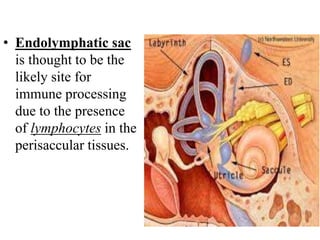
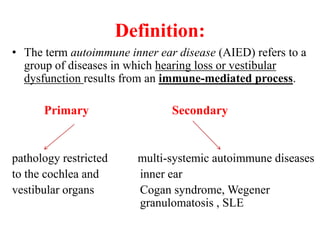
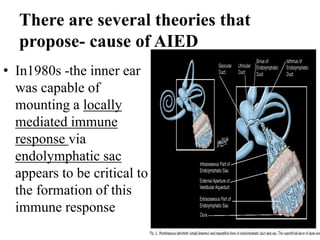
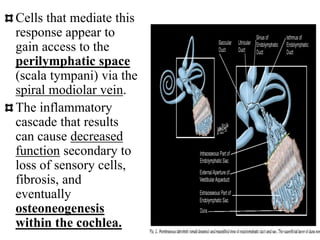
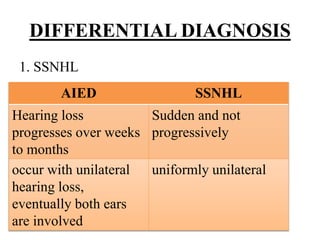
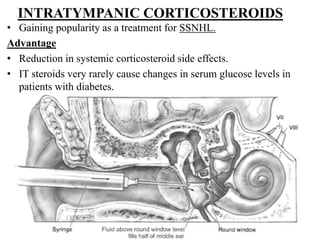
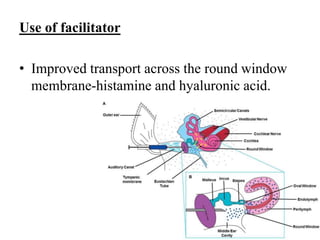
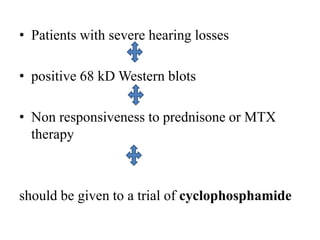
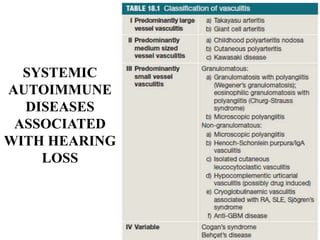
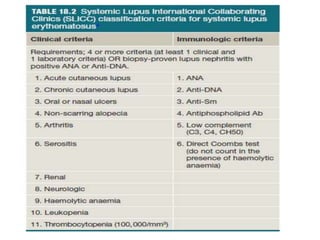
Autoimmune Inner Ear Disease (AIED) refers to hearing loss or vestibular dysfunction caused by an immune-mediated process in the inner ear. It can be primary, restricted to the inner ear, or secondary to other autoimmune diseases. The cause is thought to be an immune response triggered by antigens in the inner ear. Common symptoms include progressive bilateral hearing loss over weeks to months. Treatment involves corticosteroids, with intratympanic injections as an alternative. Other immunosuppressants may be used if steroids are not effective. Systemic autoimmune diseases like Cogan syndrome, Granulomatosis with polyangiitis, and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus can also cause