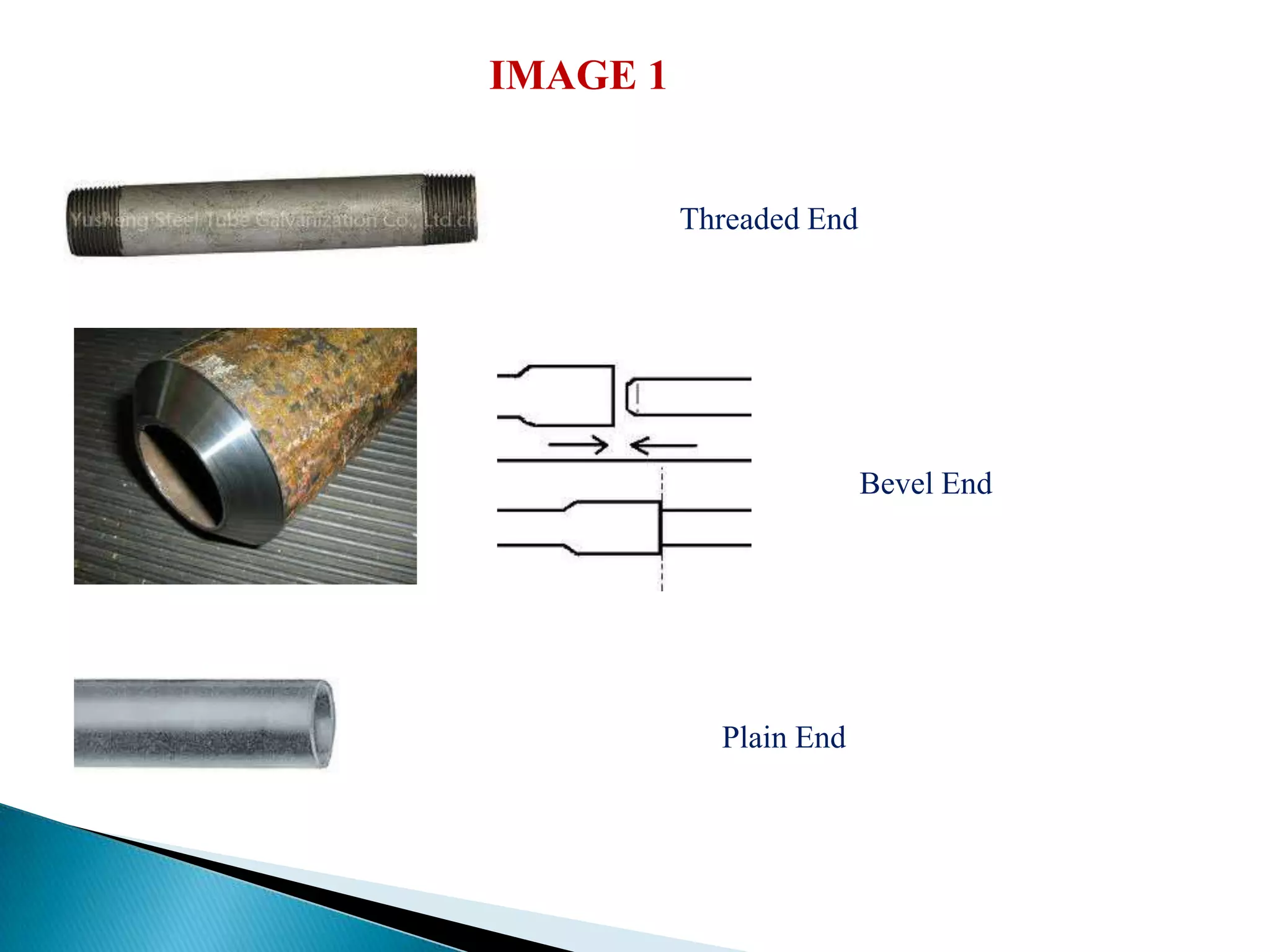
This document discusses oil transfer pipes. Pipelines are the most economical method for transferring oil compared to other methods like trucks and rail. The key aspects discussed are pipe materials, dimensions, standards, end preparations, sizes, manufacturing methods, and operating conditions pipes may encounter like pressure, temperature, and corrosion. Factors like material, wall thickness, diameter, length, end type, and manufacturing process are considered when specifying pipe requirements. Pipes transfer fluids and are circular, while tubes can have other shapes.