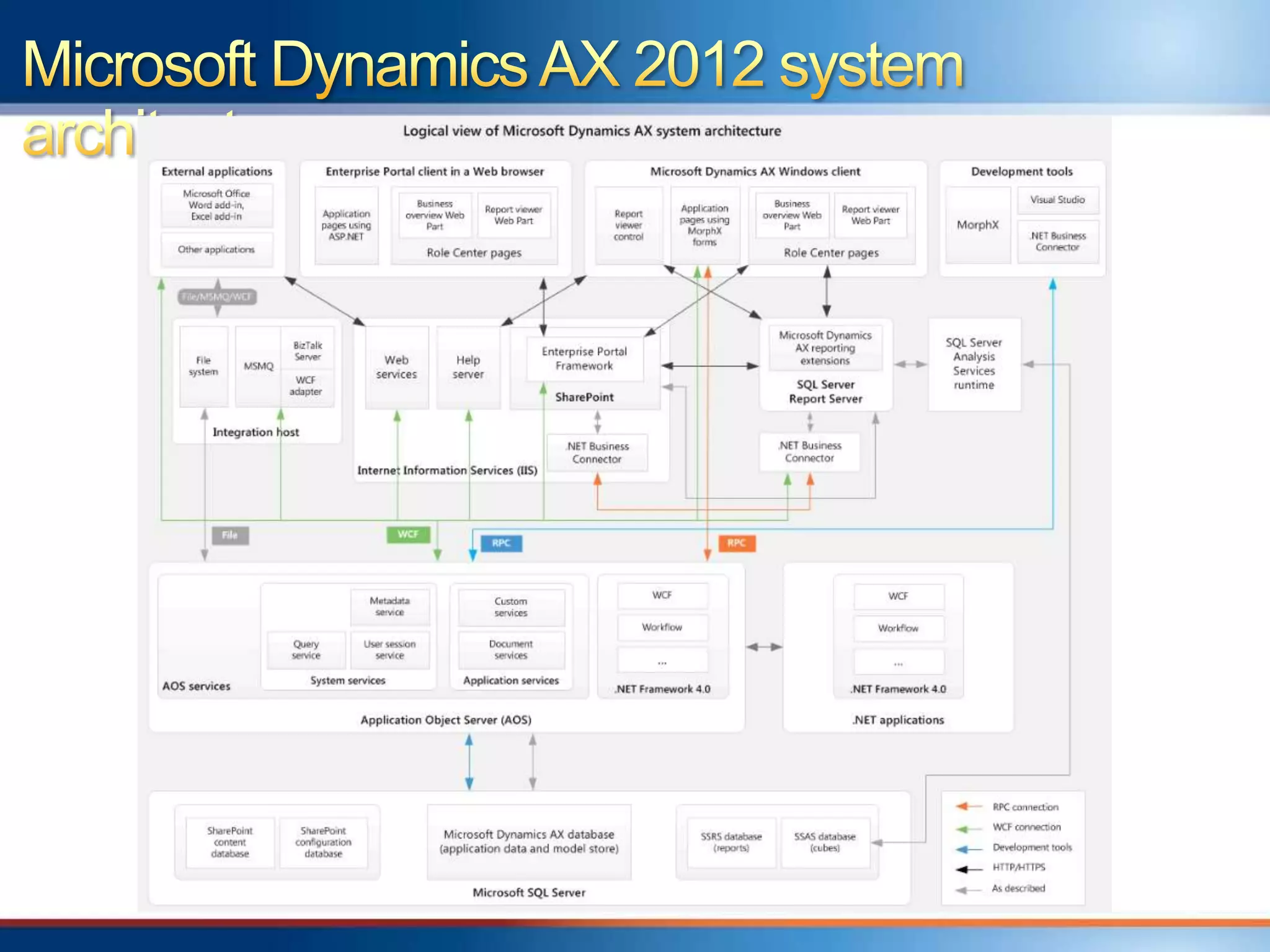
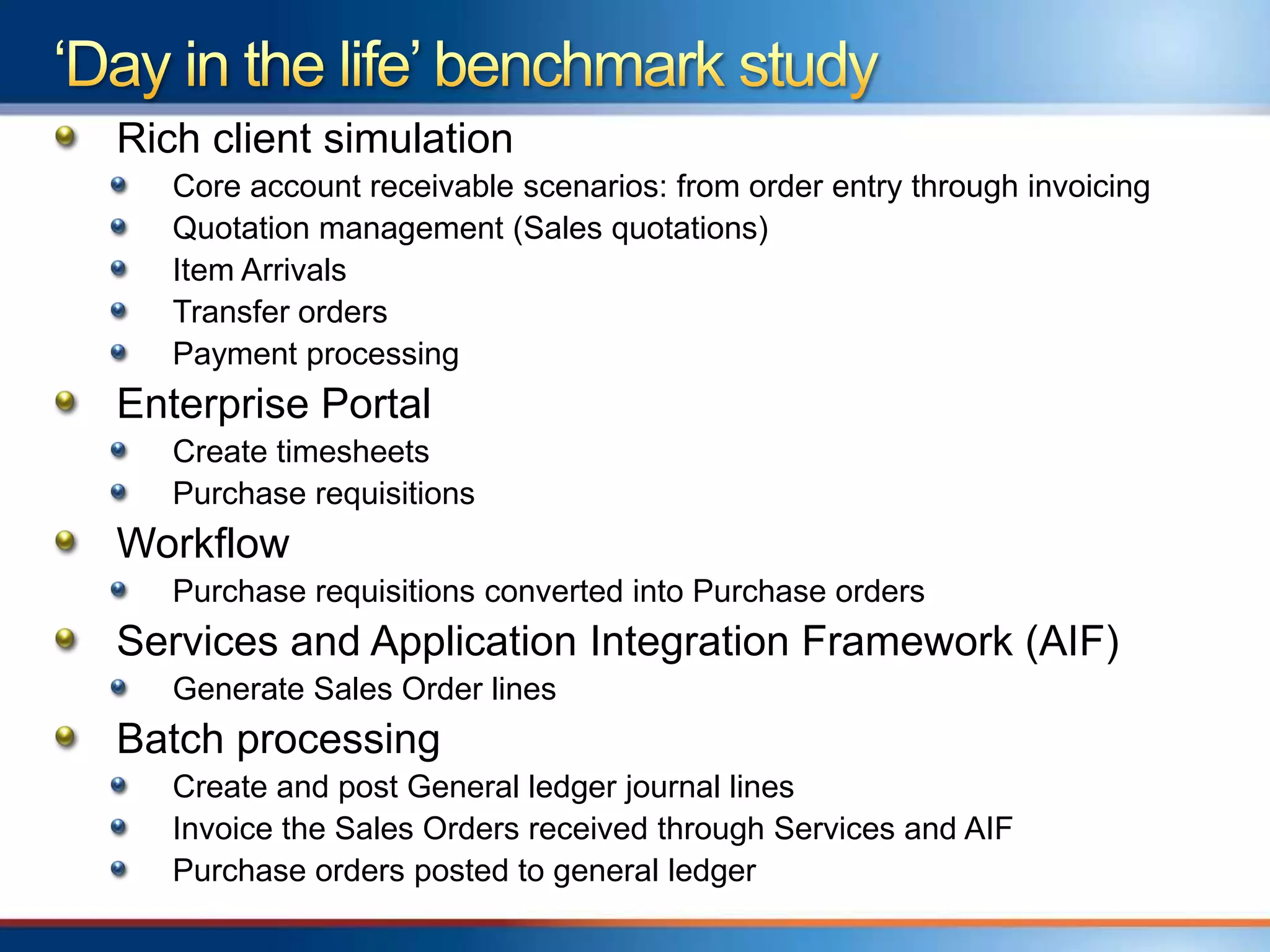
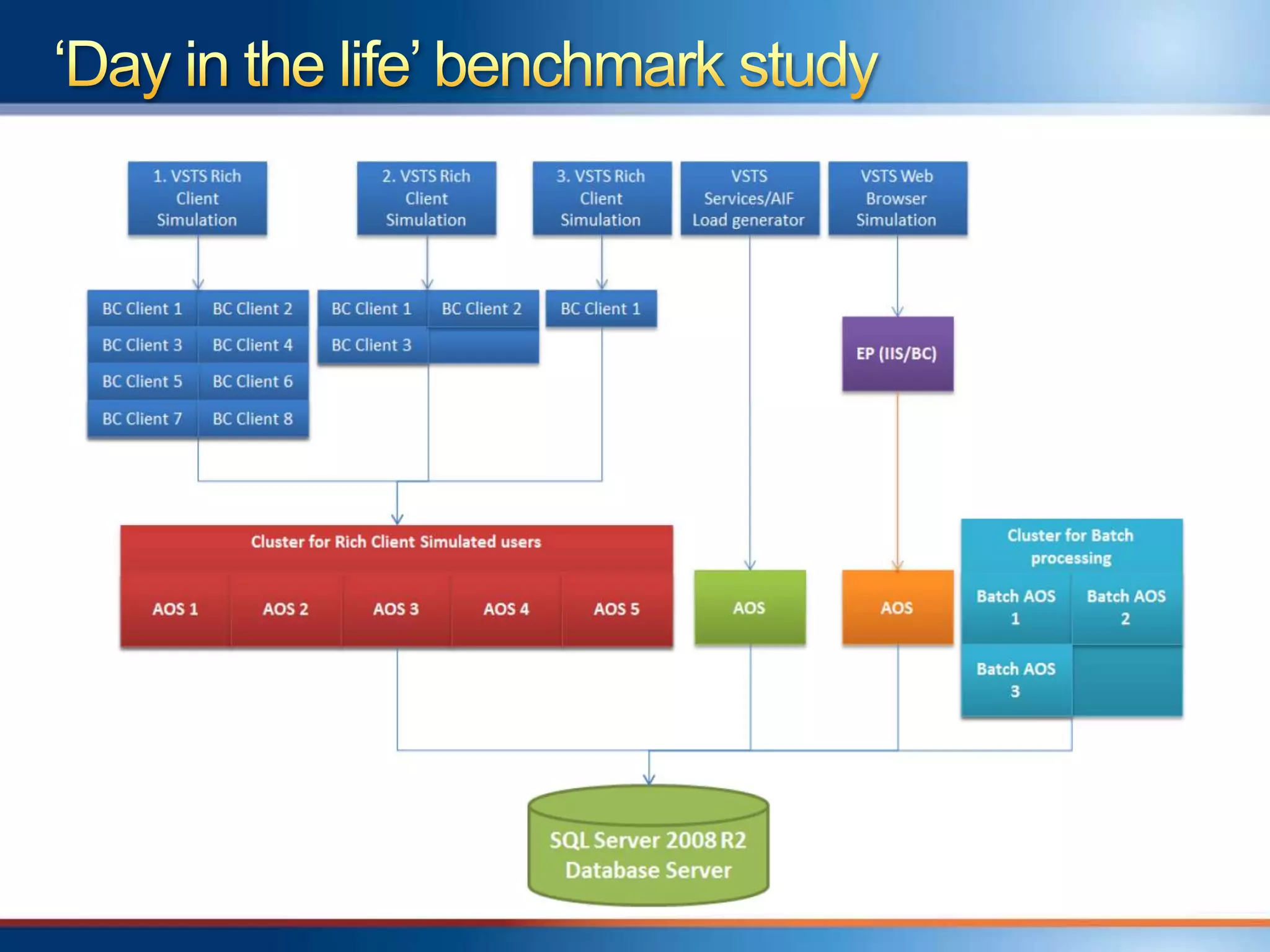
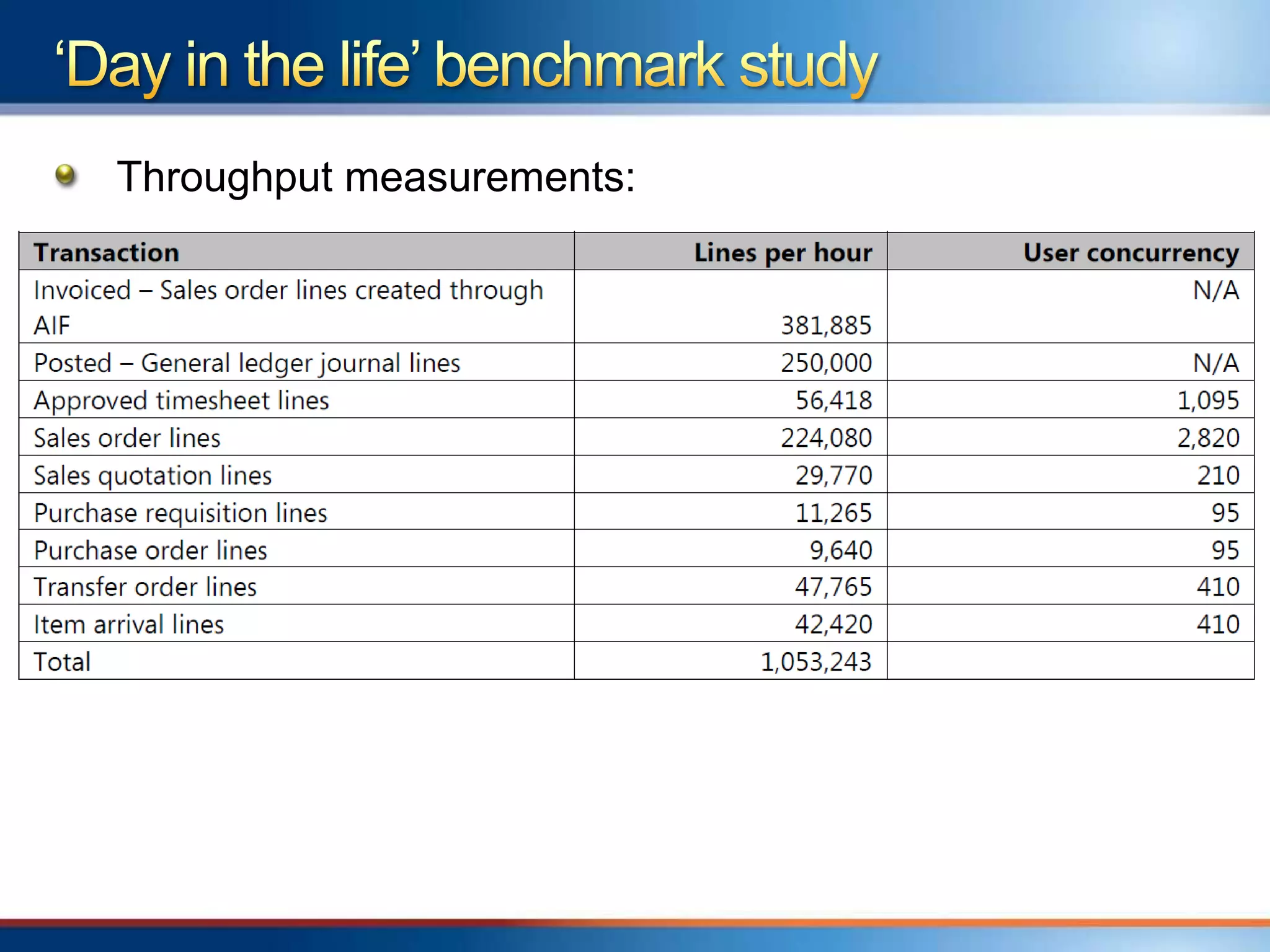
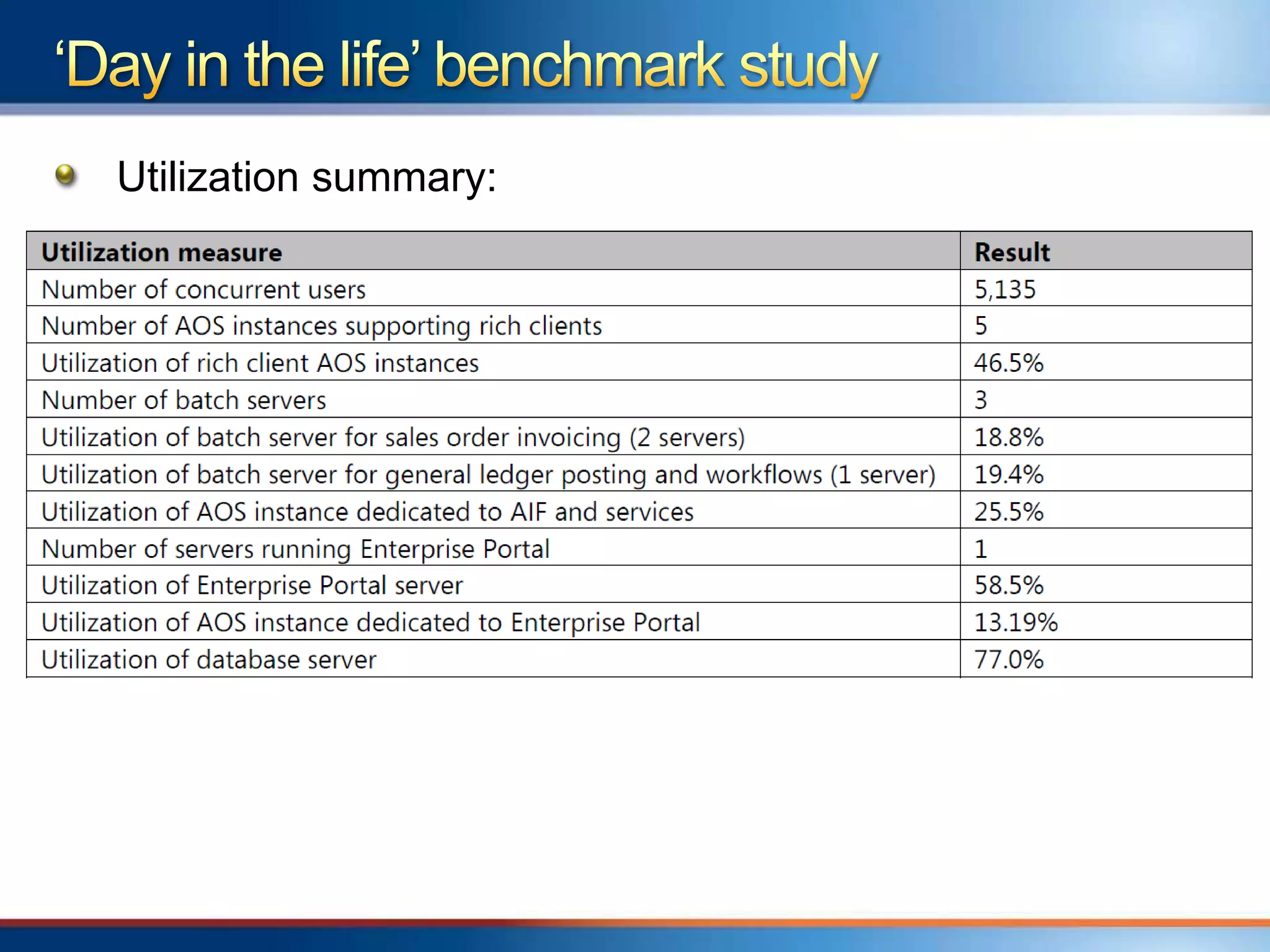
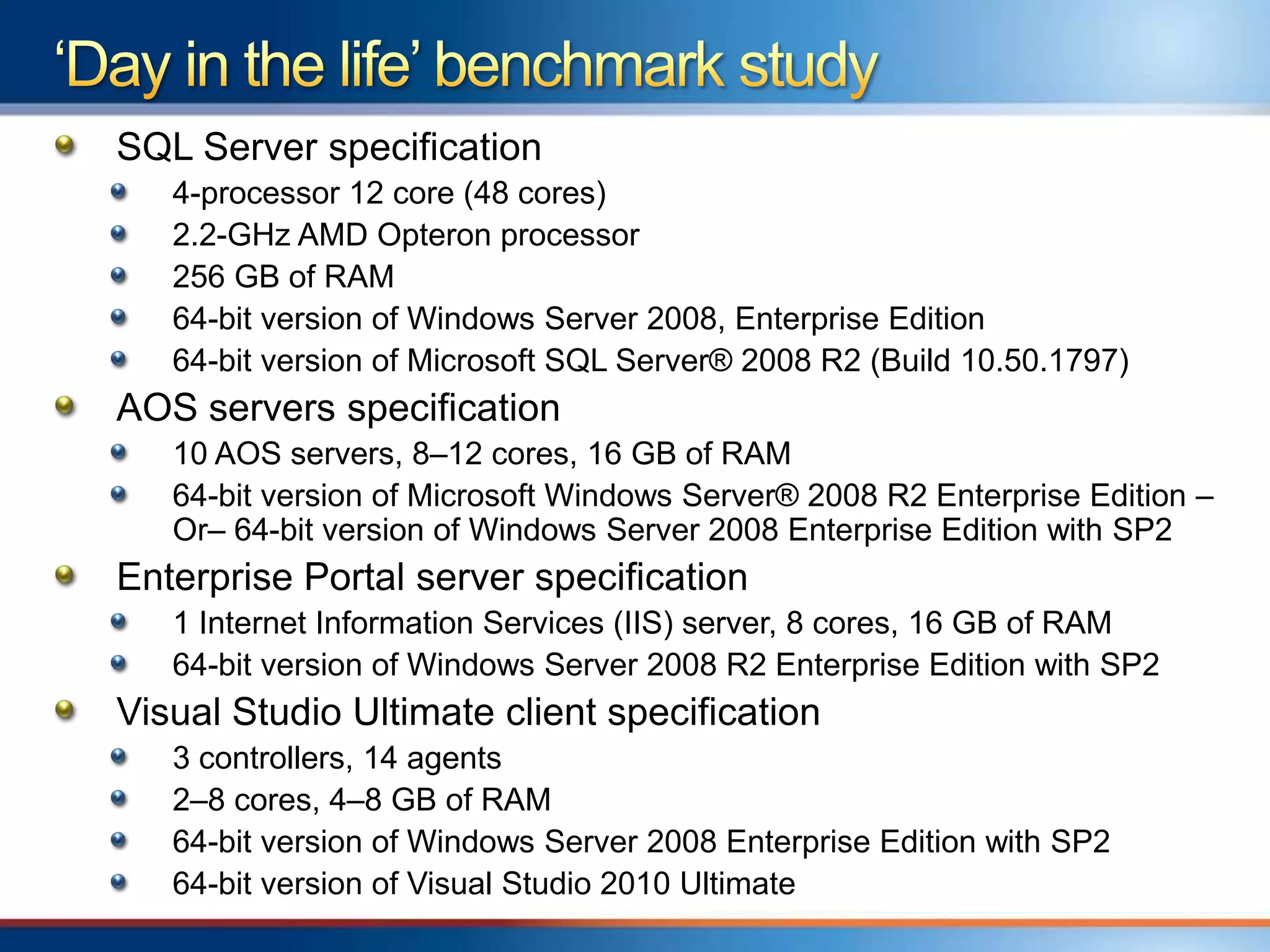
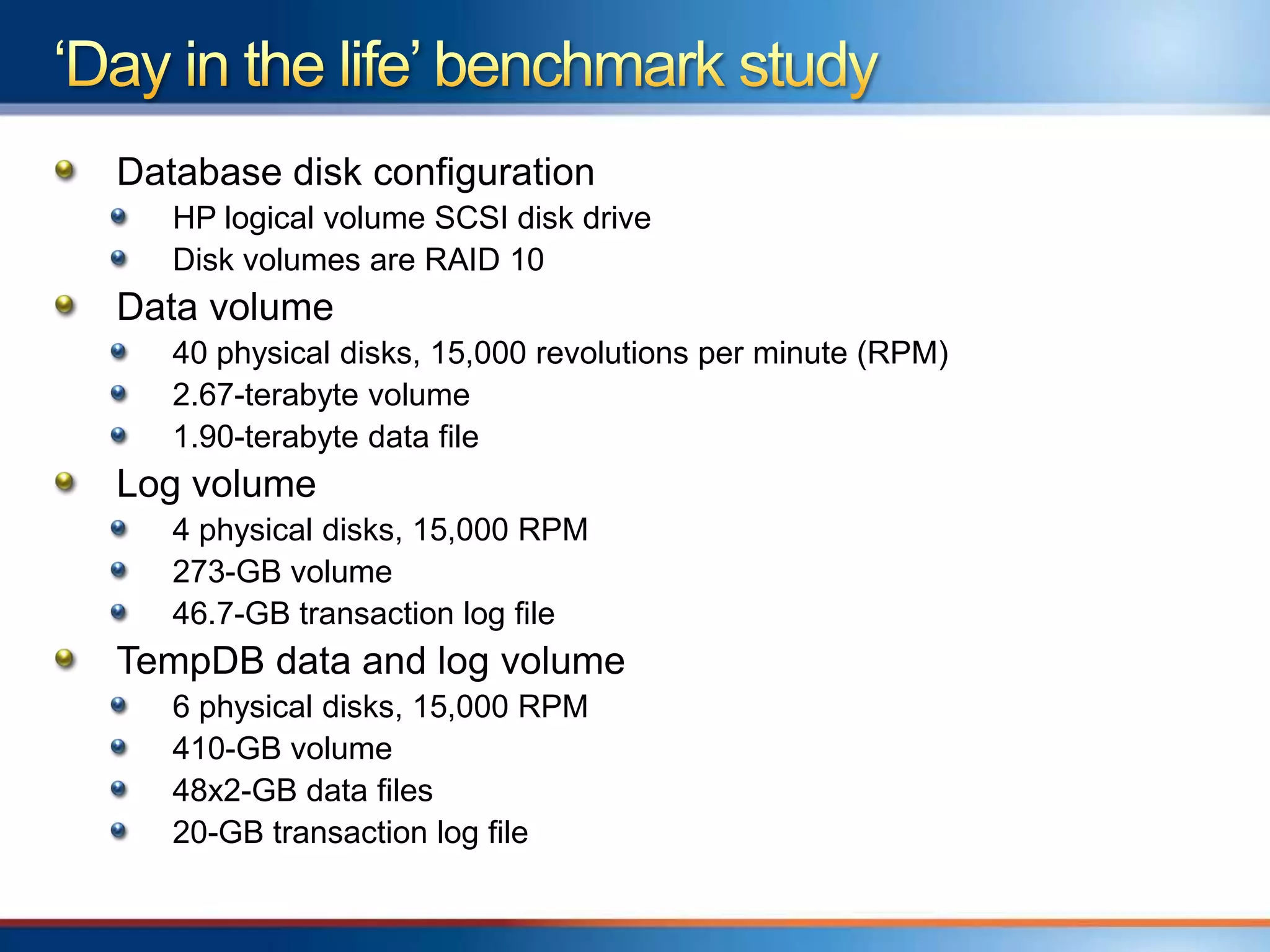
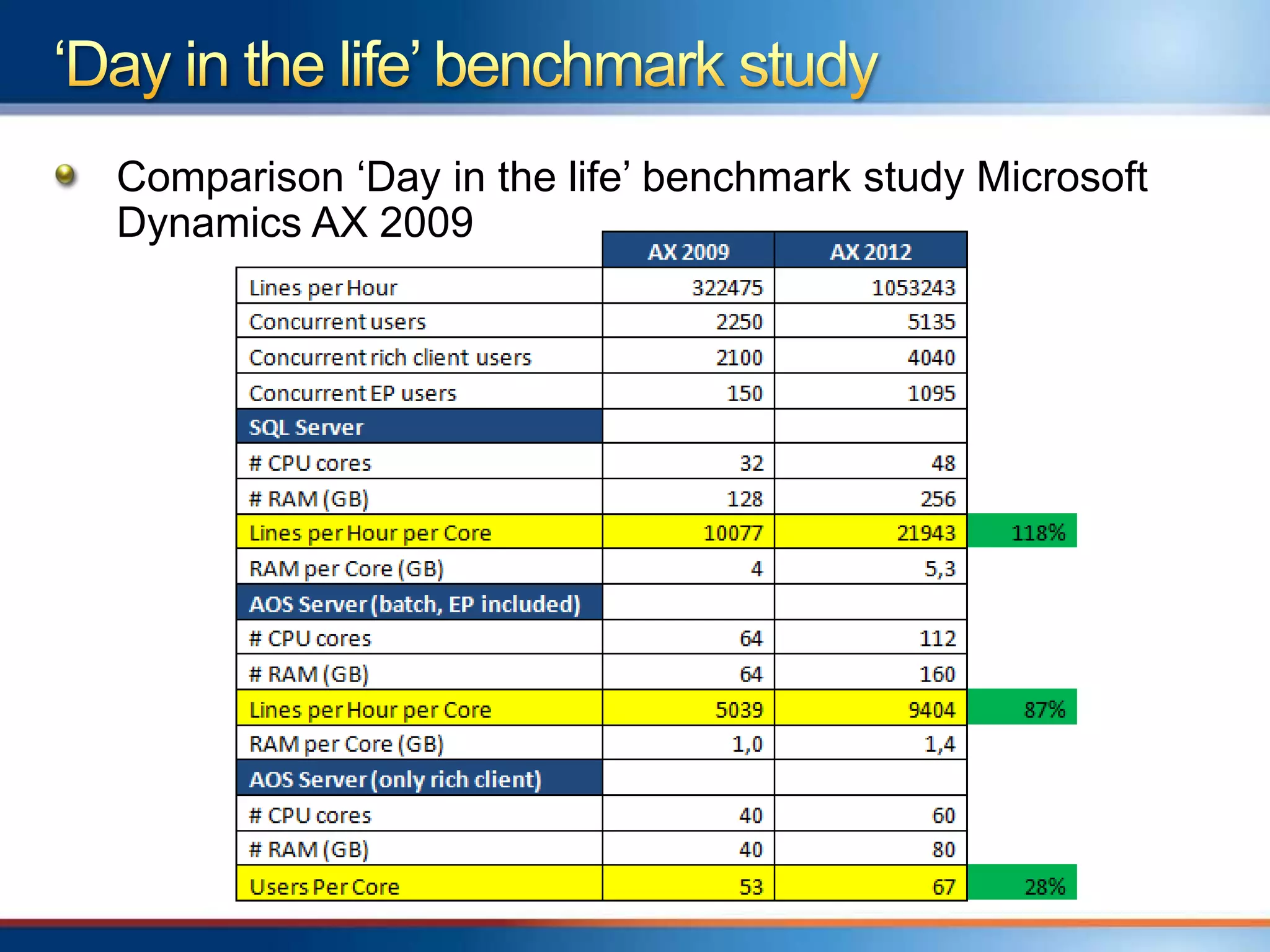
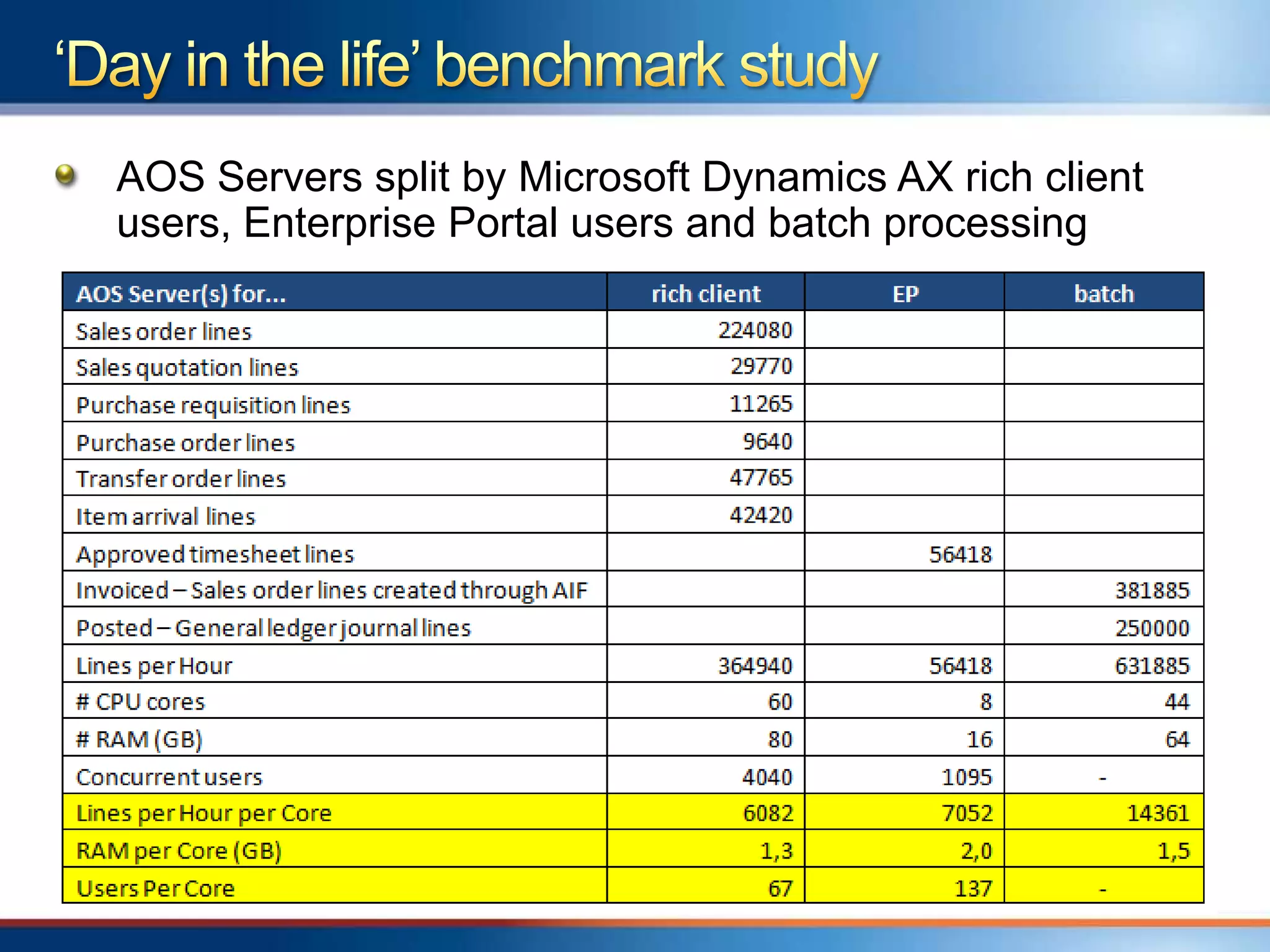
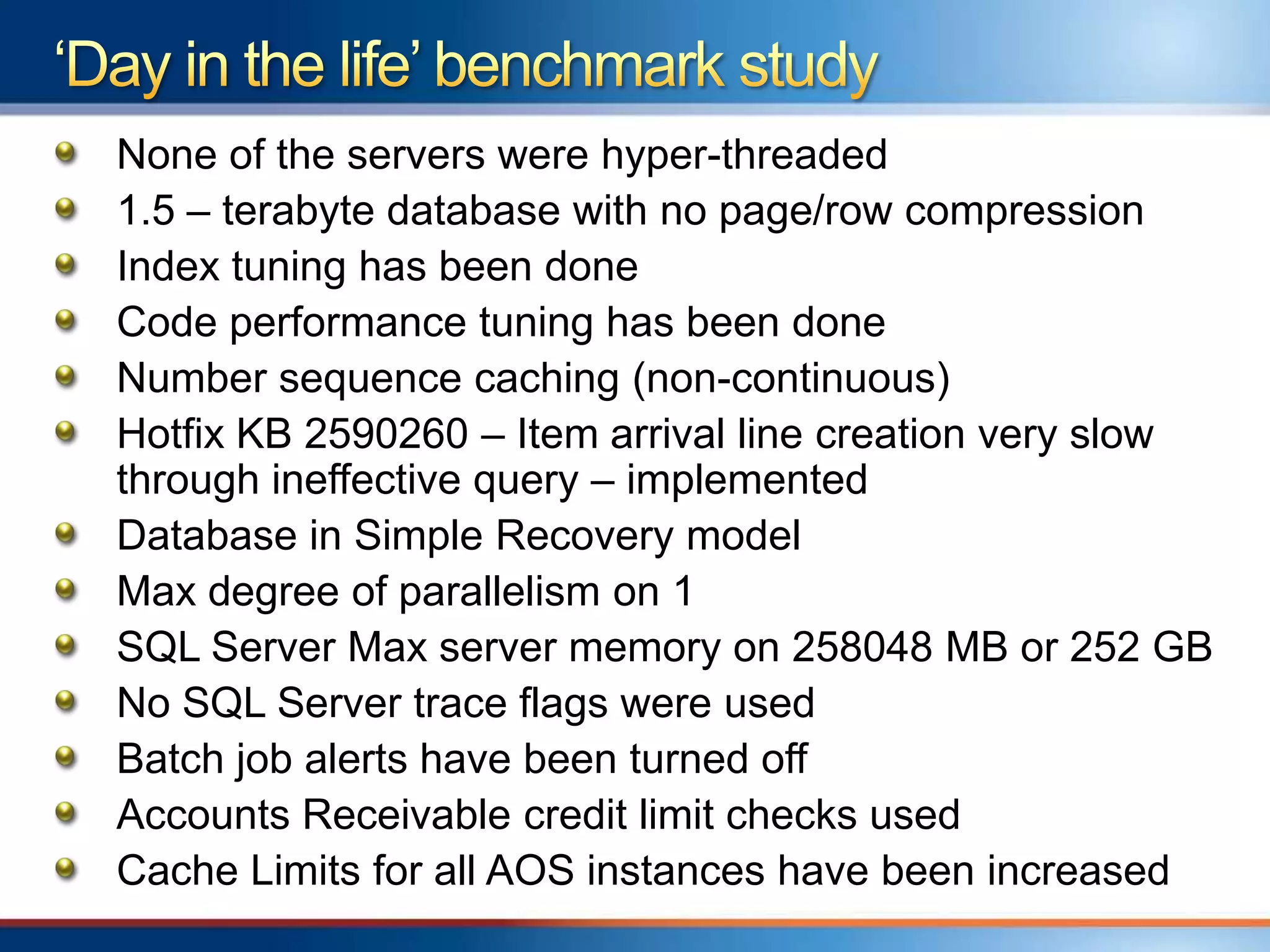
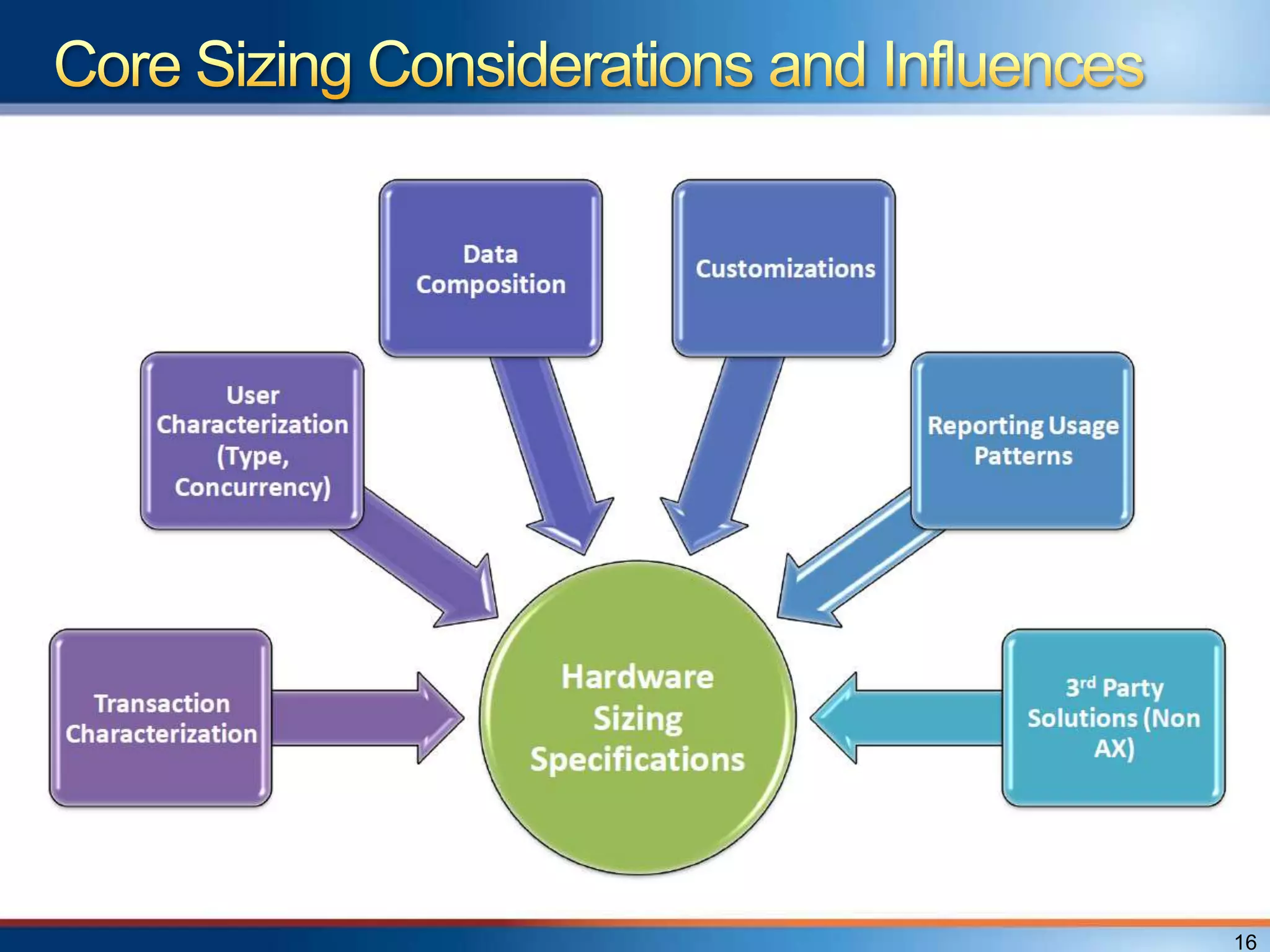
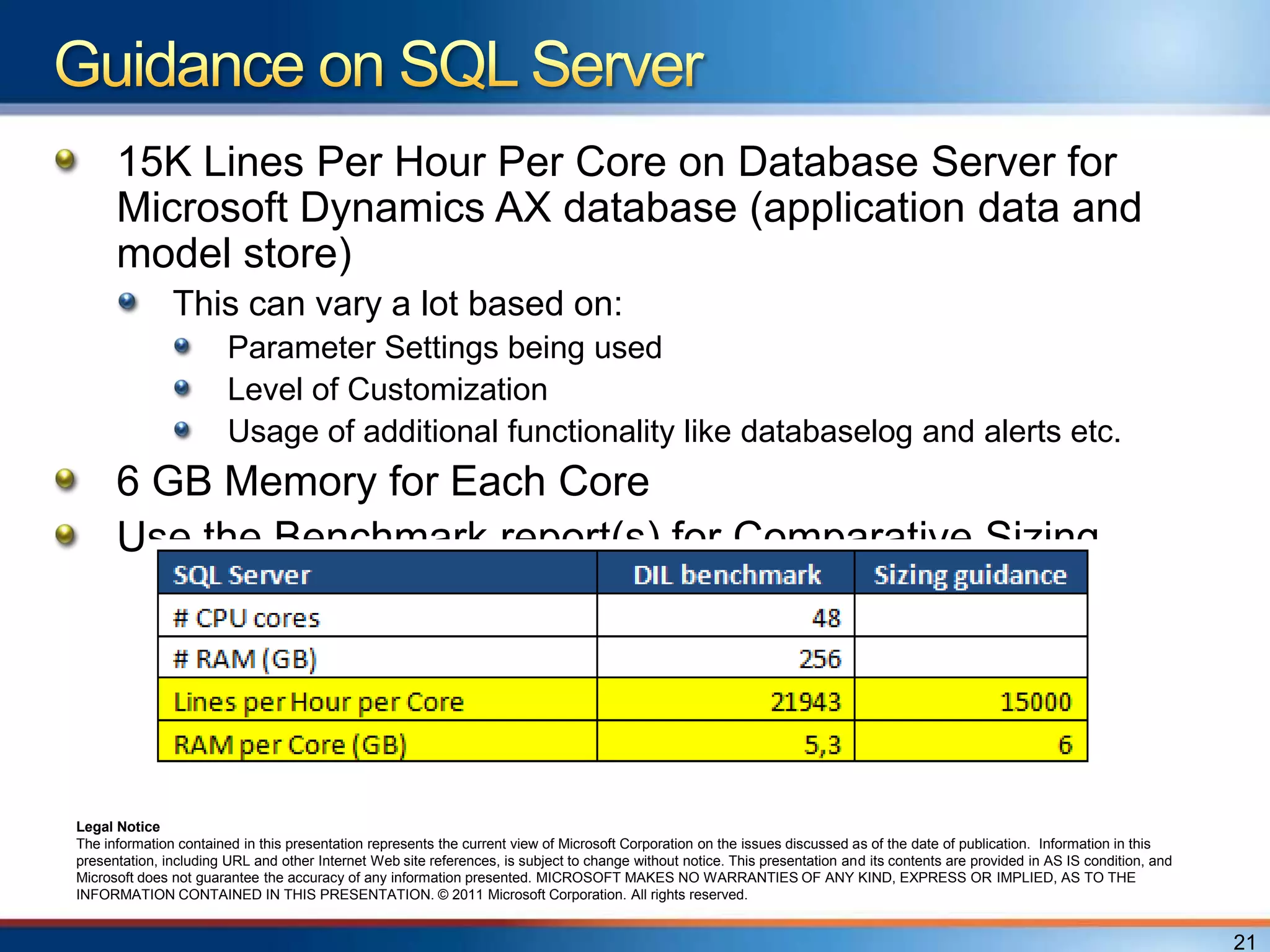
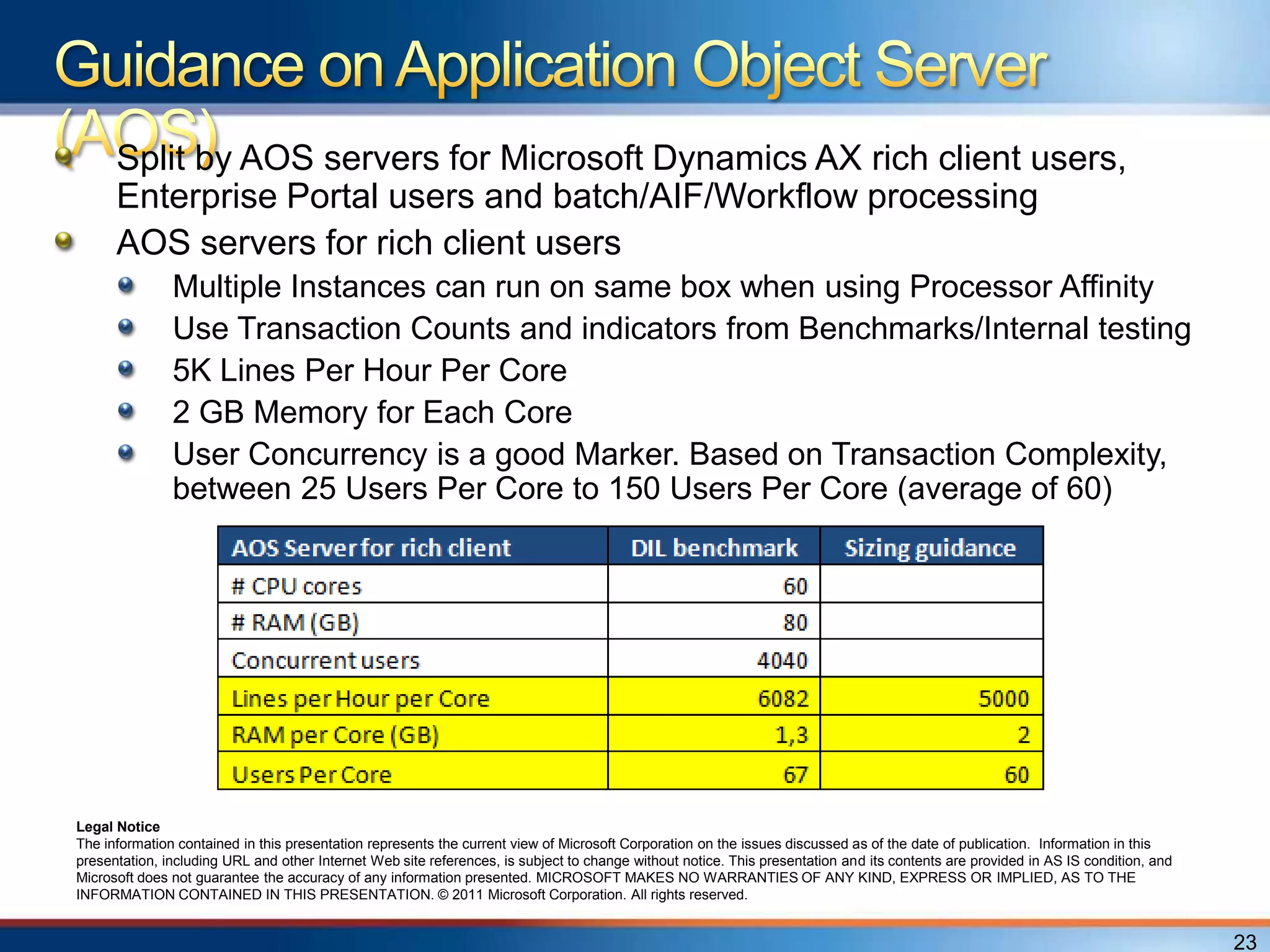
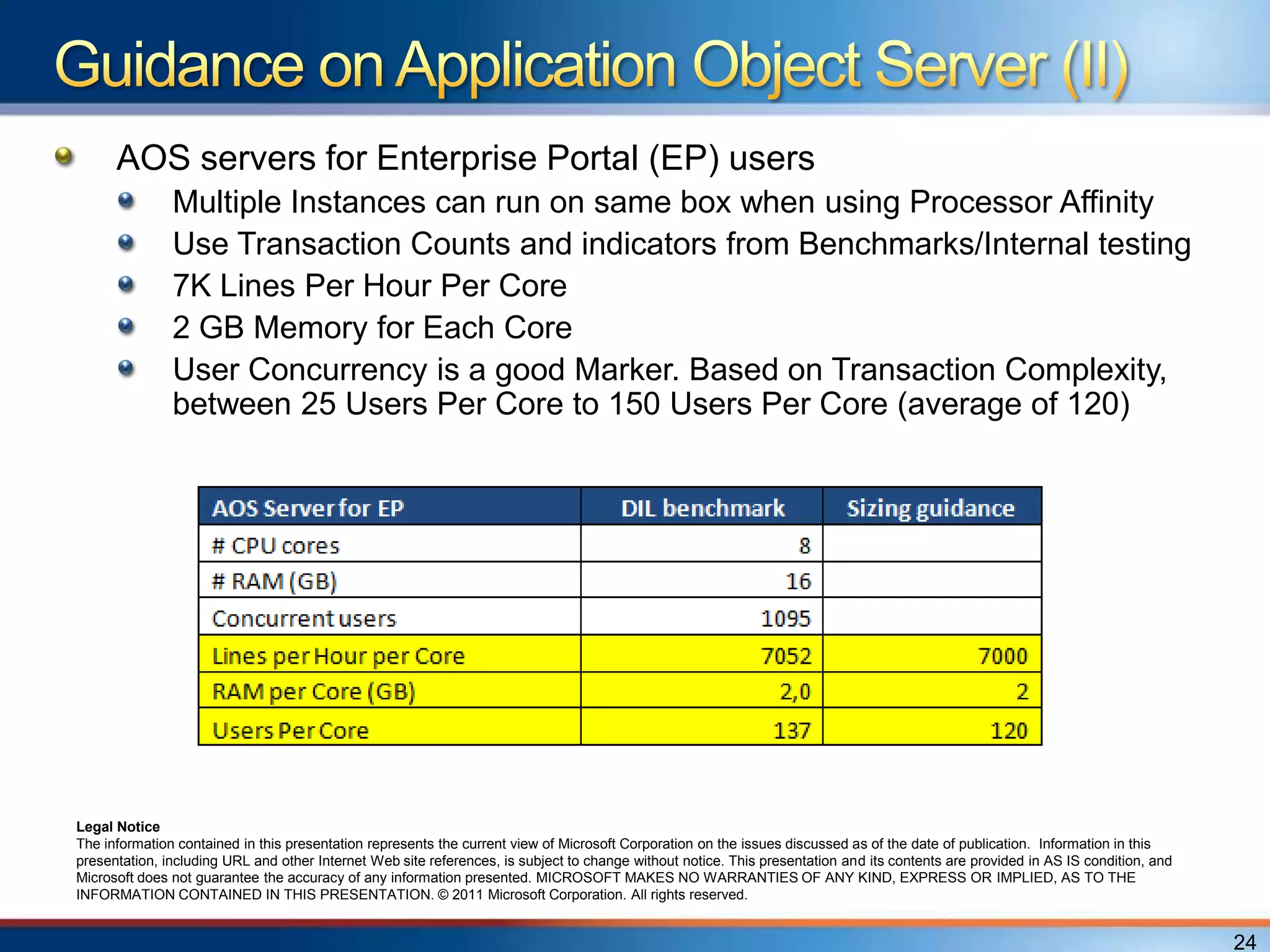
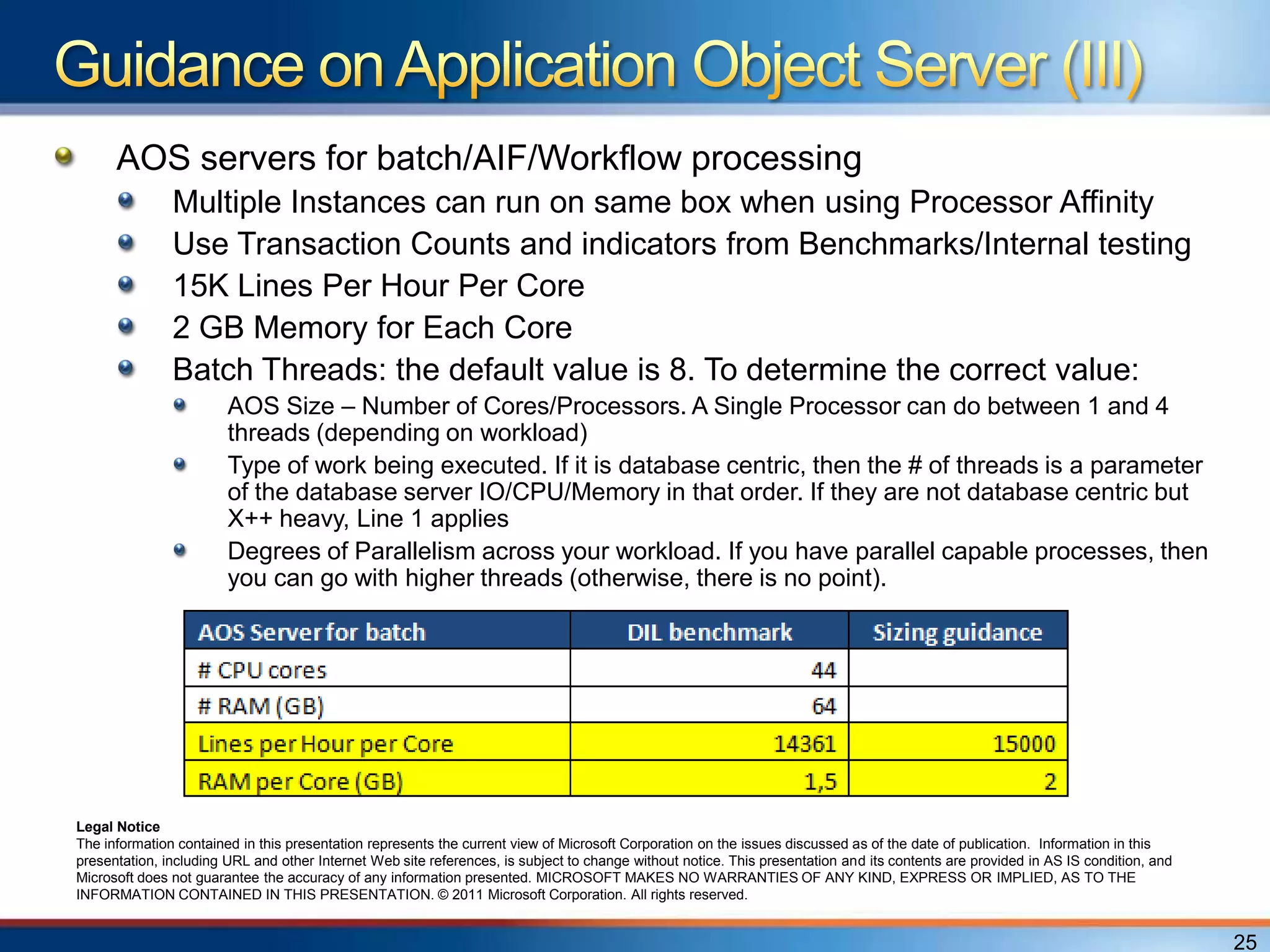
The document provides an overview of a "Day in the life" benchmark study conducted on the Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 system architecture. It discusses the study's findings on throughput and utilization. It then provides initial sizing guidelines for AX components like the database server, AOS servers, and future portal. It recommends sizing based on transaction volume and defines criteria for concurrent users.