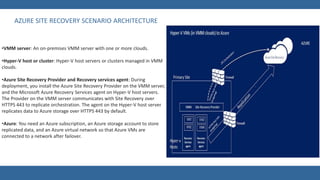
Azure Site Recovery allows users to replicate on-premises virtual machines and physical servers to the cloud (Azure) or a secondary datacenter to contribute to business continuity and disaster recovery strategies. It can be deployed through either the classic Azure portal or the new Azure portal, and supports replication of VMware VMs, Hyper-V VMs, and physical servers managed by System Center Virtual Machine Manager (VMM) to Azure. The process involves setting up Azure infrastructure like storage and networks, installing agents on-premises, configuring replication settings, and testing failovers to ensure successful disaster recovery capabilities.