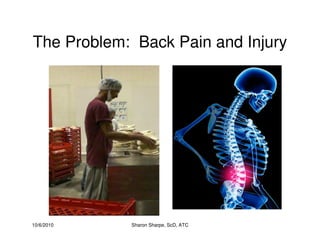
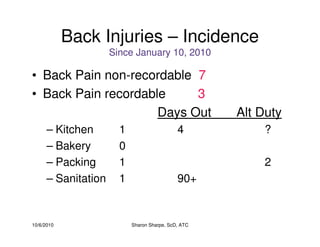
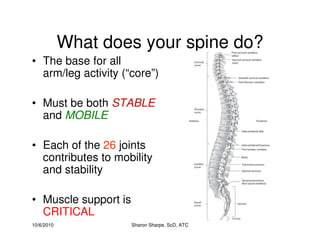
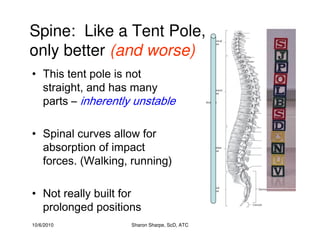
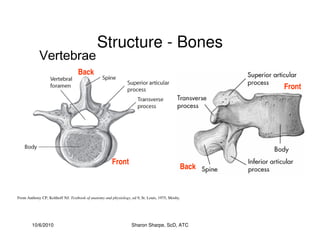
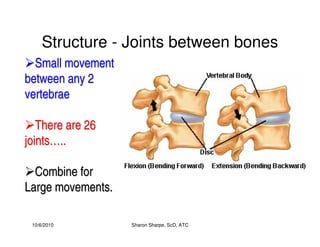
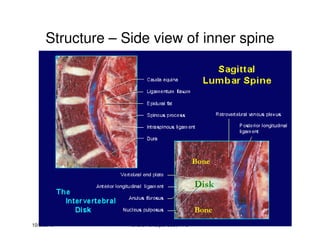
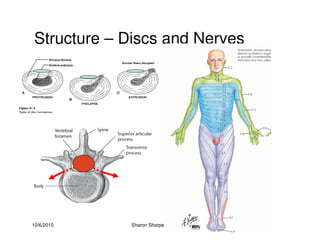
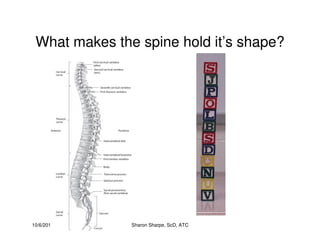
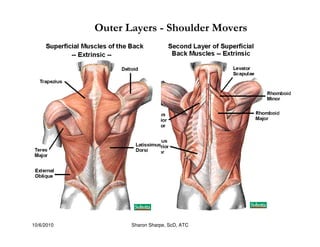
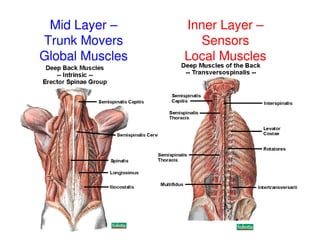
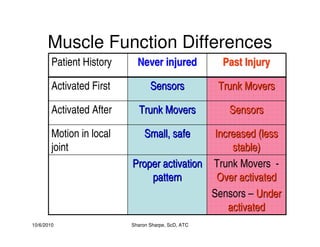
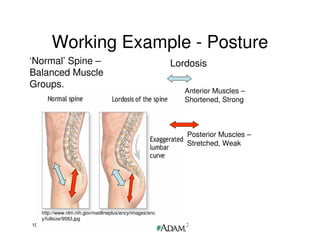
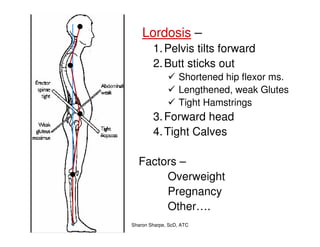
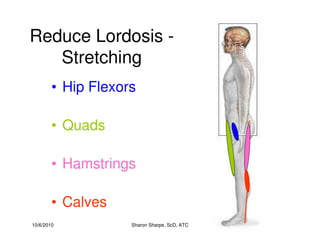
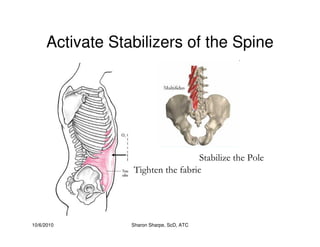
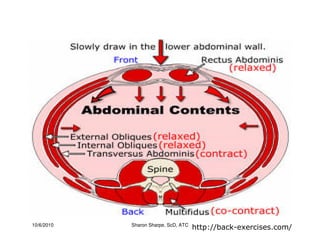
The document discusses targeted programs to reduce back injuries. It notes that back pain is a problem at a workplace and outlines various causal factors like employee ergonomic errors, prolonged positioning, and sudden movements. The document summarizes spine anatomy including bones, joints, discs, and muscles. It emphasizes the importance of both stability and mobility in the spine. The document recommends a targeted exercise program that includes stretching tight muscles, strengthening weak muscles, and learning to activate local spinal stabilizer muscles before larger trunk movers to help reduce the incidence of back pain and injuries. It discusses resource needs for implementing such a program.