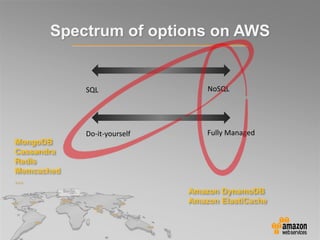
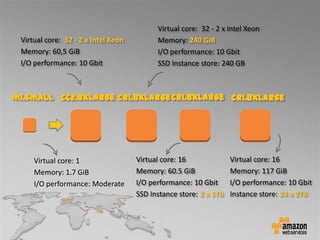
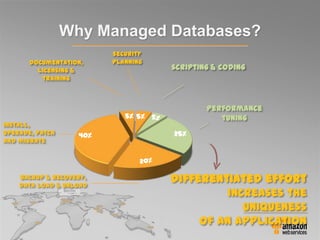
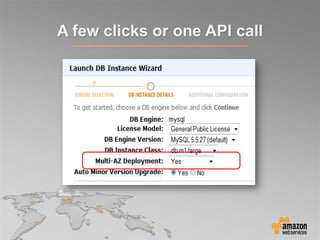
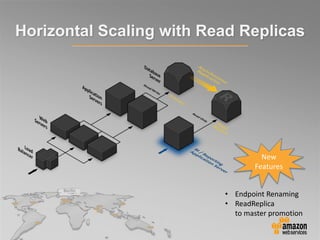
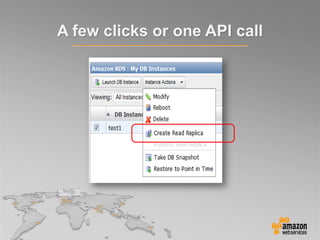
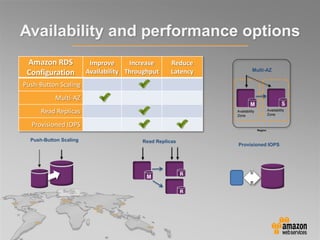
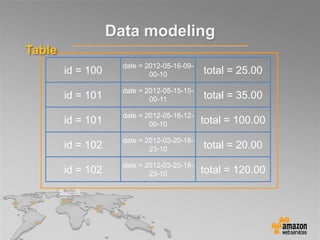
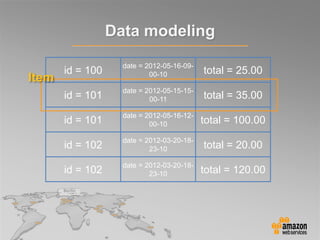
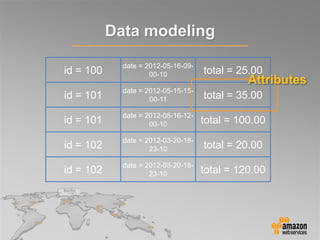
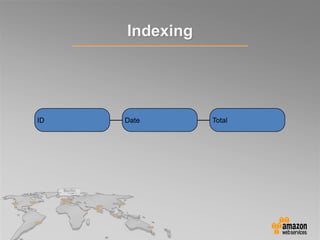
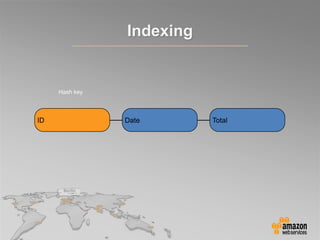
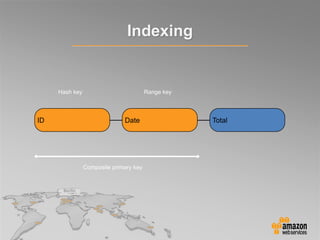
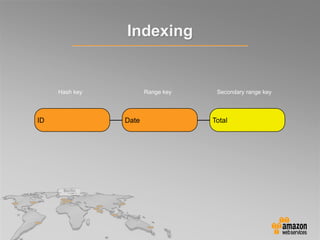
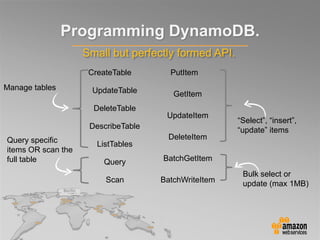
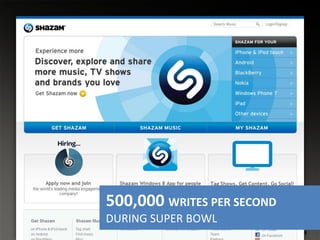
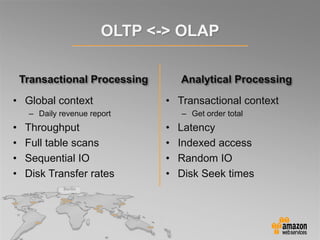
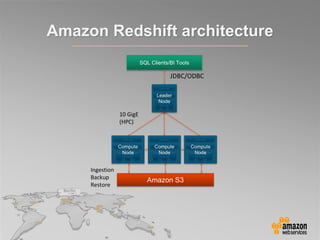
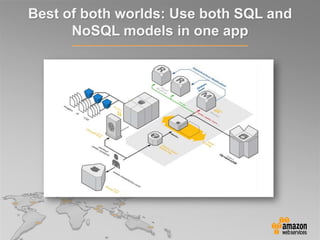
This document provides an overview of database options on AWS, highlighting the ease of starting applications with various services. It discusses the differences between SQL and NoSQL databases, the benefits of managed services like Amazon RDS and DynamoDB, and the considerations for choosing the right database solution based on application needs. Additionally, it covers features of Amazon Redshift as a managed data warehouse for analytical processing.