Embed presentation
Download to read offline







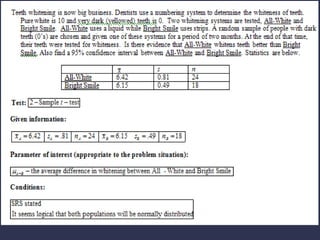

This document outlines the steps for conducting a hypothesis test comparing the means of two independent samples. The test assumes simple random sampling, independent samples that are much larger than the sample sizes, and approximately normally distributed sampling distributions. The steps are: 1) state the null and alternative hypotheses, 2) choose a two-sample t-test analysis, 3) calculate the t-statistic and p-value, 4) compare the p-value to the significance level and reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis.








