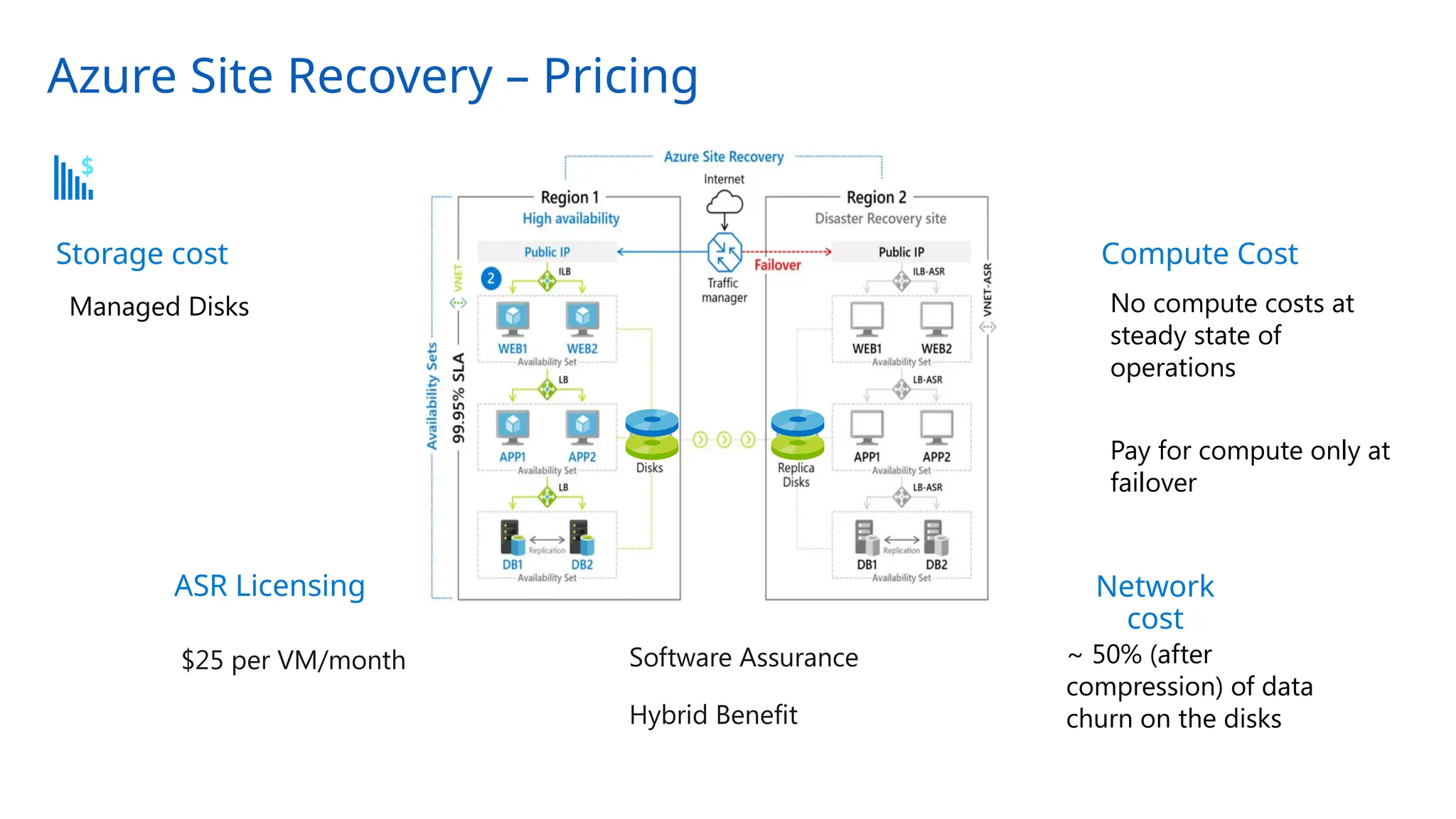
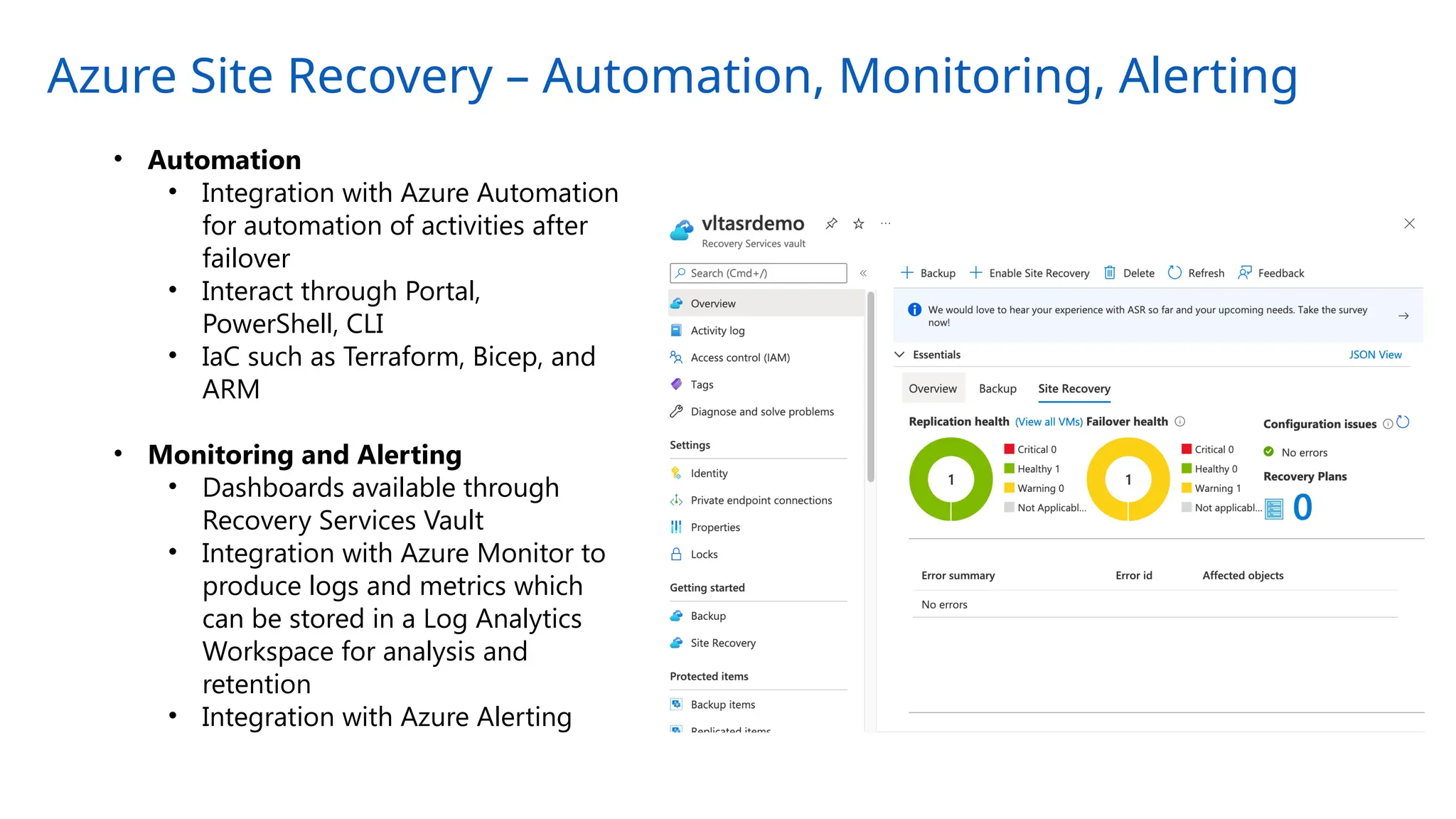
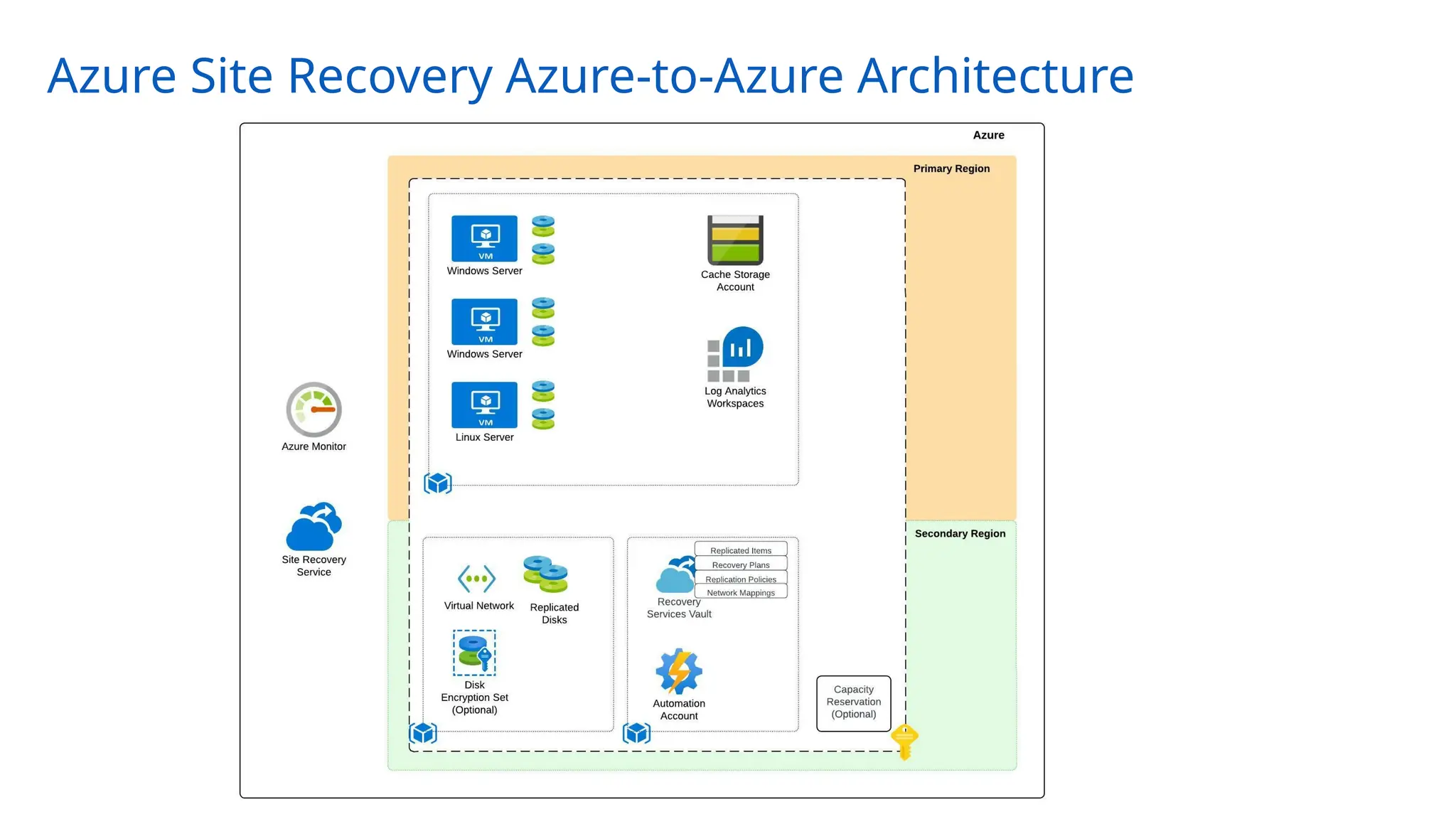
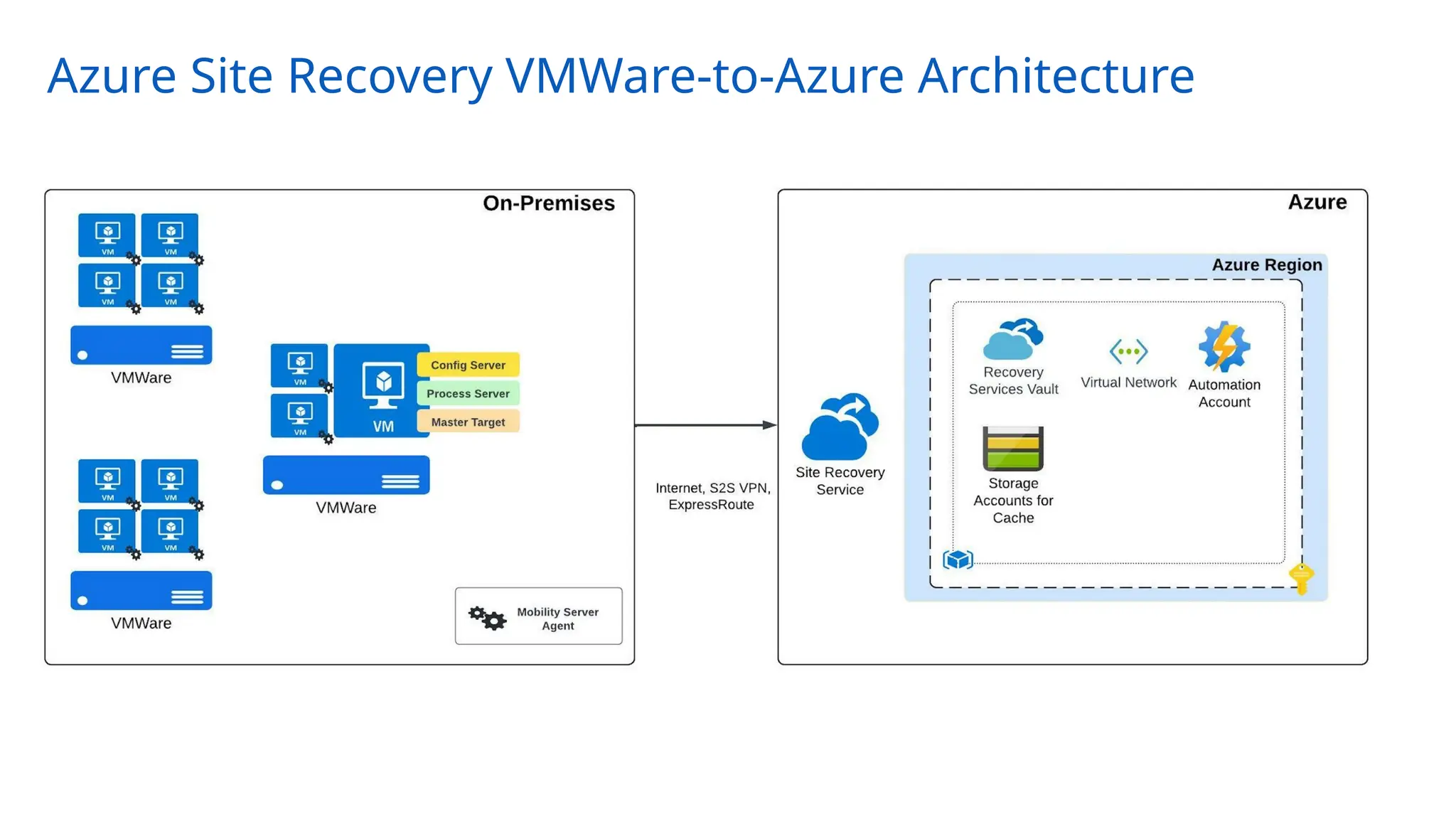
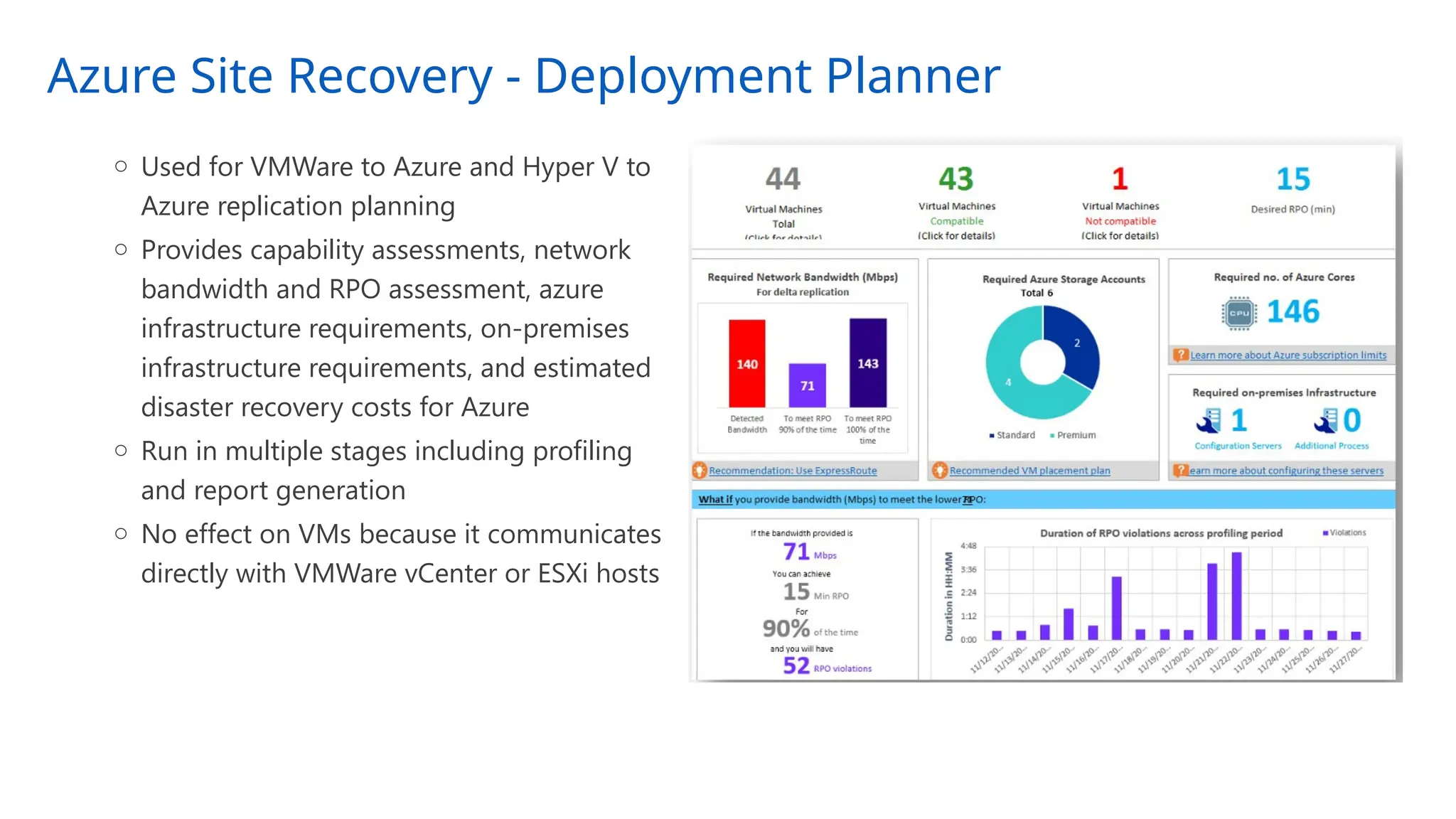
The document provides an overview of Azure Site Recovery, detailing its use cases, terminology, and key features. It explains concepts related to business continuity and disaster recovery, along with architectural components and pricing considerations. The document also includes best practices for deployment and automation, ensuring effective planning and implementation for users seeking to leverage Azure Site Recovery.