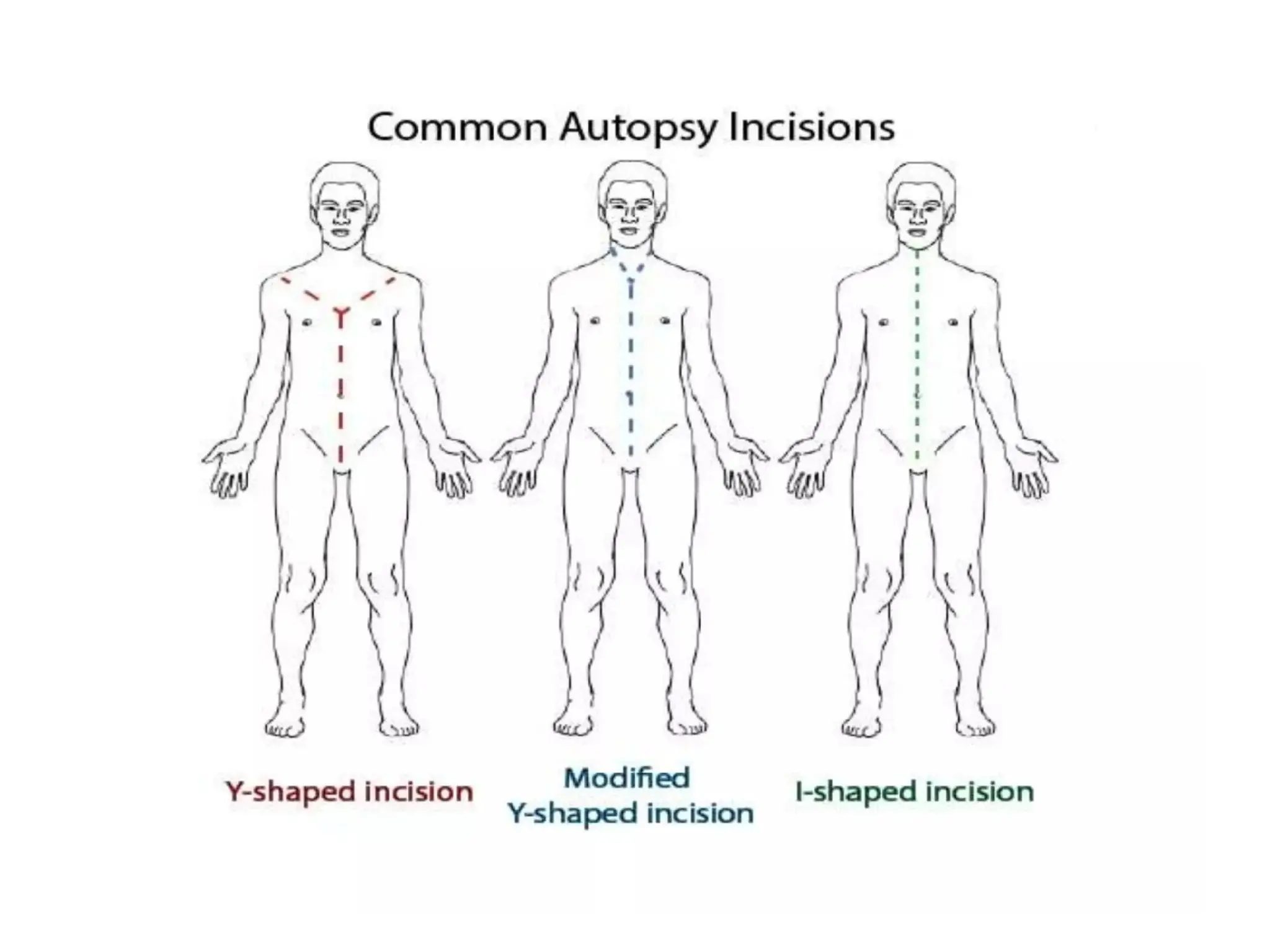
An autopsy is a systematic examination of a deceased individual for medical, legal, or scientific purposes, requiring a thorough investigation of all body organs. The objectives include identifying the cause of death, recognizing diseases, and gathering data for education and statistical purposes. The document outlines various autopsy types, techniques, and the essential components of an autopsy room.