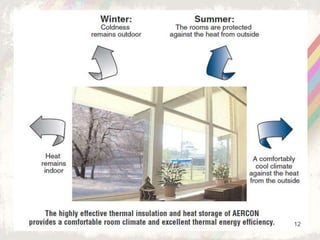
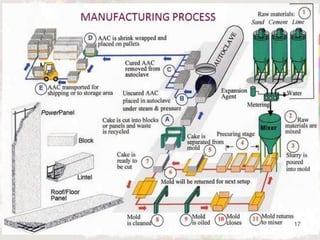
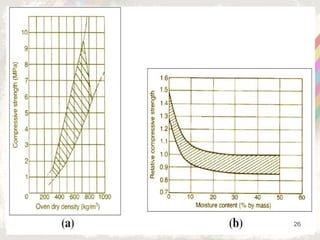
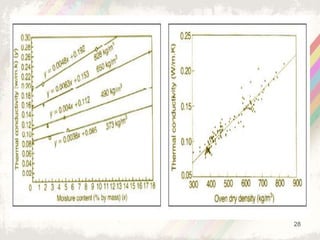
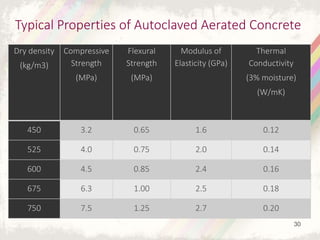
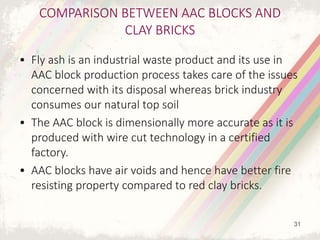
Autoclaved aerated concrete (AAC) blocks were developed in the 1920s in Sweden to address timber shortages and have gained widespread acceptance globally, particularly in the Middle East. They are made from a mixture of cement, fly ash, and water, which results in lightweight, insulating blocks that contribute to reduced construction loads and better energy efficiency. With superior acoustic and fire-resistant properties, AAC blocks also support environmental sustainability by utilizing industrial waste and reducing the need for traditional clay bricks.