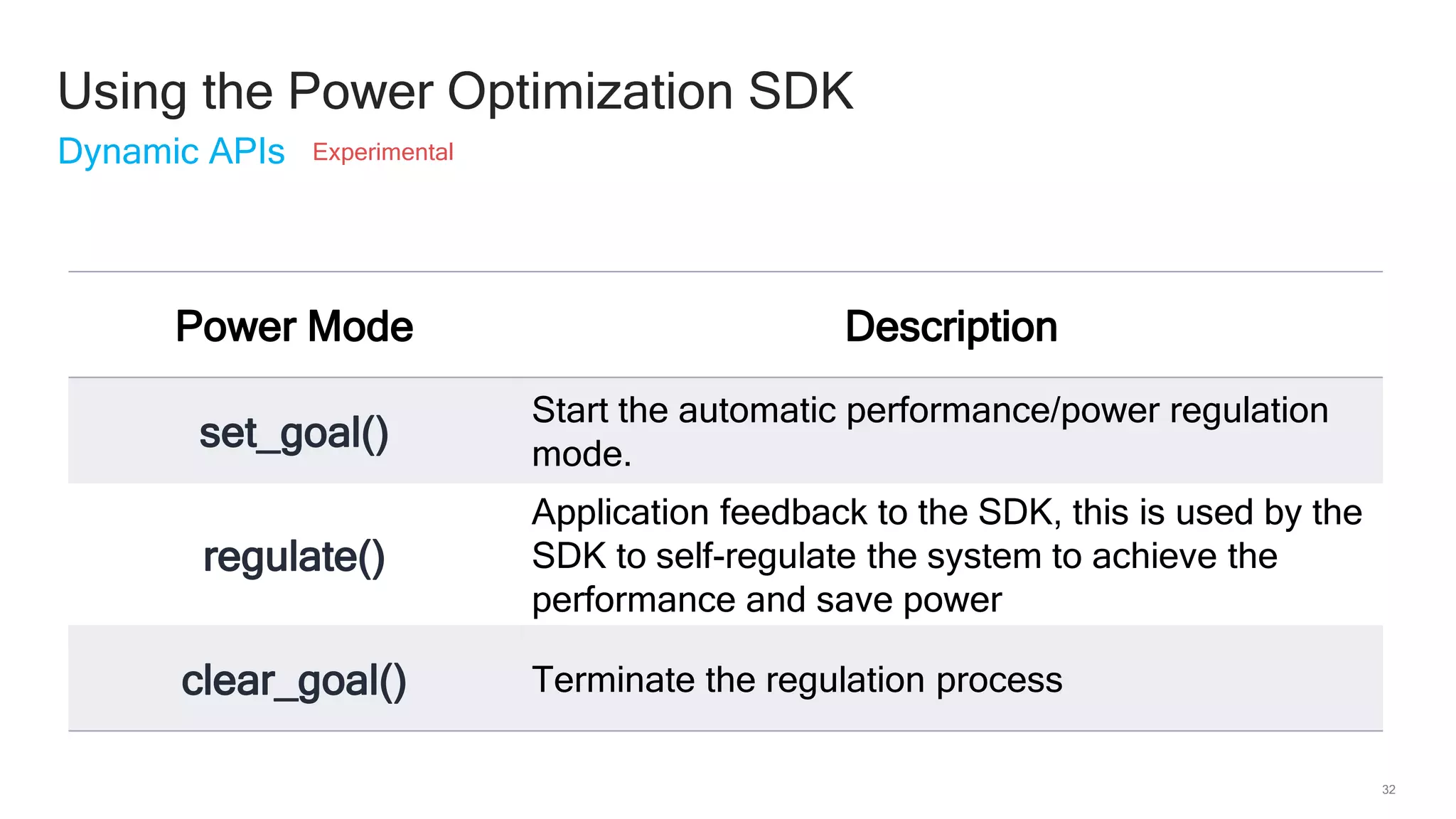
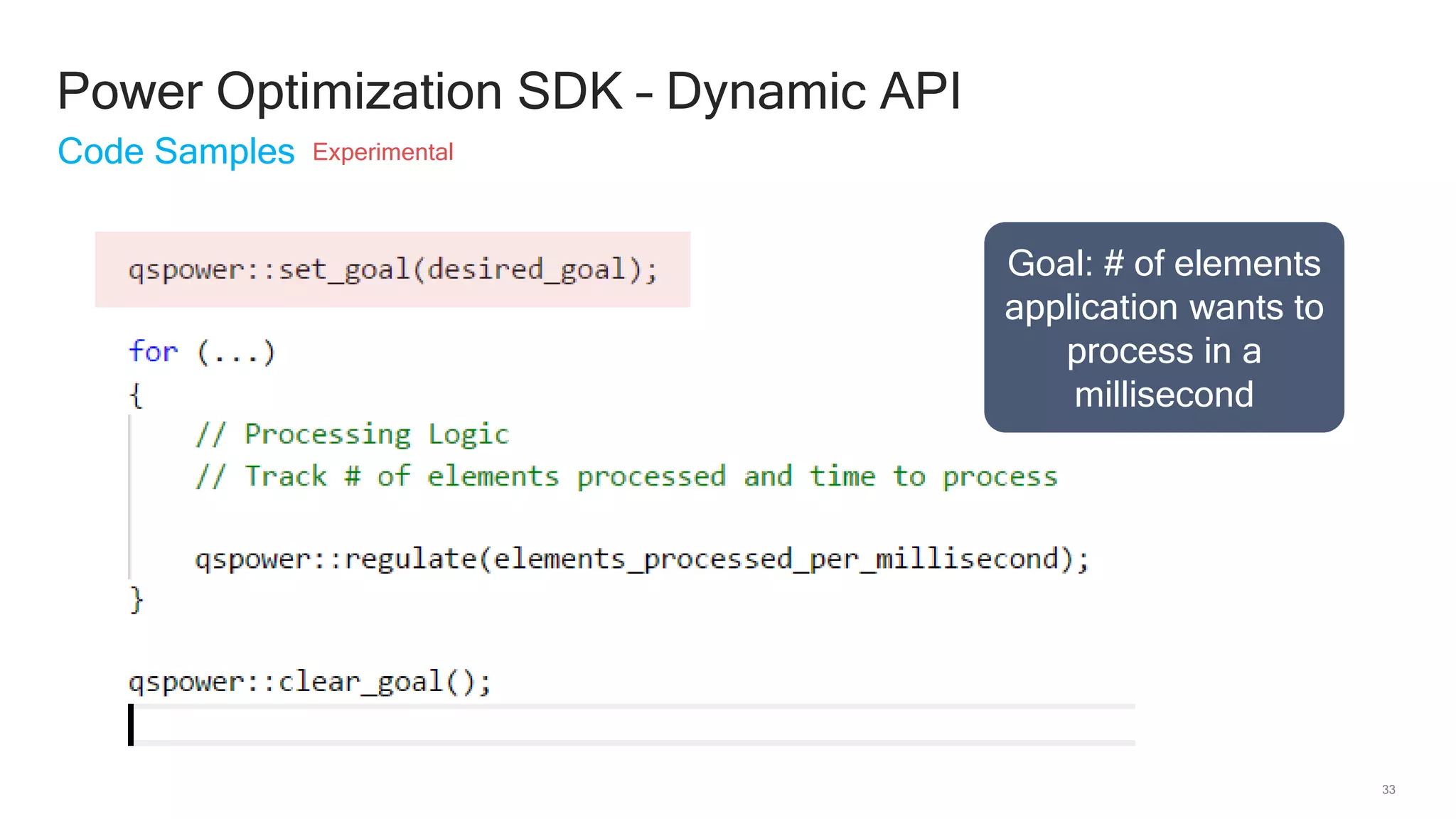
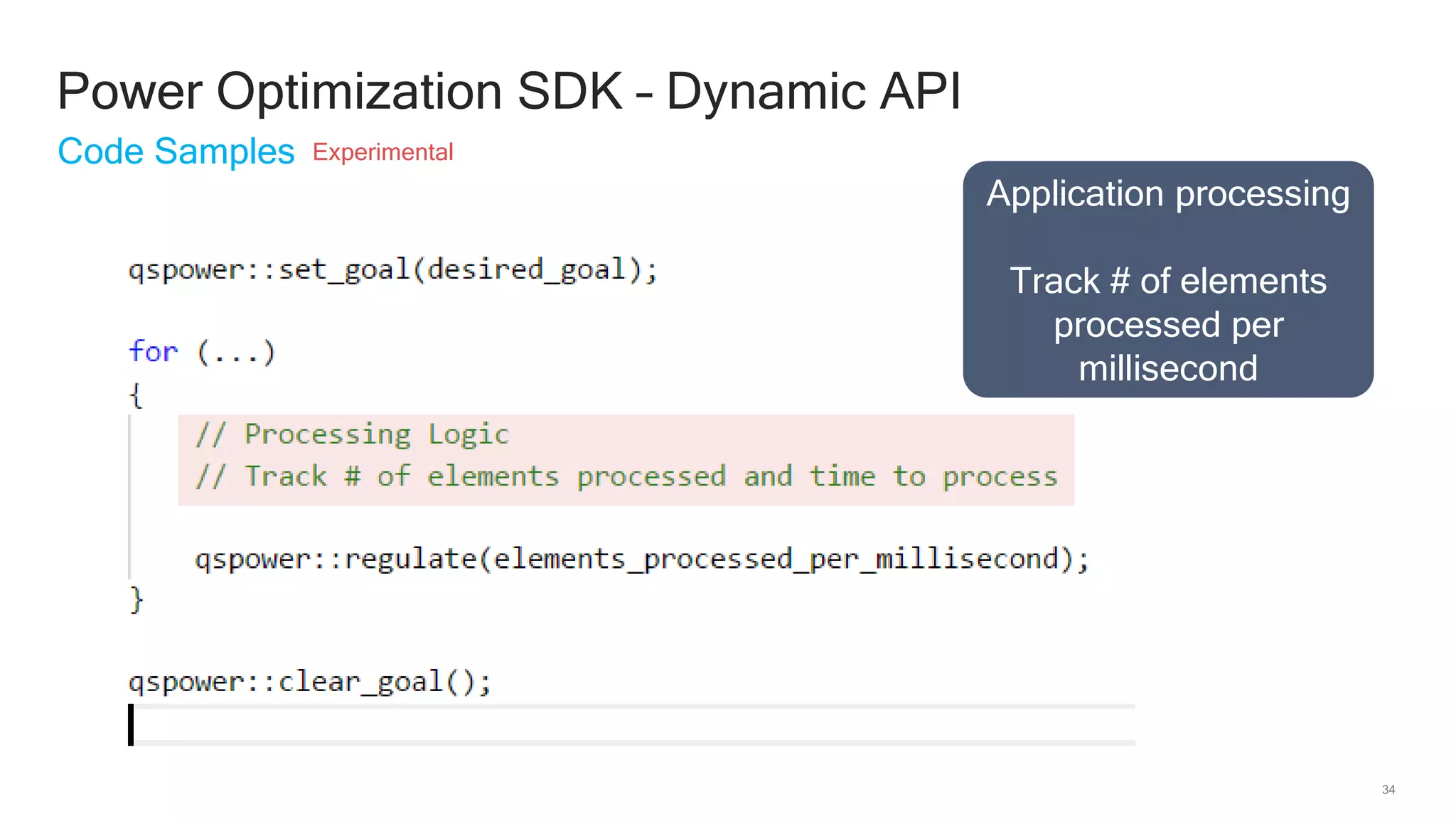
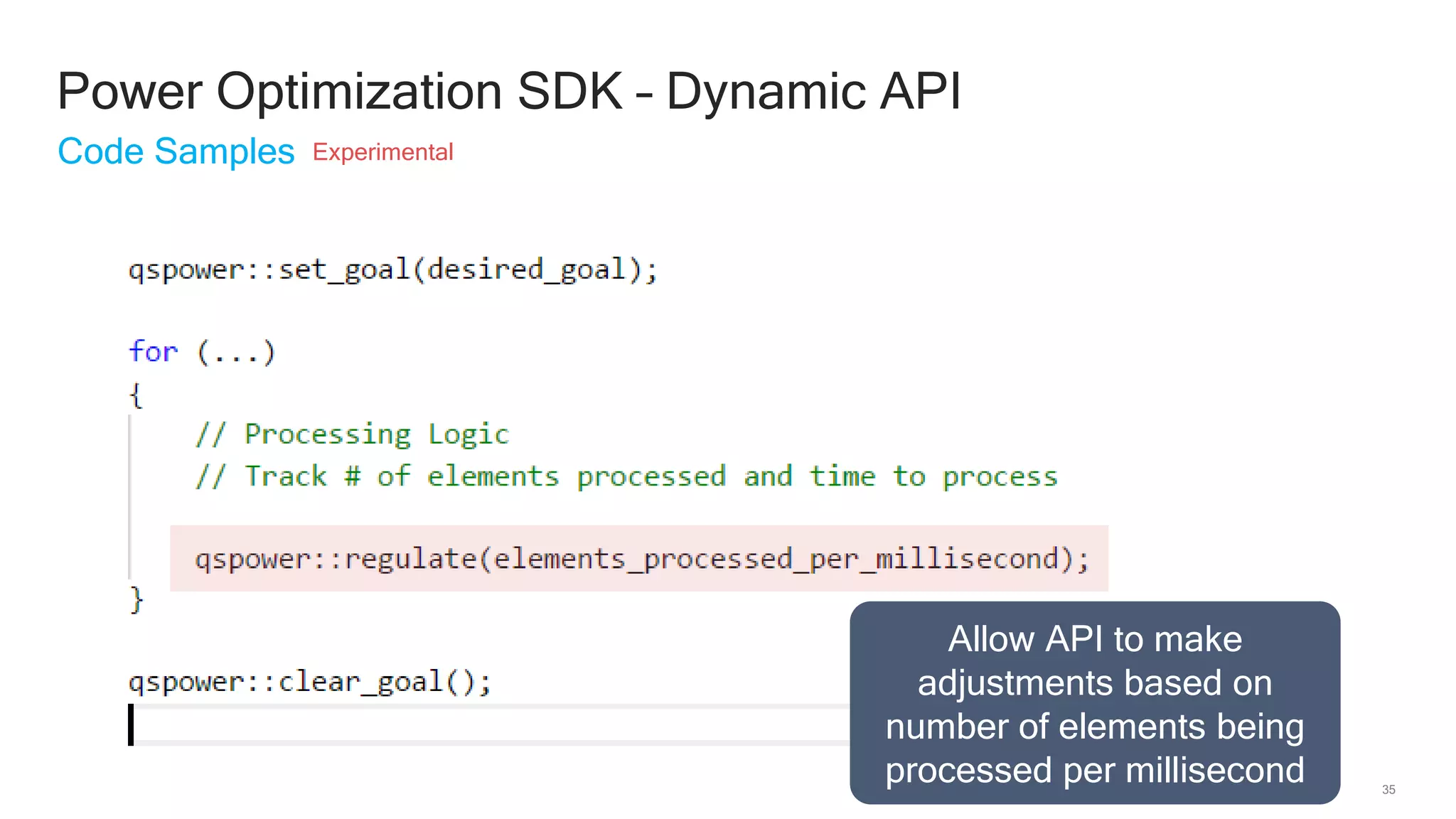
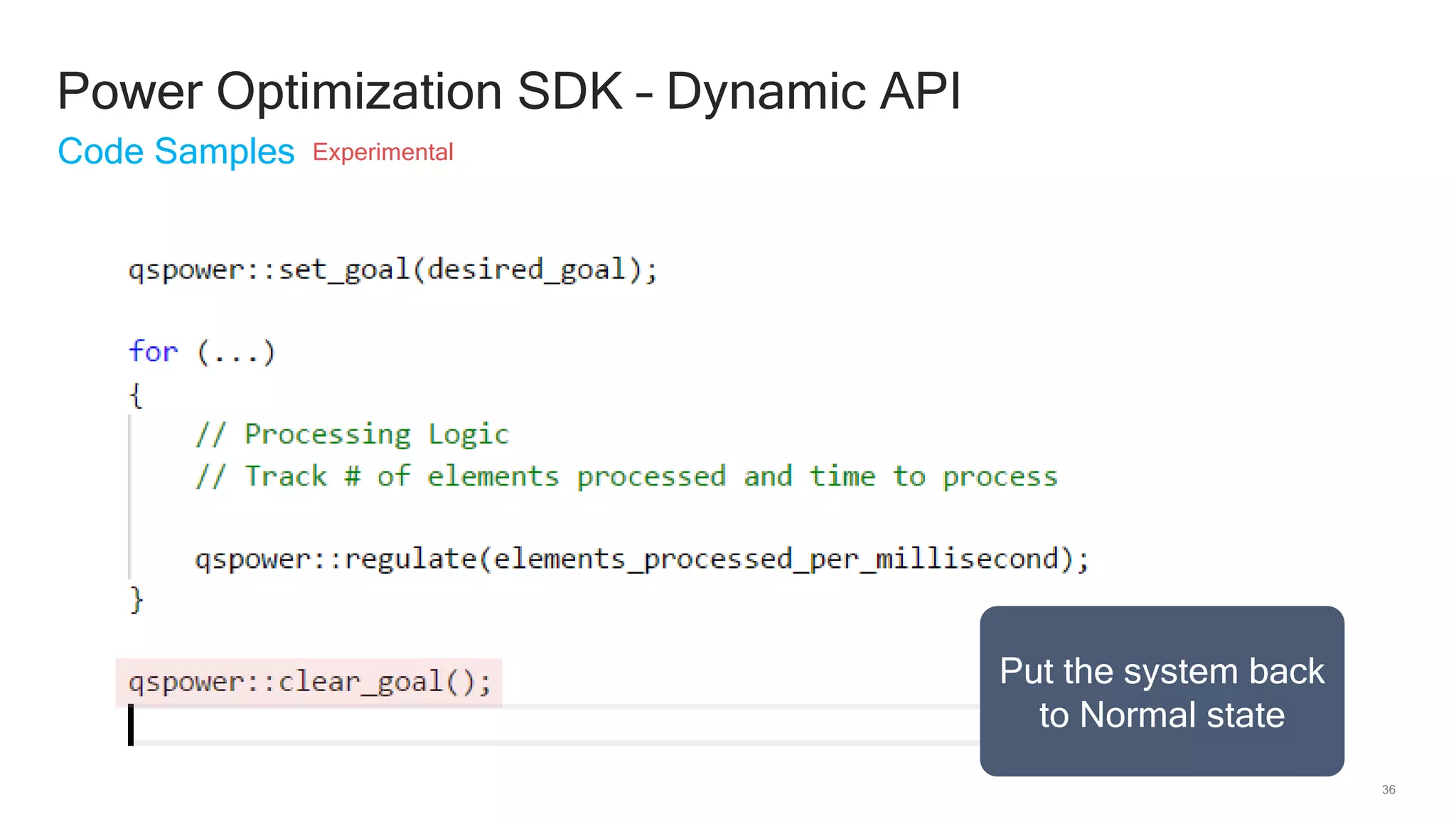
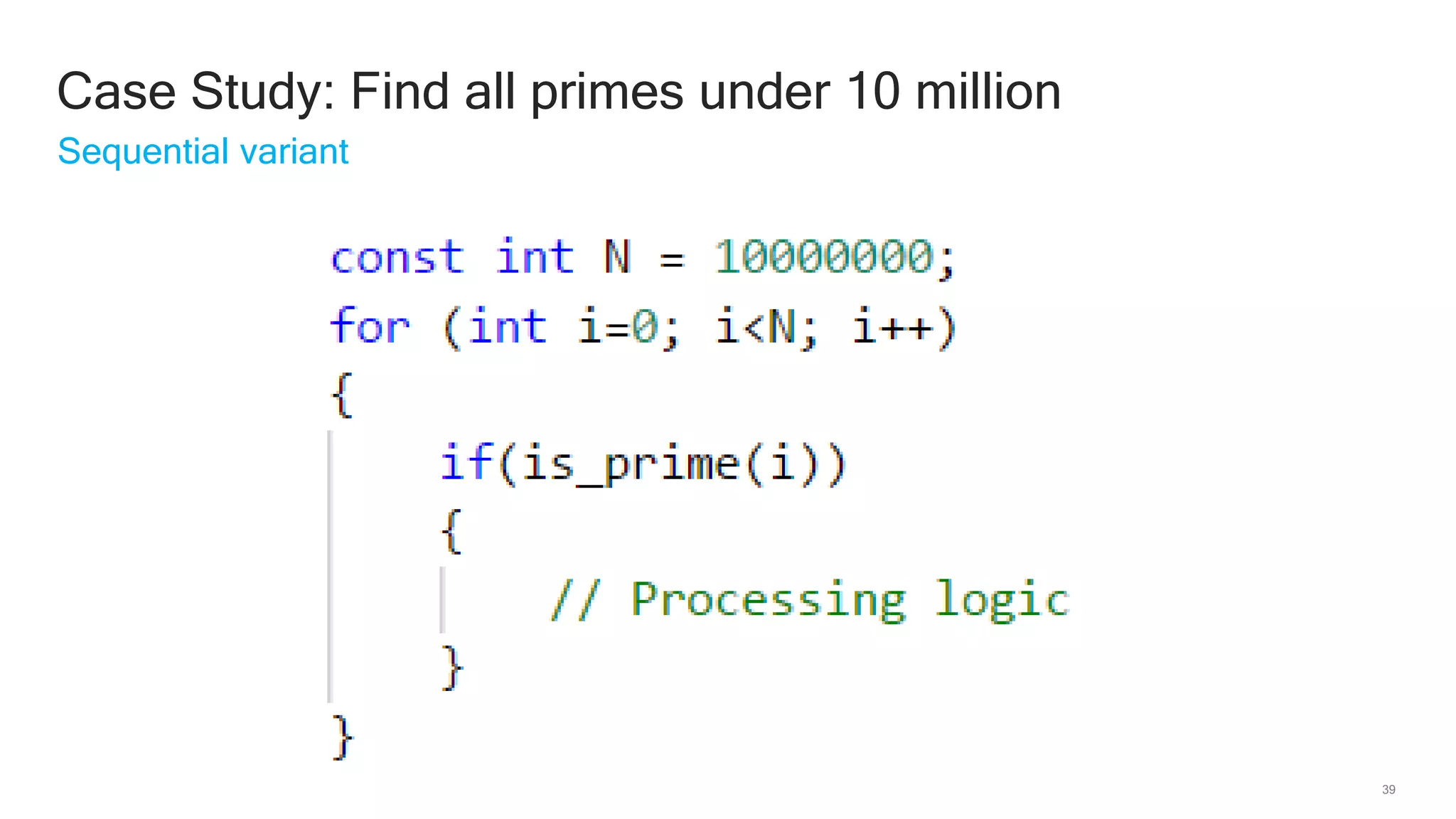
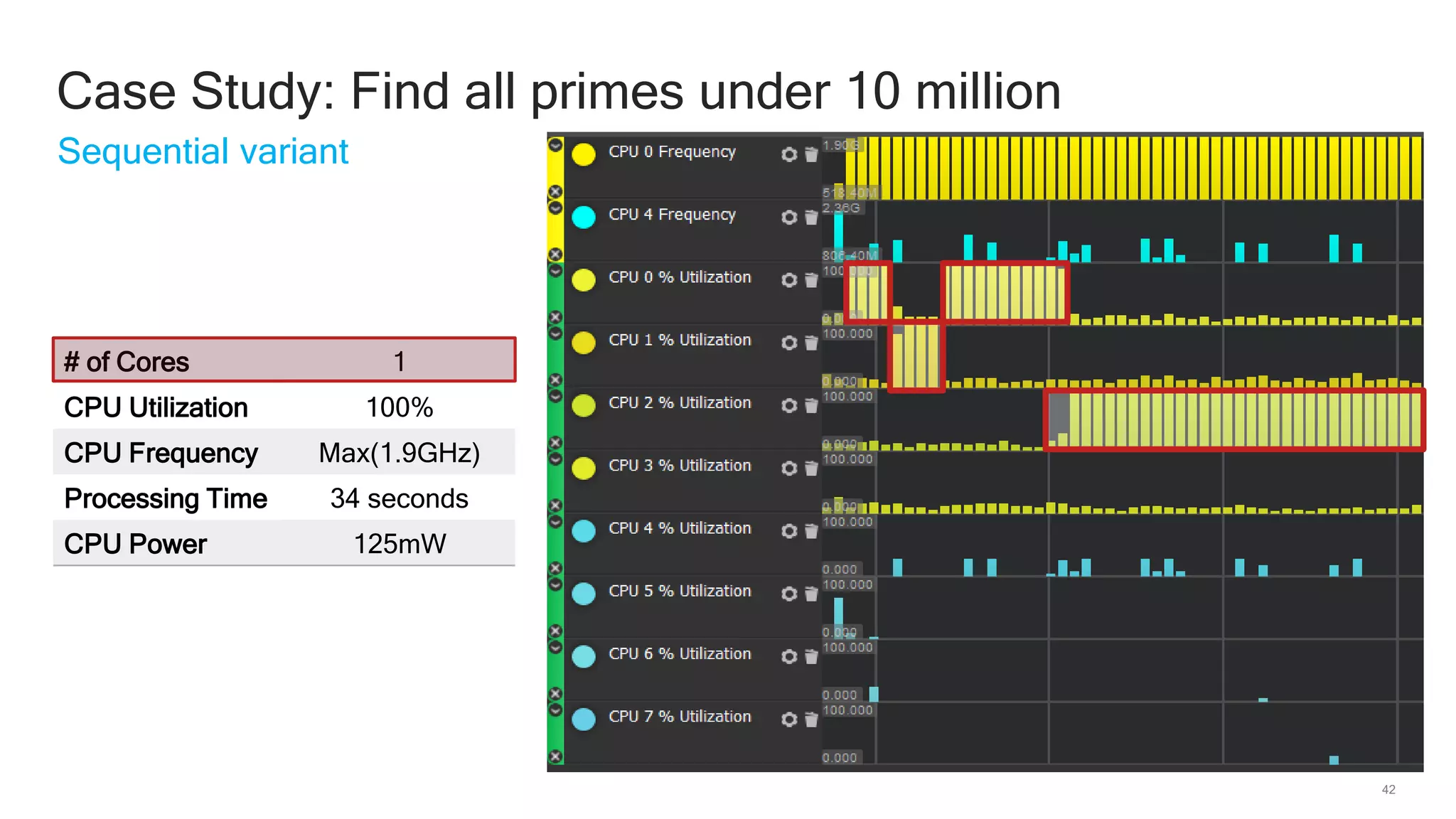
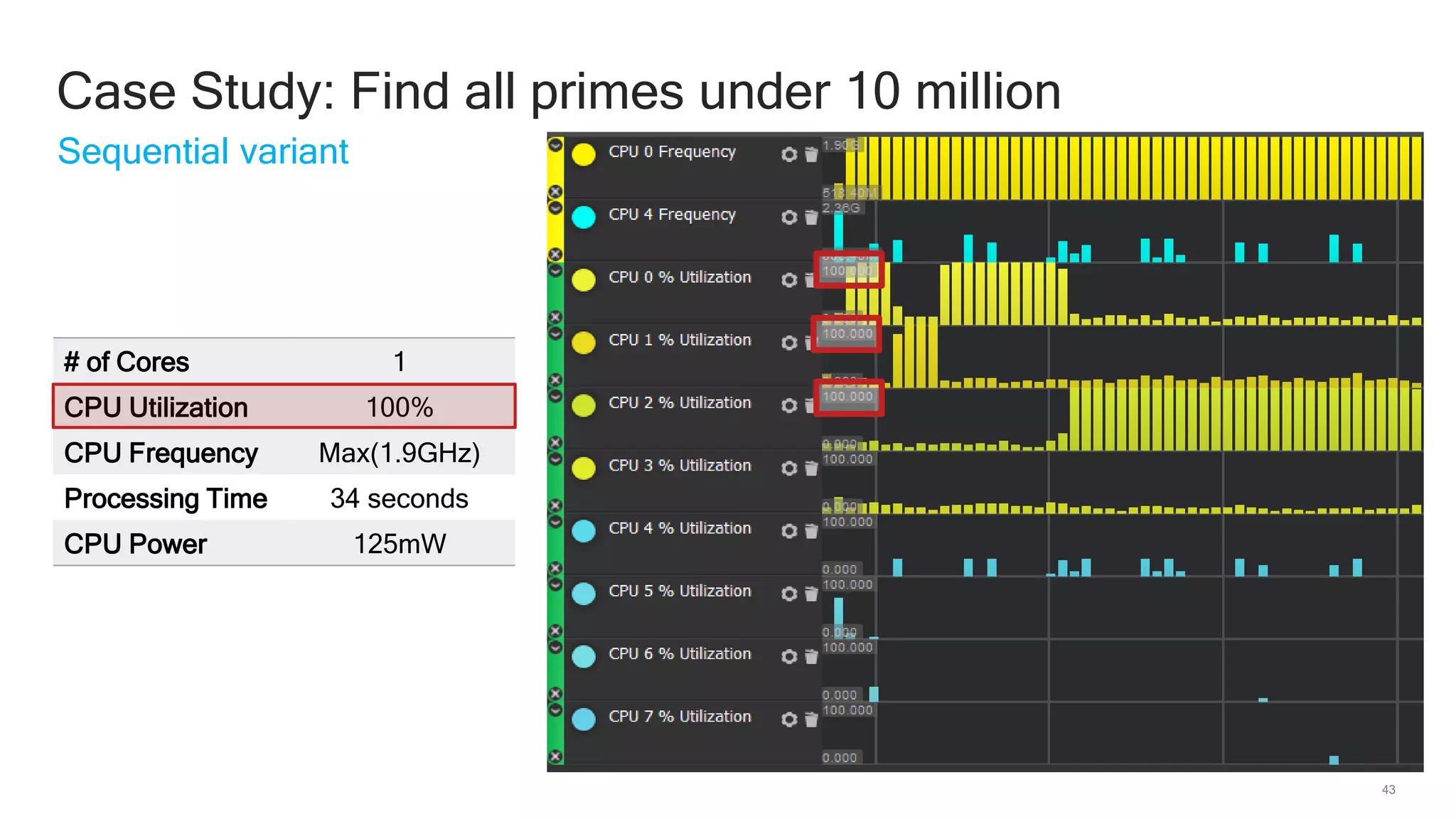
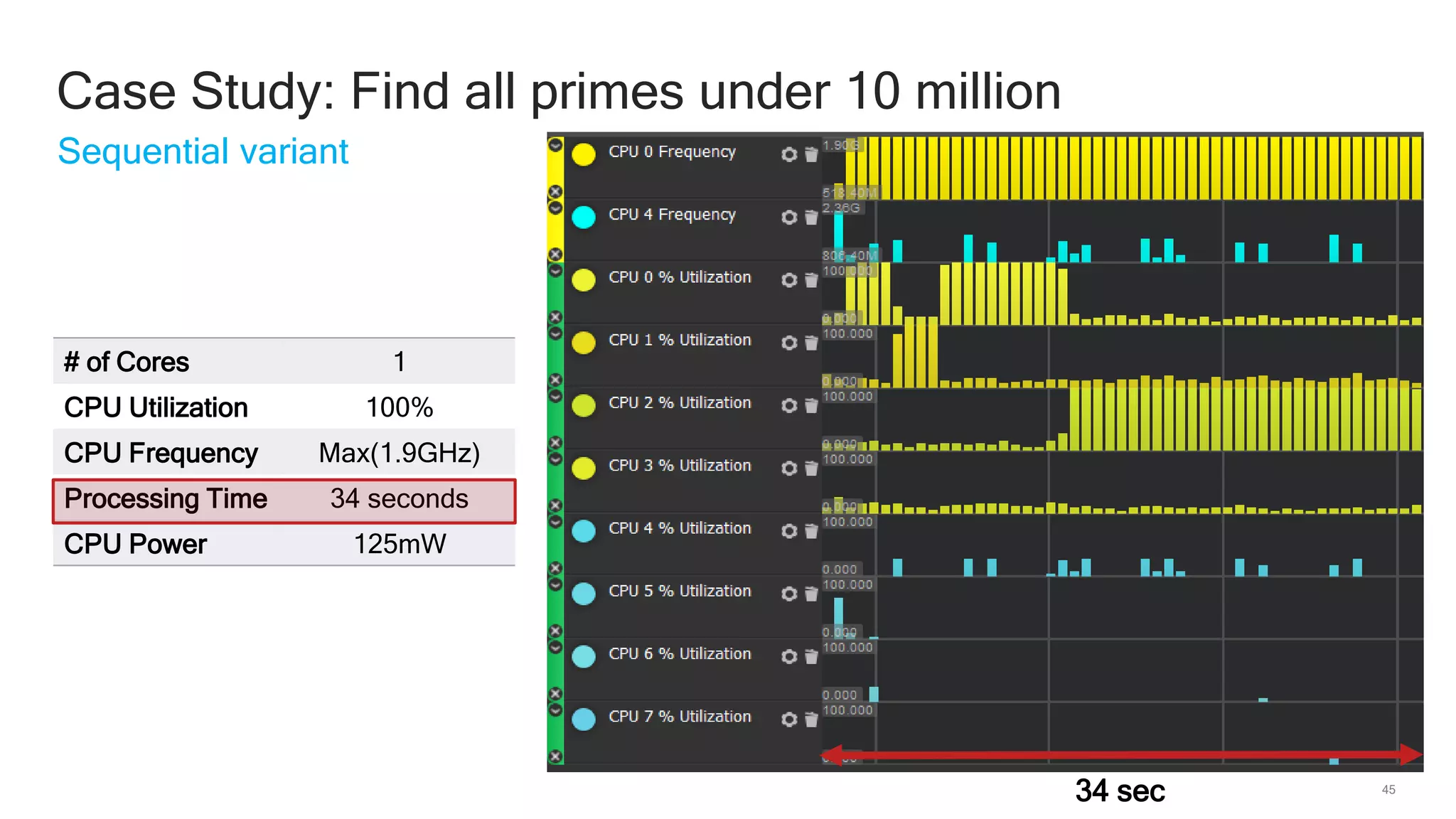
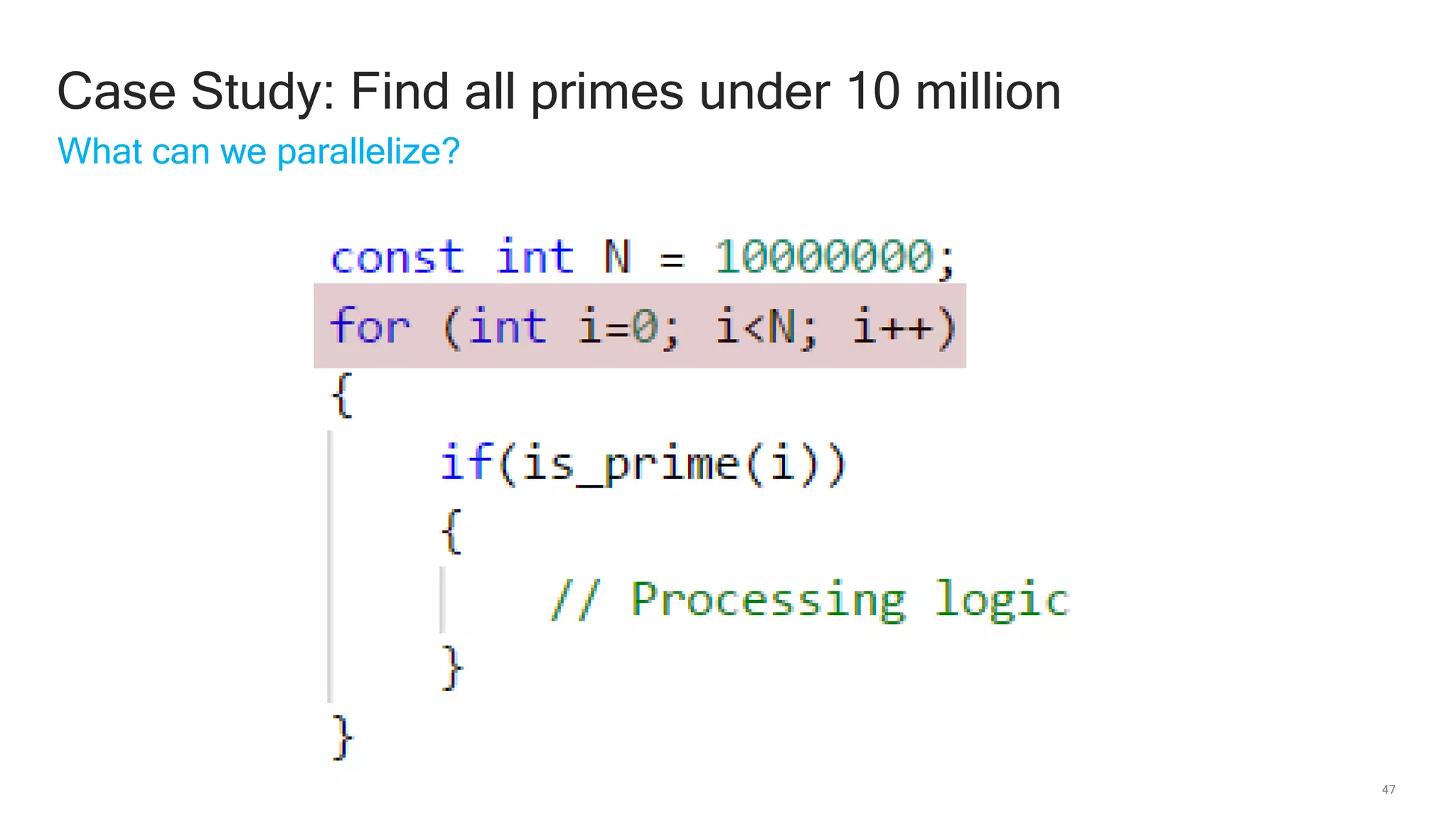
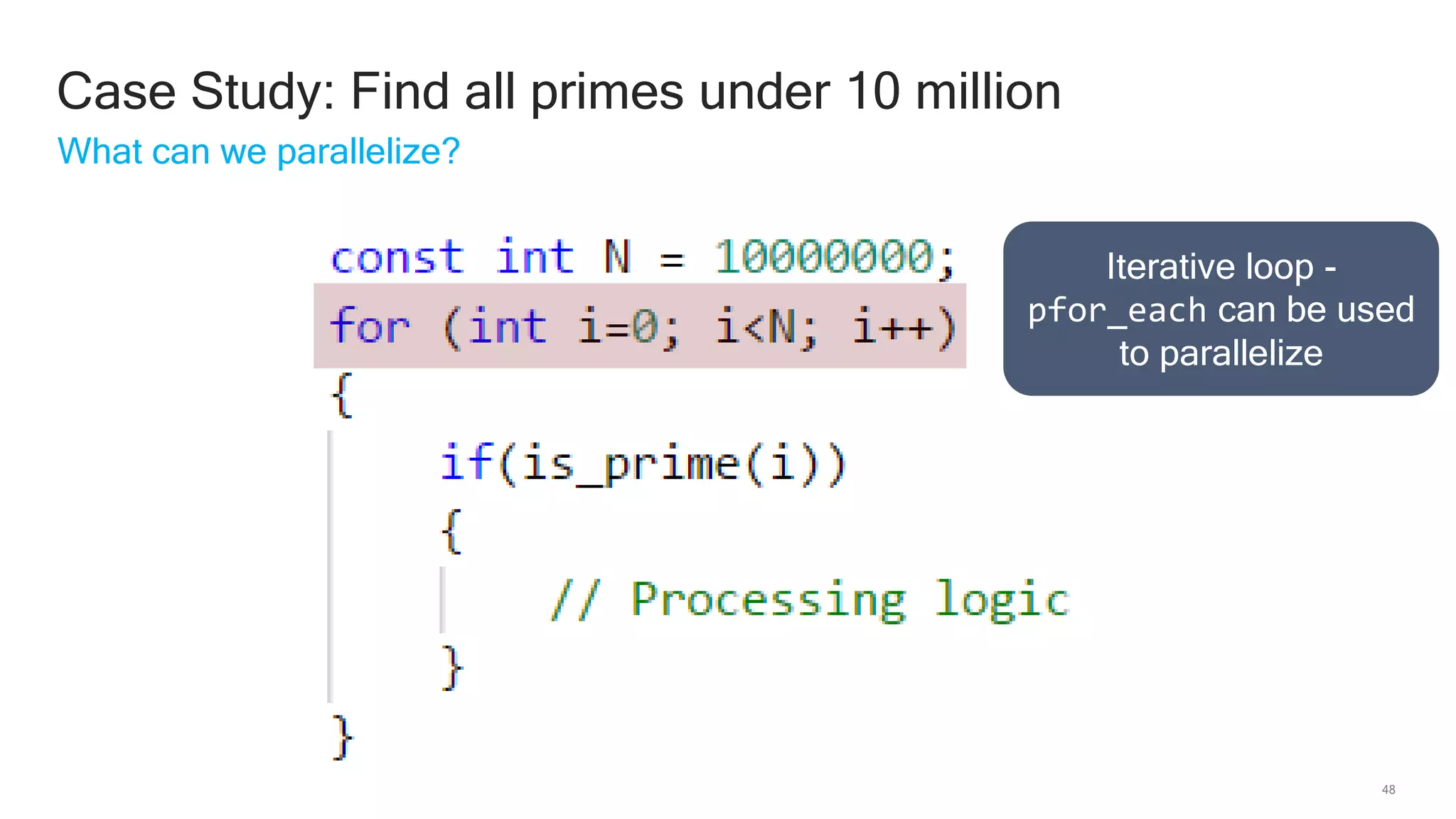
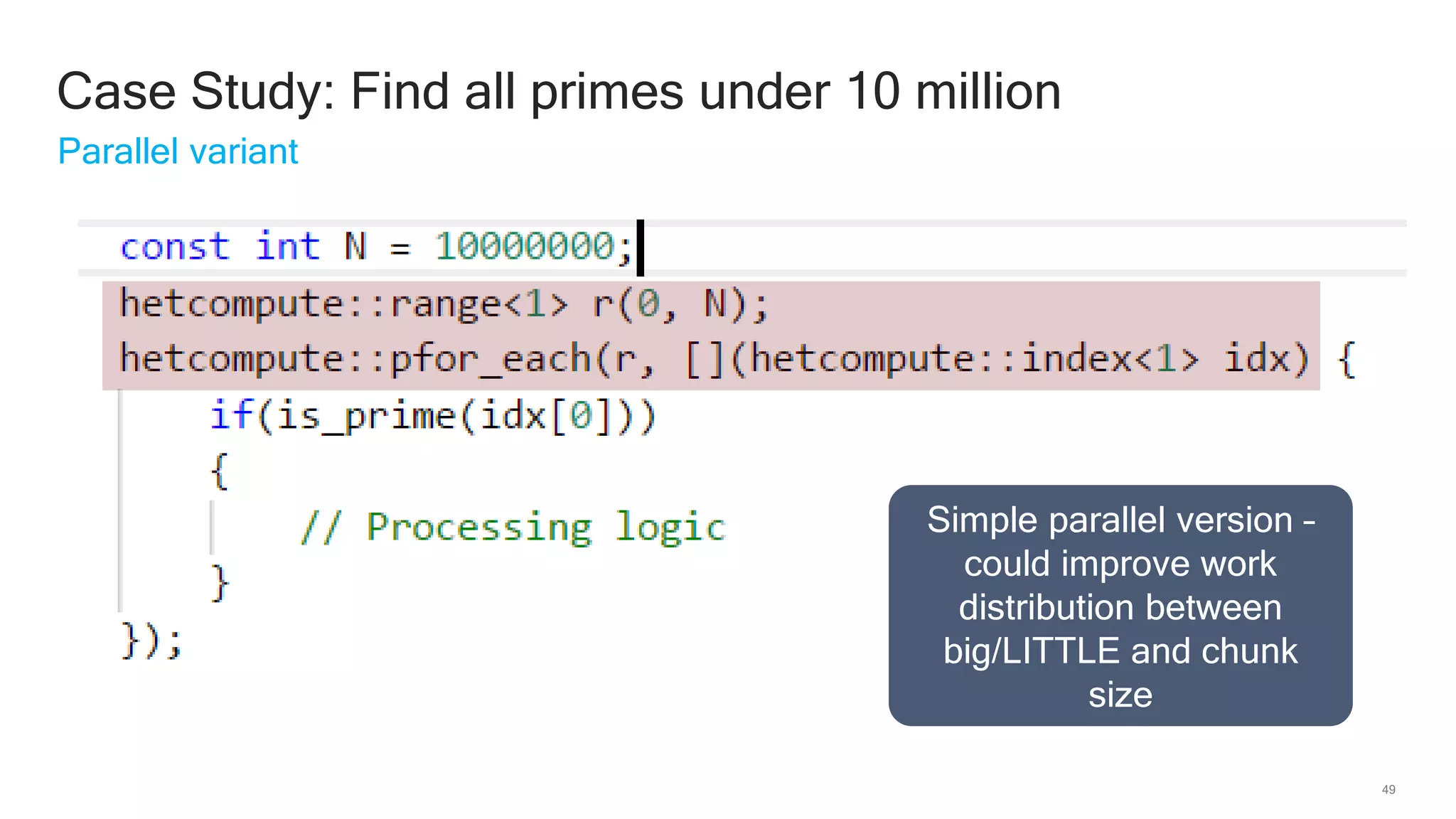
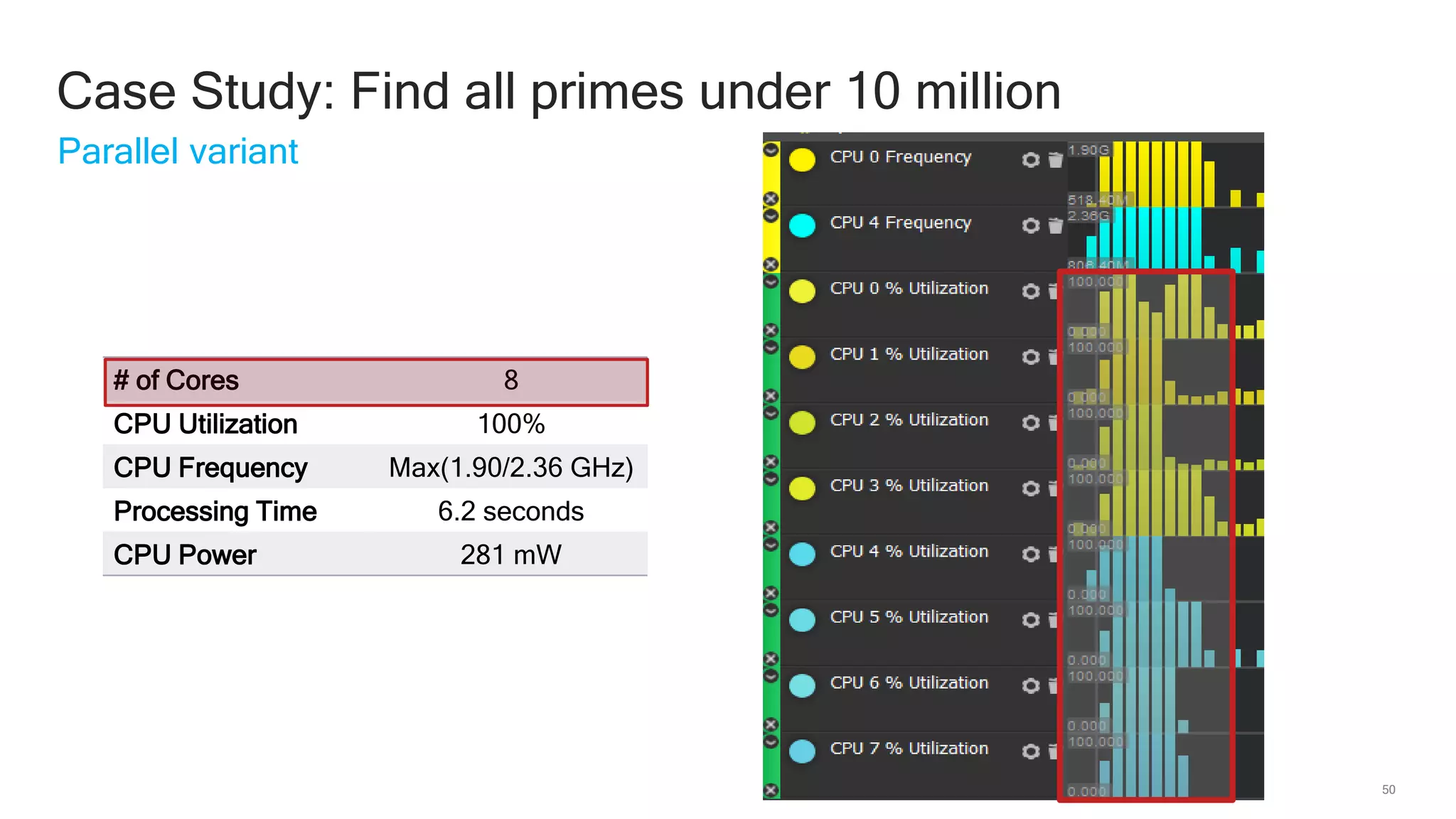
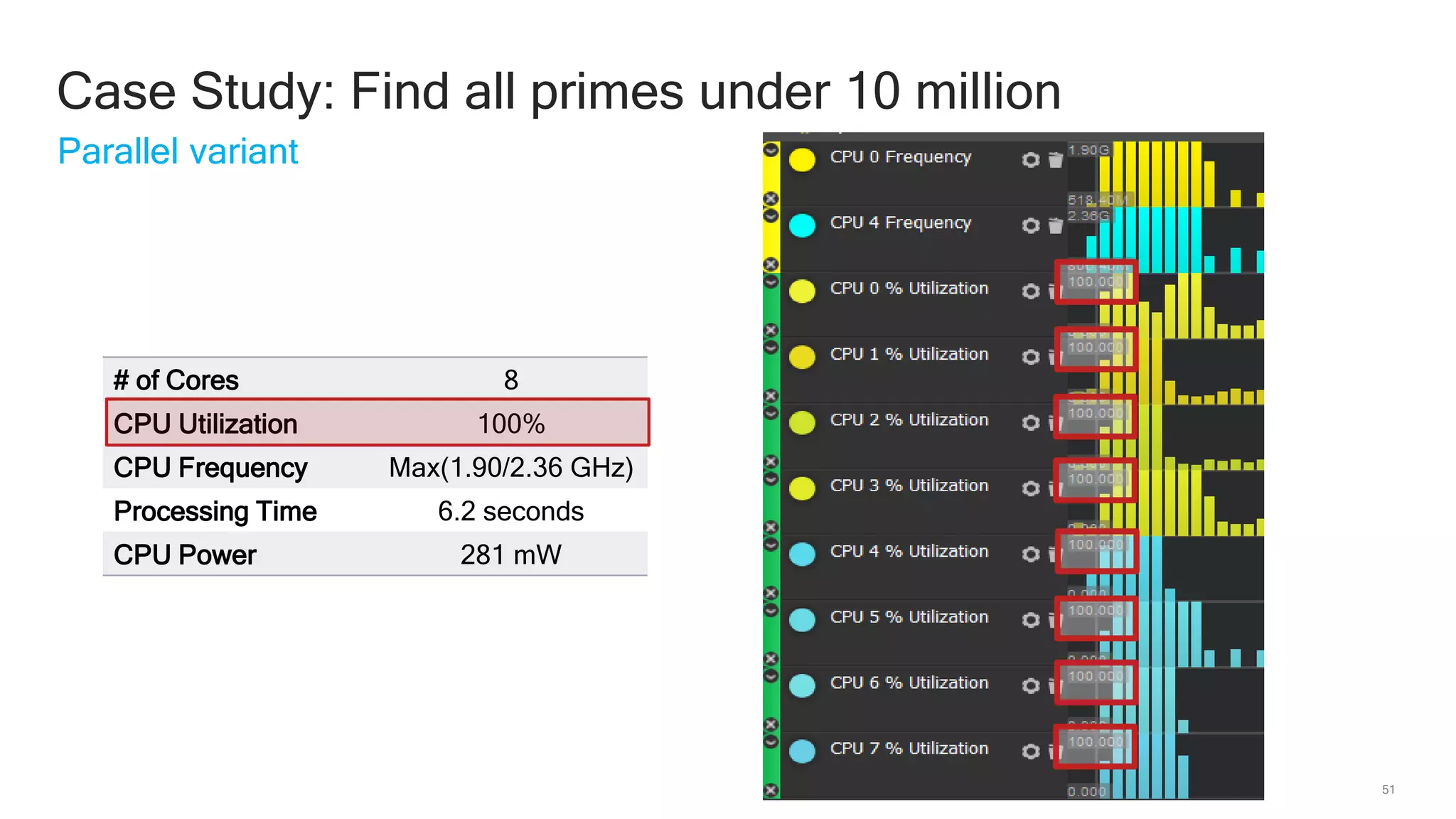
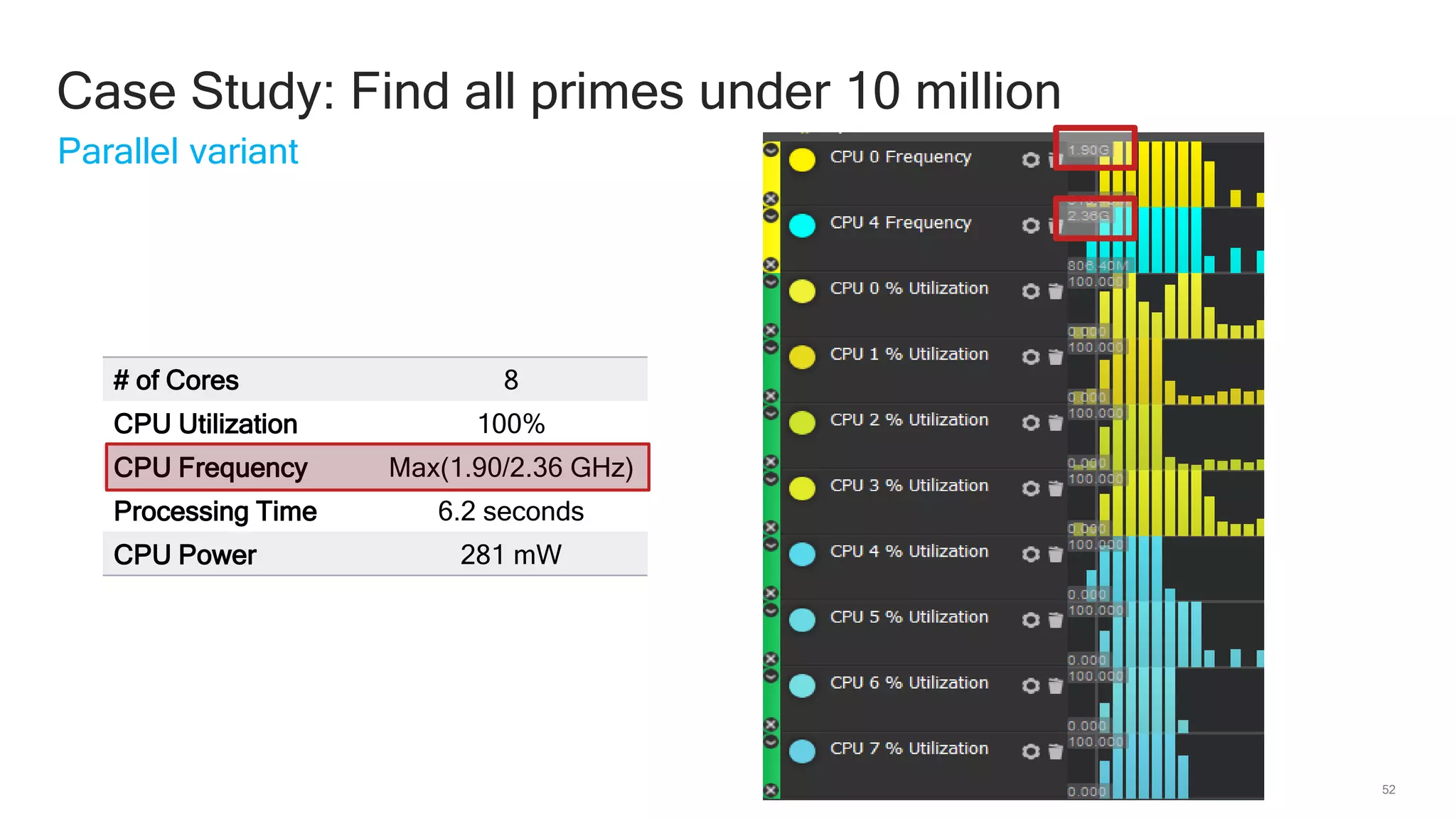
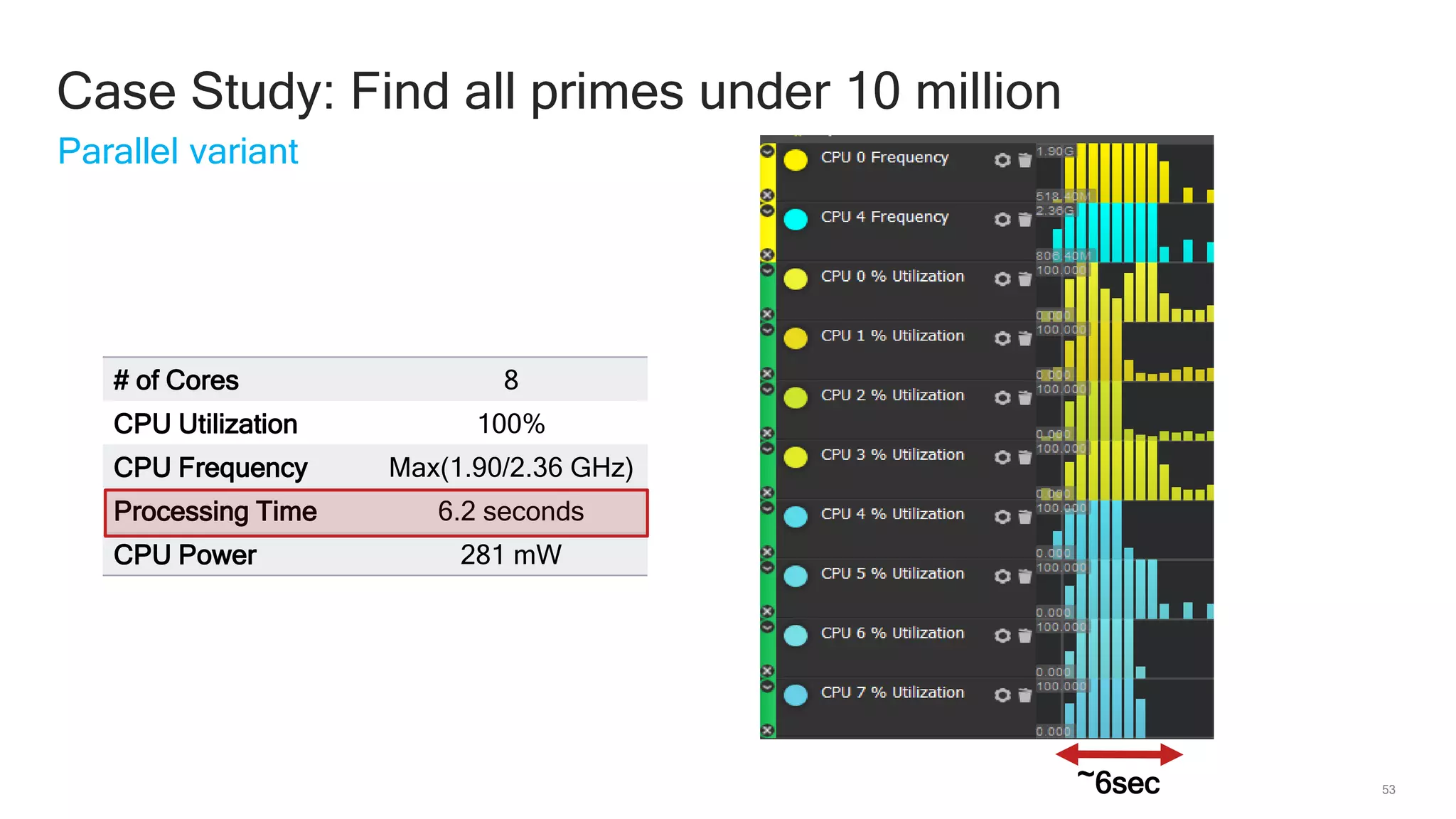
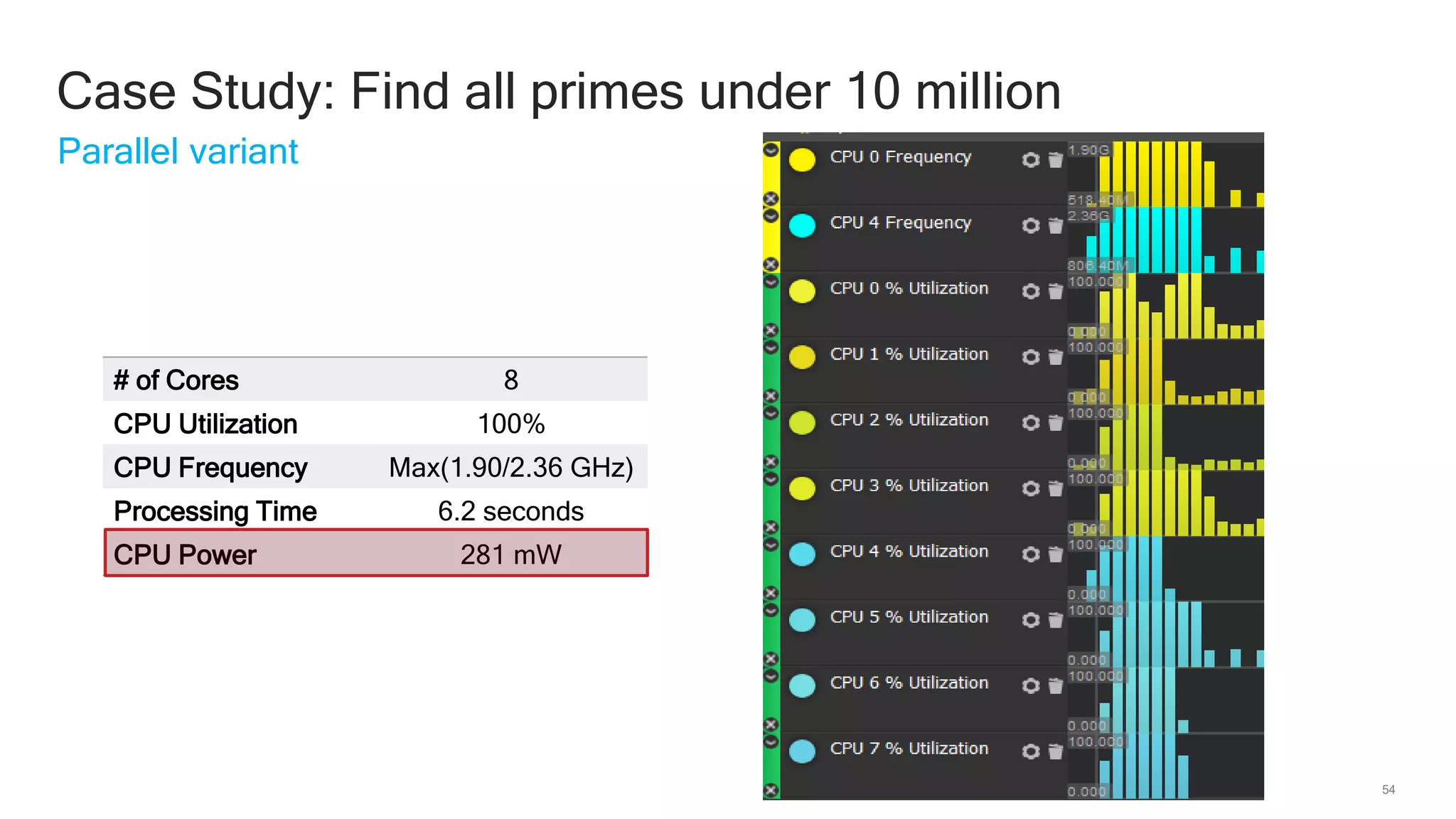
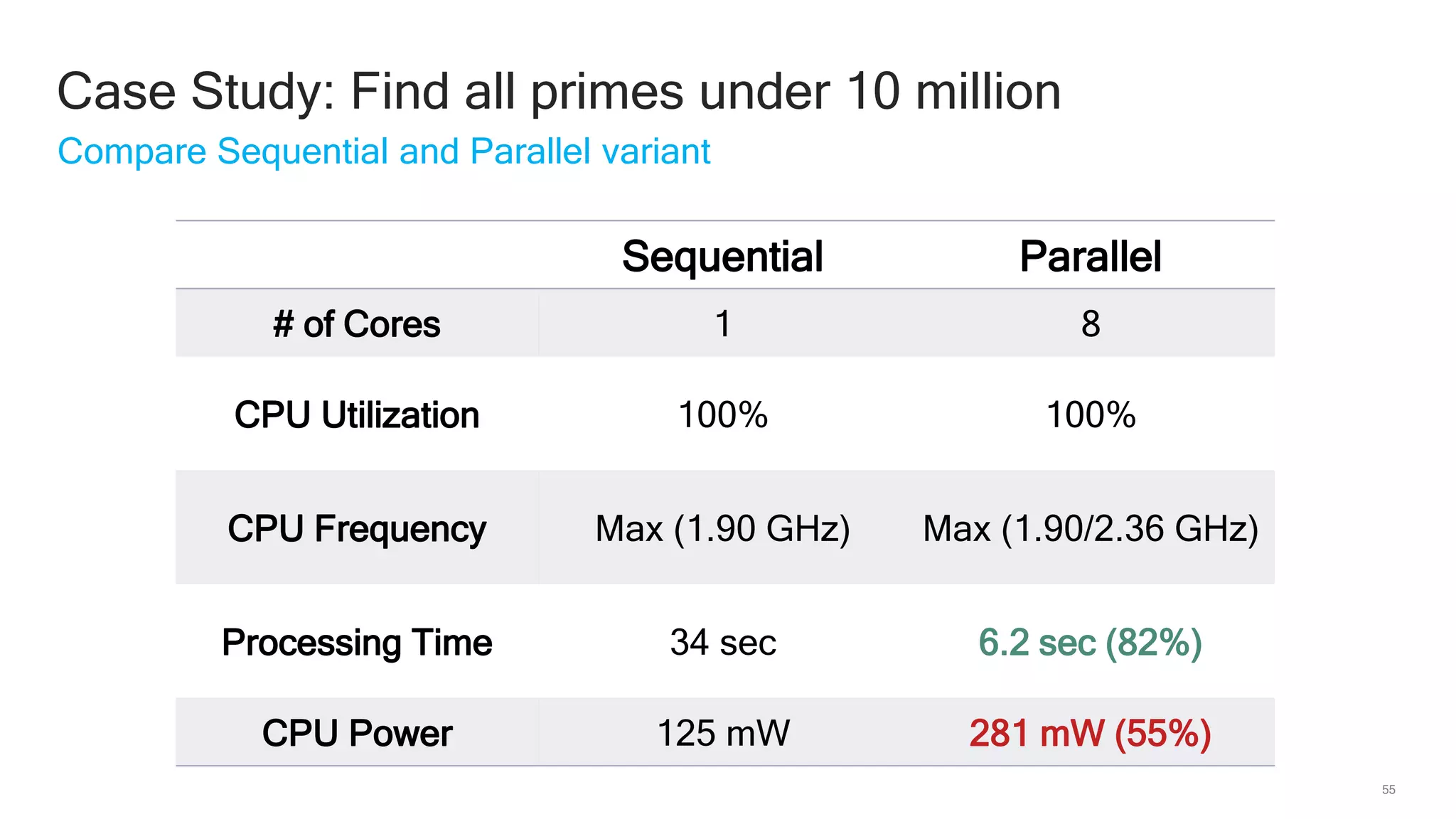
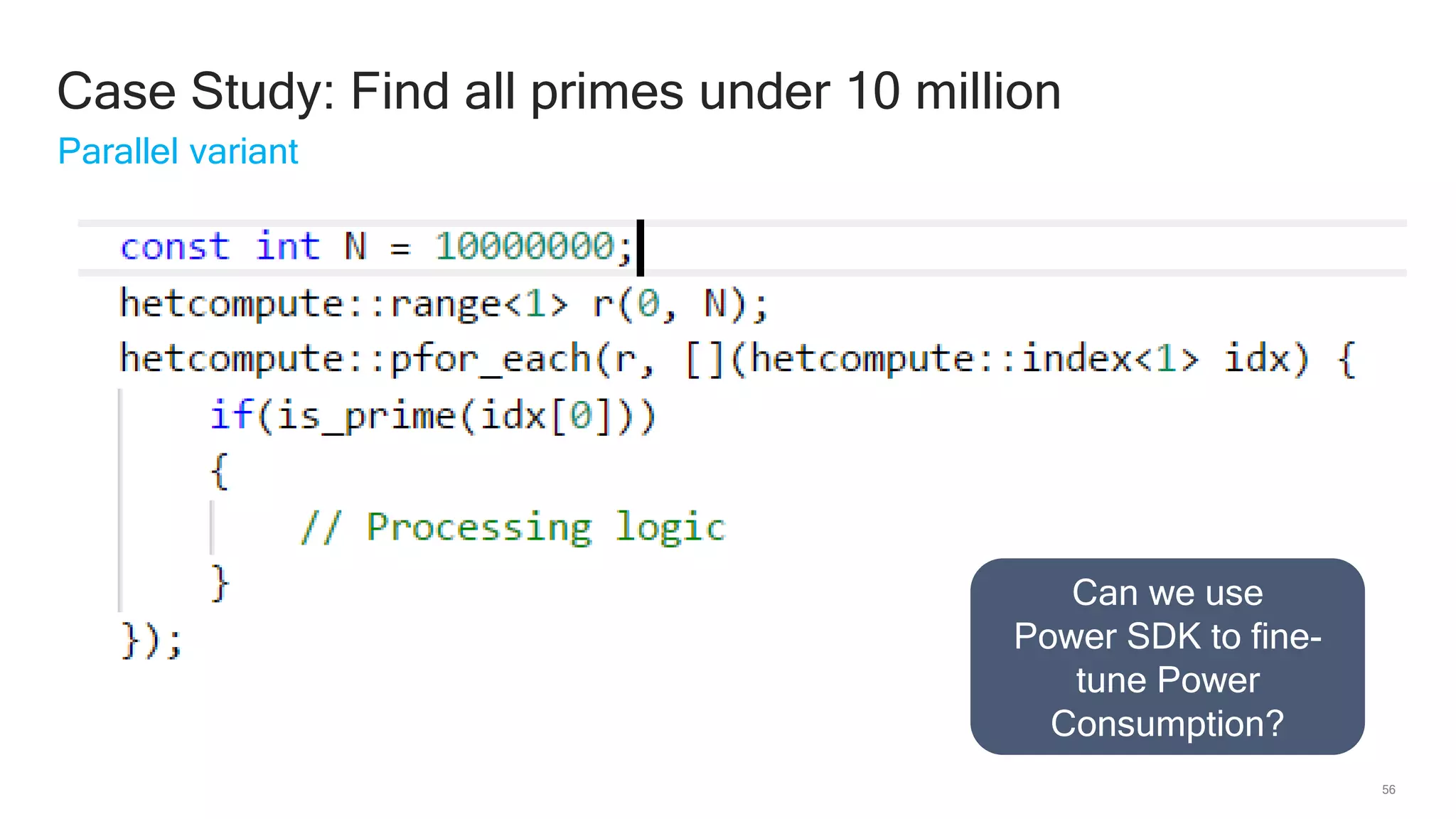
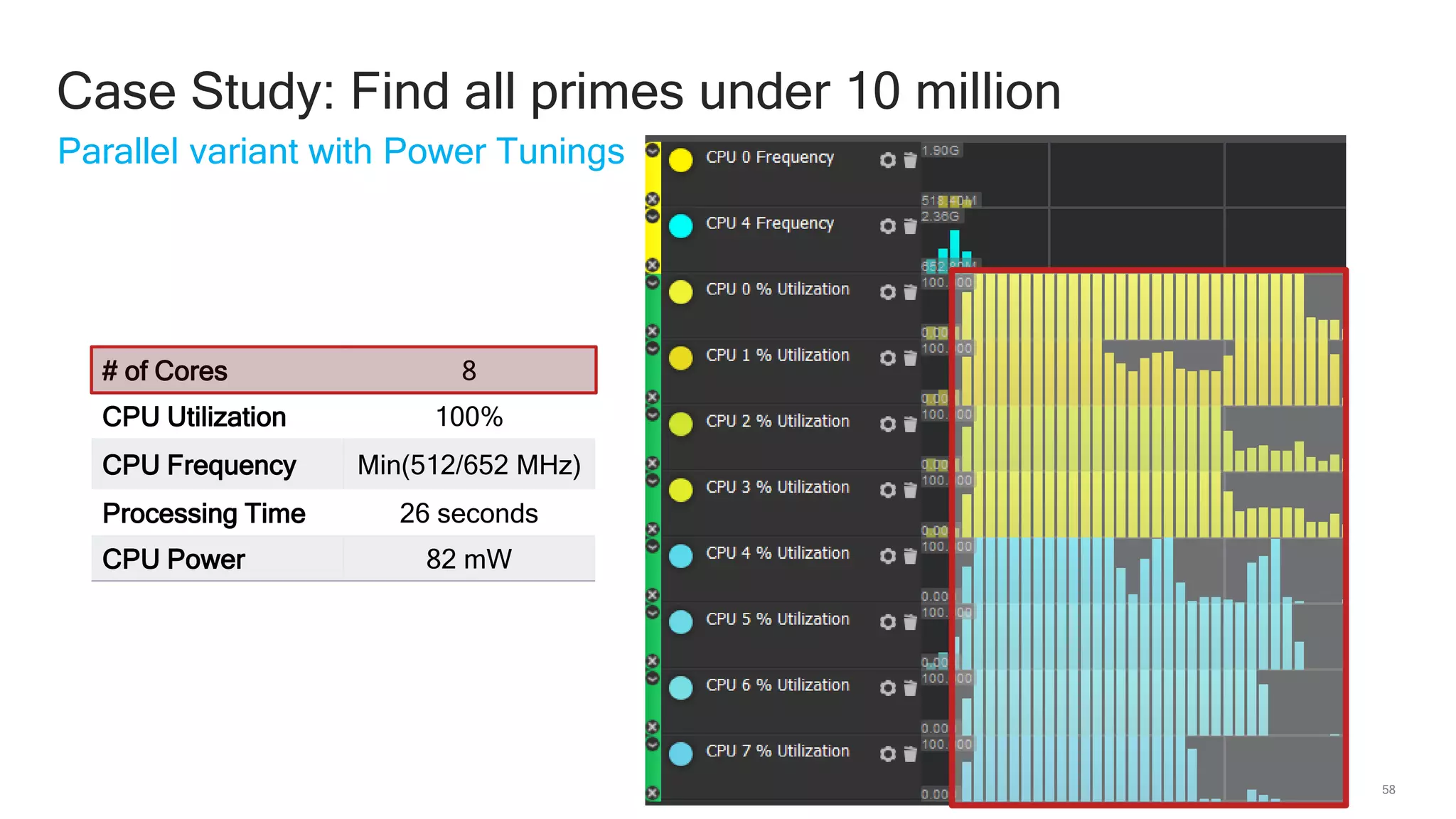
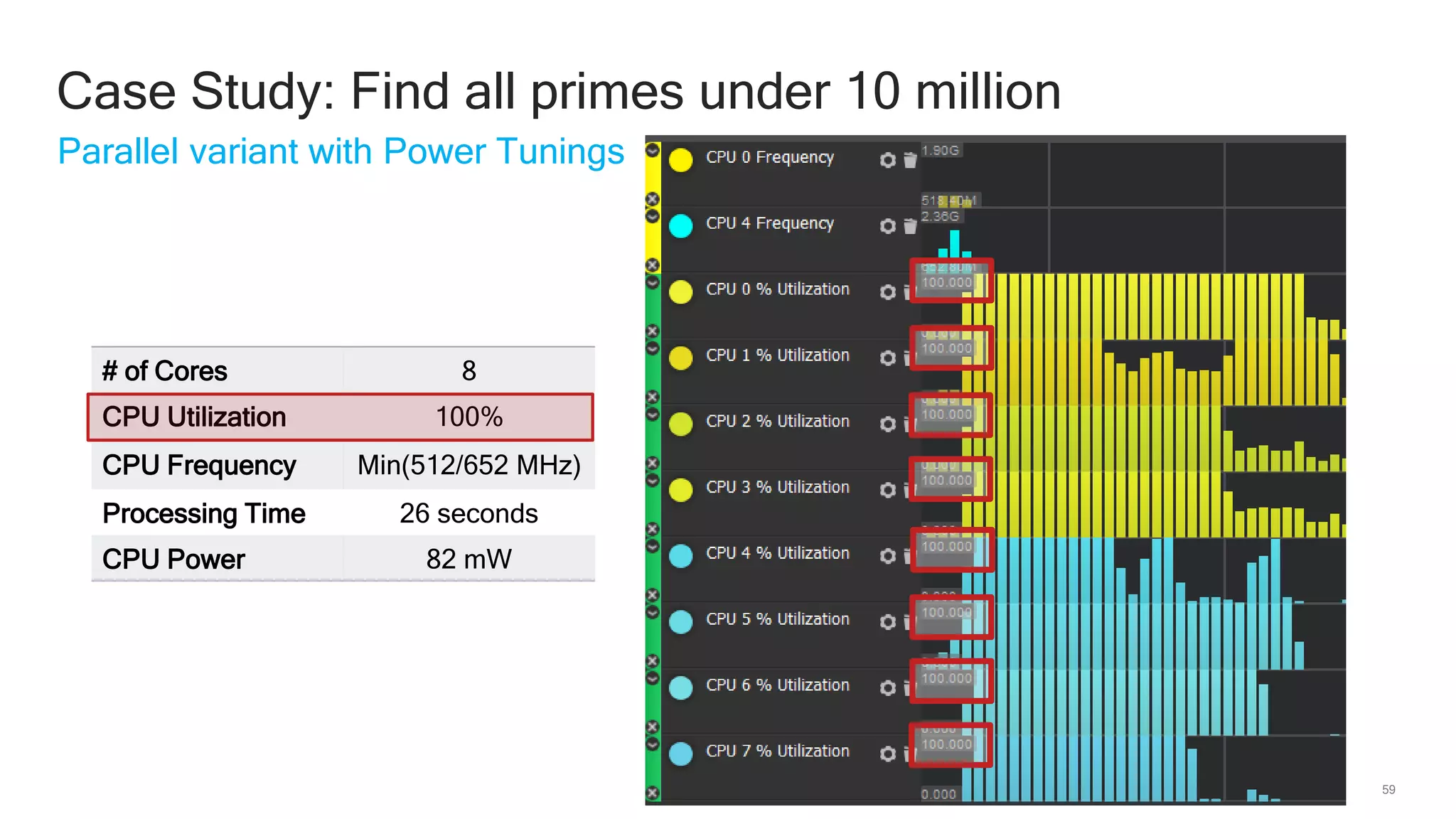
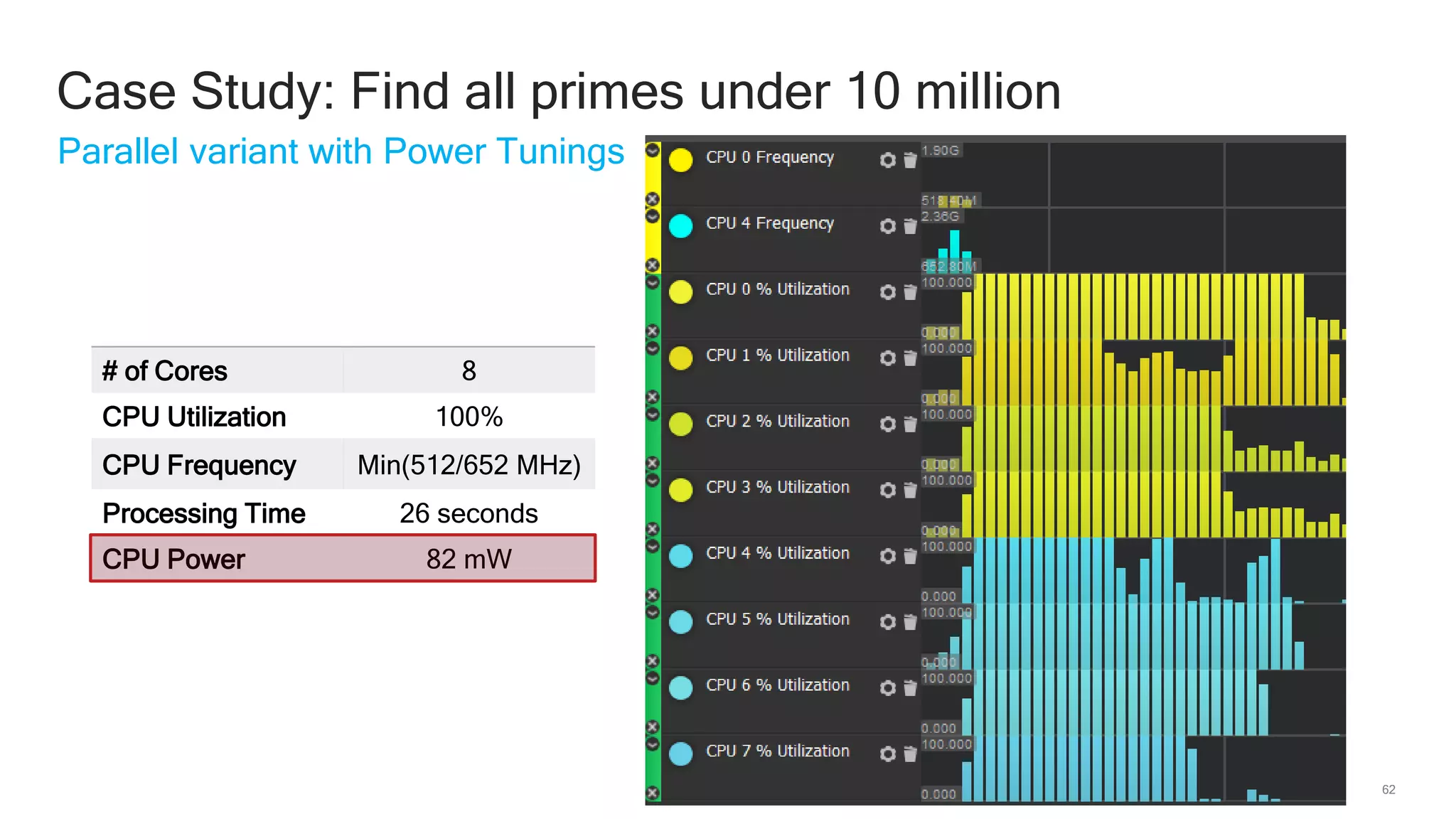
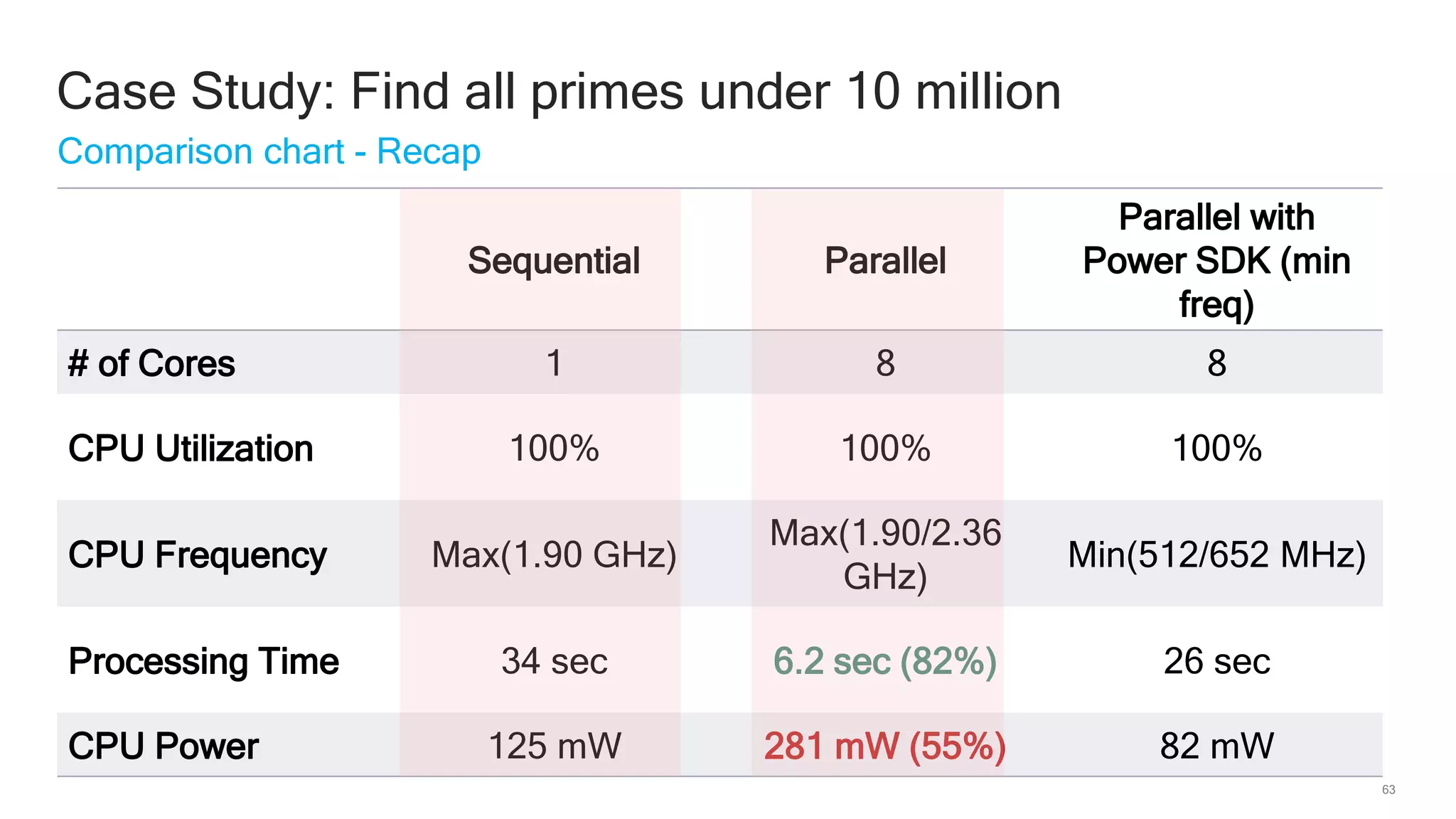
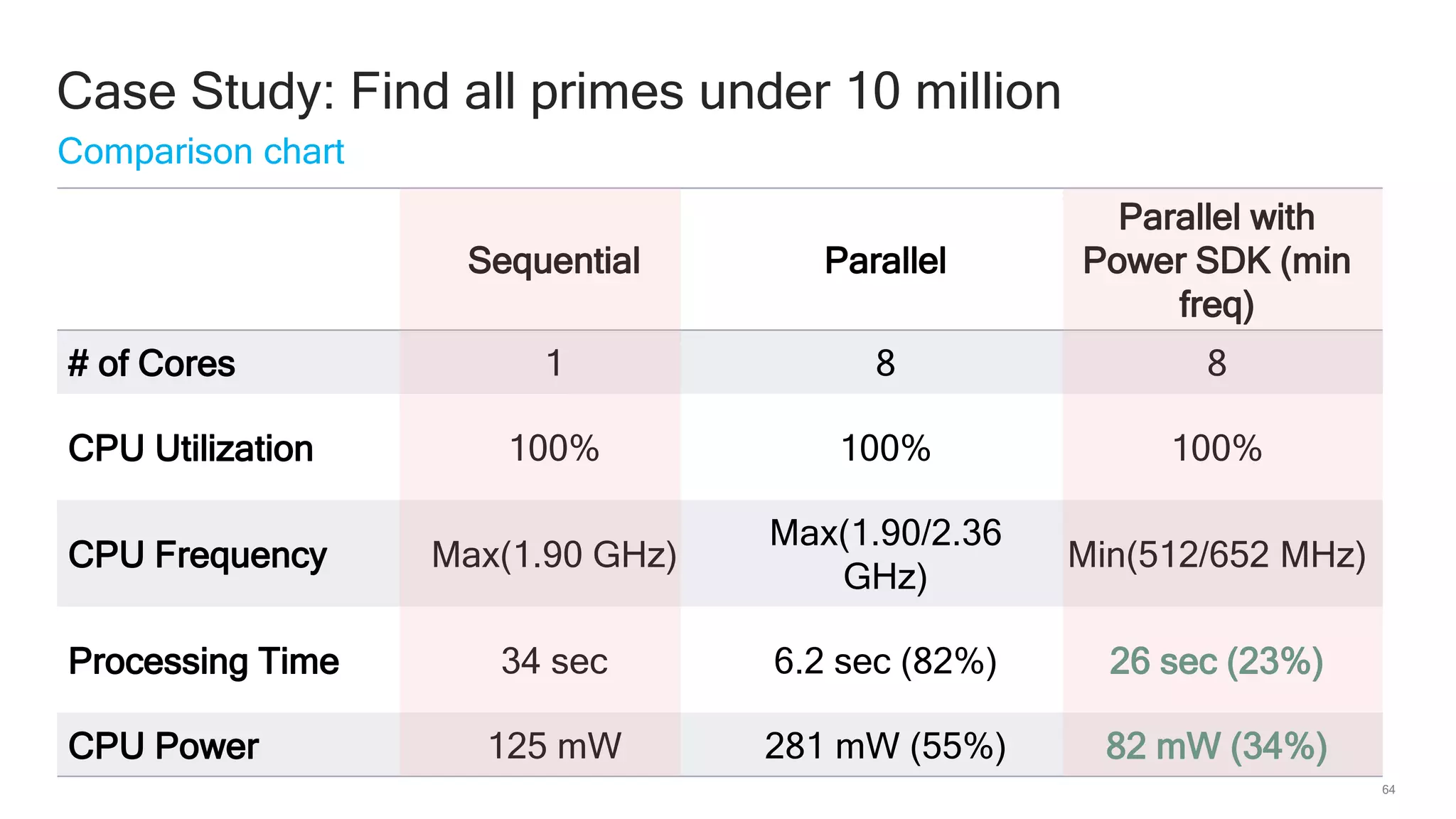
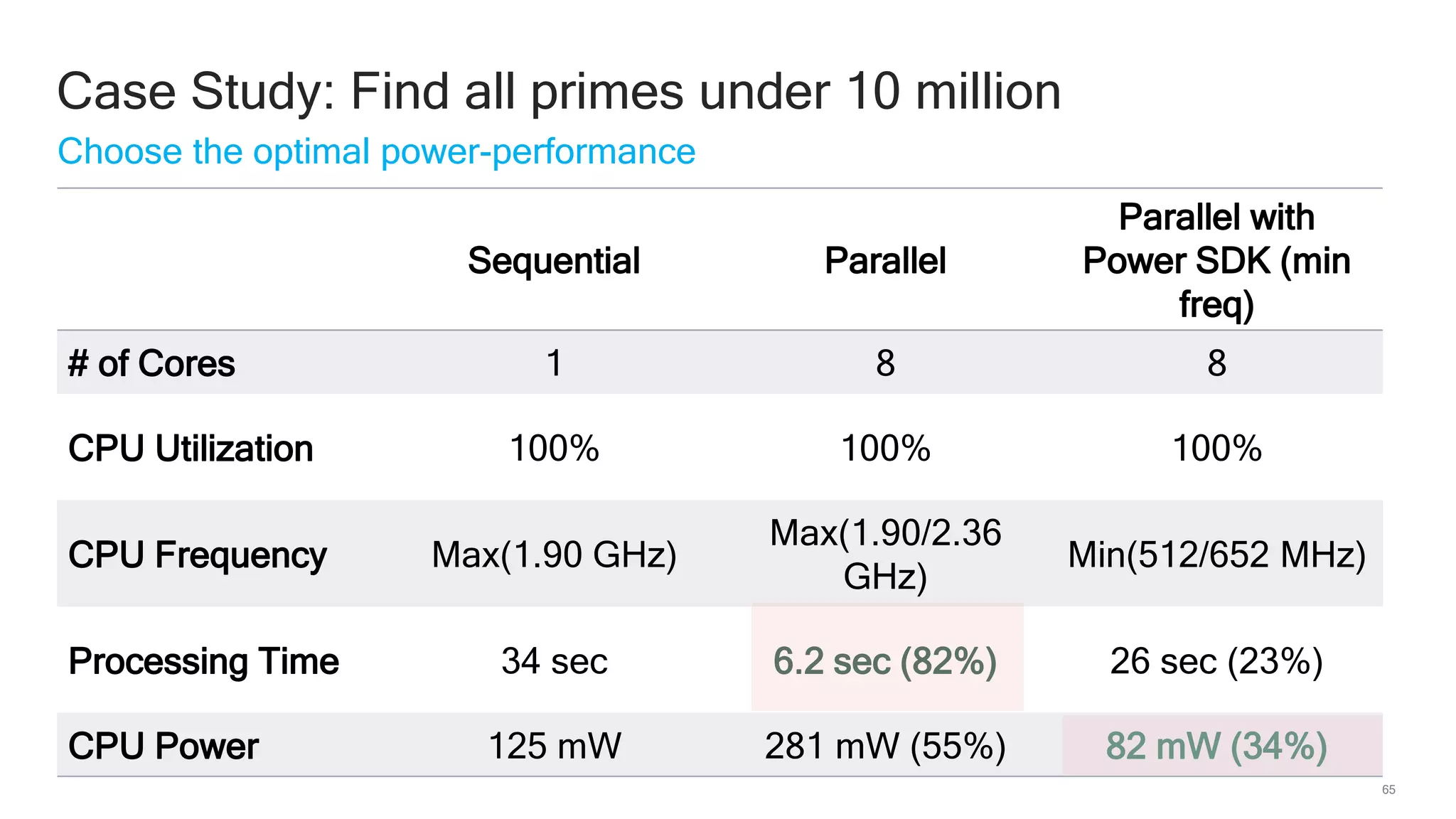
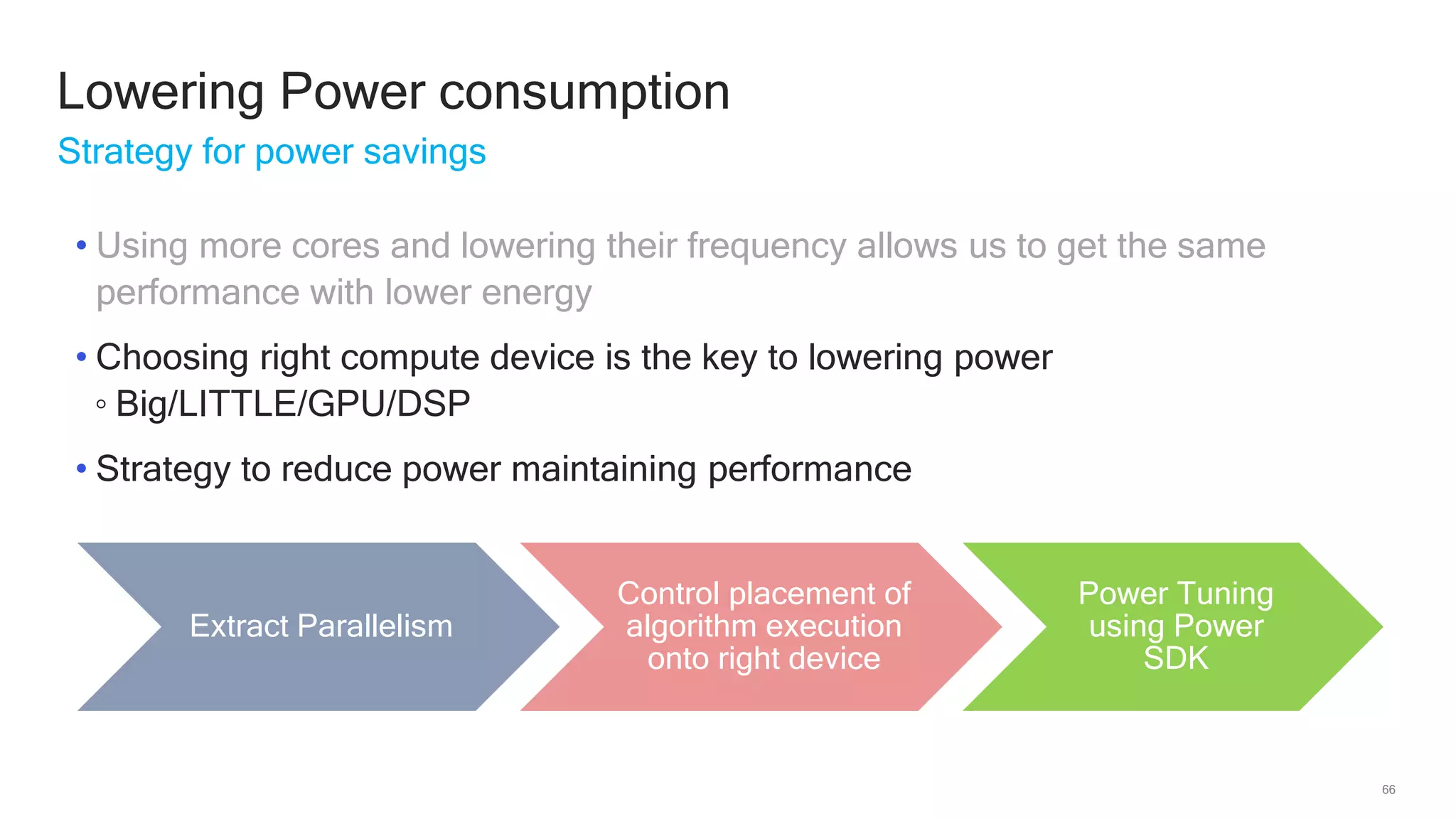
The document discusses Qualcomm's heterogeneous compute SDK for mobile applications that enables efficient task execution across CPU, GPU, and DSP while managing data effectively. It emphasizes patterns for parallel programming, task management, and power optimization techniques through a dedicated SDK, allowing developers to fine-tune performance and energy consumption. Case studies demonstrate how utilizing these tools can significantly improve processing efficiency and reduce power usage.