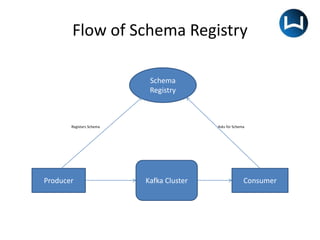
The document outlines the Kafka Schema Registry, a shared repository that manages record schemas for data serialization and schema evolution in Kafka. It details how producers and consumers interact with the registry, configuration options, and various REST calls for managing schemas. The Schema Registry provides reusable schemas, defines relationships, and supports independent evolution of producers and consumers.




![Format of Data
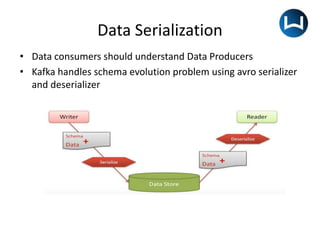
• Either the message key or message value or both can be
serialized as Avro
• It has subject which defines a scope in which schemas can
evolve
• Schema Registry does compatibility checks only within the
schema subject
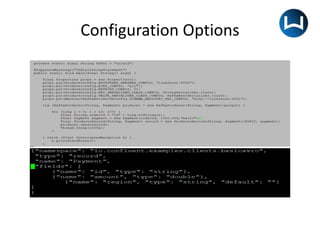
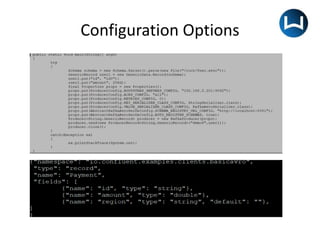
• The schema file is an avsc file which contains namespace,
type, name, fields
• Data in topic is stored as [MagicByte][Schema ID][Data]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/schemaregistry-190110085545/85/Schema-registry-9-320.jpg)


